
Cybersecurity researchers at Check Point have uncovered a new critical vulnerability affecting Windows Server 2003–2019 versions with a CVSS 10 out of 10 criticality rating.
17-year software flaw leads to remote code execution (CVE-2020-1350) dubbed by Check Point "SigRed" and could allow an unauthenticated remote attacker to gain domain administrator privileges over target servers and take full control of the IT infrastructure organizations.
An attacker could exploit the SigRed vulnerability by sending specially crafted malicious DNS queries to the Windows DNS server and executing arbitrary code, allowing the hacker to intercept and process user emails and network traffic, collect user credentials, and more.
In a report published on the company's blog , Check Point researcher Saga Tzadik confirmed that the flaw is dire, allowing attackers to launch an attack that can spread from one vulnerable computer to another without any human intervention. Those. the vulnerability is of an obvious "wormable" nature.
, Check Point Microsoft, Windows , , , 122 .
Microsoft , , , .
«Windows DNS Server — . , , , Windows ».
, DNS- IP- (, www.google.com ), DNS- (NS).
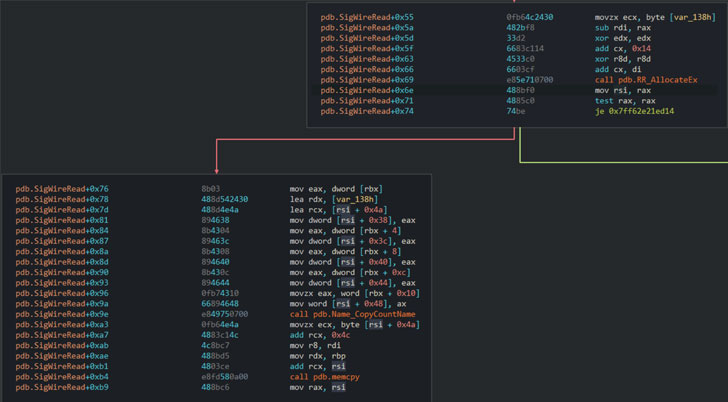
, SigRed NS («deadbeef.fun») («ns1.41414141.club») DNS- , , .
, («dns.exe!SigWireRead»), DNS, SIG 64 , .
, («RR_AllocateEx»), 65 535 , , , .
DNS, 512 UDP ( 4096 , ) 65 535 TCP, , SIG , .
, DNS- DNS, .
SigRed (, Internet Explorer Microsoft Edge Chromium), DNS- Windows , «» DNS- HTTP- DNS- - .
DNS- («dnsapi.dll») , , Microsoft DNS- DNS- .
, DNS- Windows .
As a temporary workaround, the maximum DNS message length (over TCP) can be set to "0xFF00" to eliminate the possibility of a buffer overflow:
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DNS\Parameters" /v "TcpReceivePacketSize" /t REG_DWORD /d 0xFF00 /f && net stop DNS && net start DNS