purpose
To control unmanned objects, such as a copter or an airplane, narrow-band low-speed modems are usually used. For the transmission of telemetry and unhurried control commands, such as setting flight points - this is quite enough in terms of speed. For these purposes, it is more important to ensure uninterrupted control of the control channel rather than chasing the speed, which can be measured in seconds.
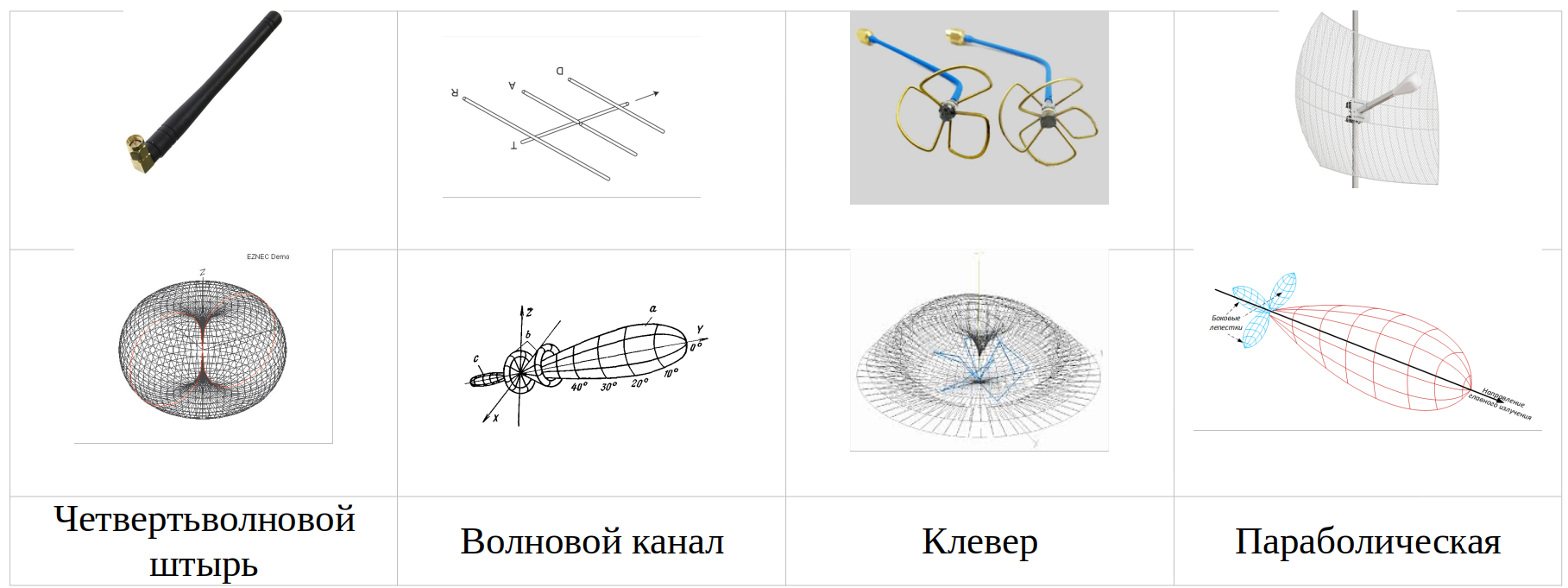
A typical solution in this area is the use of an omnidirectional antenna with an integrated receive-transmitter, such as sx1233, AX5043, on board, and an antenna with a high gain (HG), such as a wave channel or clover, on the ground.
As long as there is line of sight, everything should be fine.
But, as you know, not only is the ground not flat, but line-of-sight with a sufficient power budget does not guarantee successful communication. And the reason for this is often interference.
When the aircraft flies past a powerful source of radio emission with the same frequency of the channel, then the onboard antenna is exposed to an effect that significantly exceeds the signal from the remote transmitter, and it is impossible to filter out the bandpass filter.
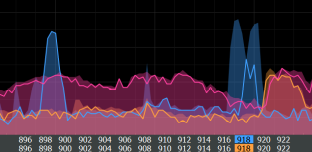
, . , .
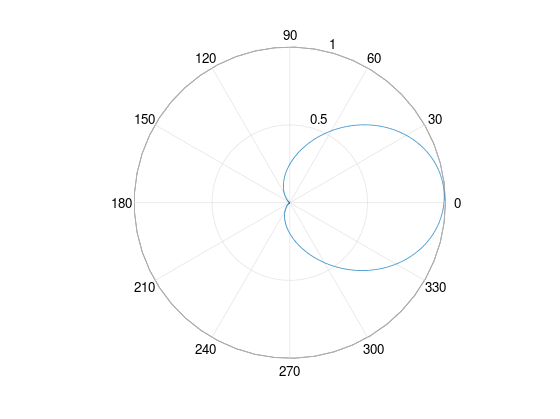
— , . : .
.
( ) (. . ) , .

« », AD8340. , / (/, SNR).
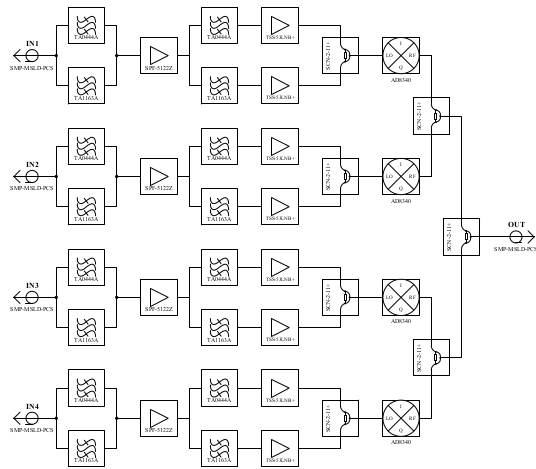
: , , — . , , .
: . .. — .
: — :)
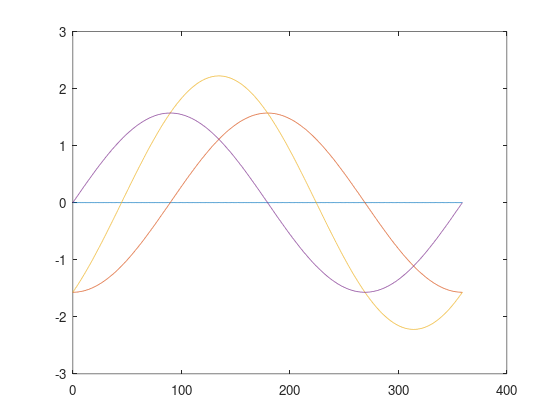
, ‑ . , , (antenna diversity) . , .
.
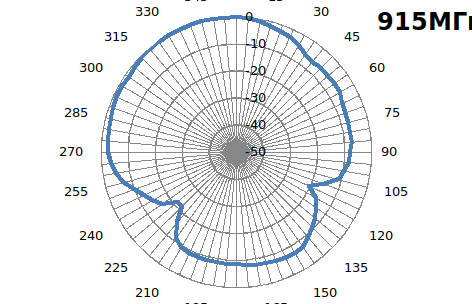
, - .
. - , , . .
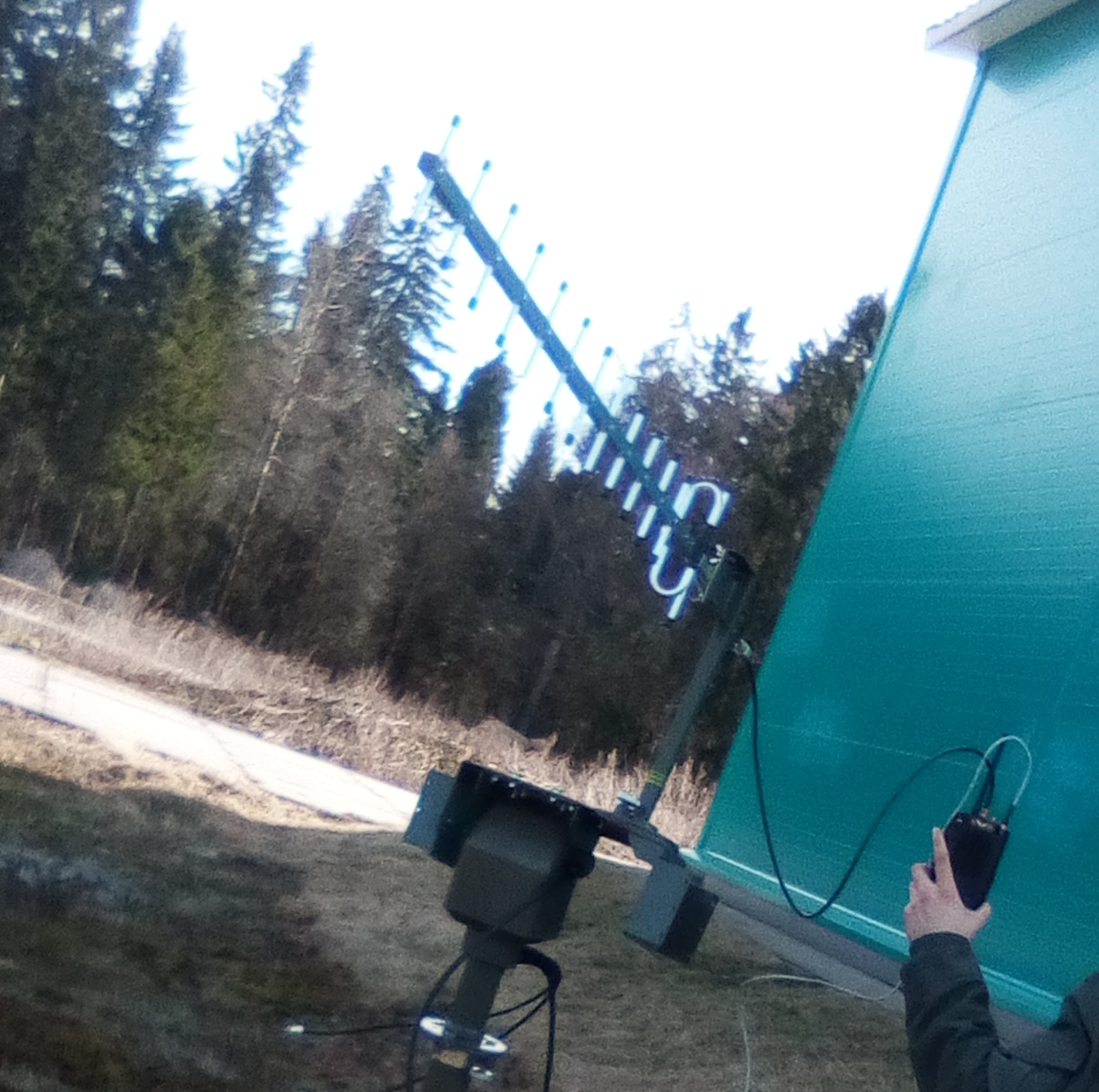

— .
— , .
, . , . , , . , (, ..). ( ), .
, , , . , . — .
‑ , ‑, . , .
. — . , . , , .
, , . high speed design, , .
. , .