In anticipation of the start of the " Machine Learning. Professional " course , we share the traditional translation of useful material.
In this article, you will learn what can only be learned by spending countless hours of study and practice.

About this project
Kaggle — . - . , , , , , .
164 . . , , Kaggle.
data science Kaggle, . , , .
, . , . , , , .
, . « Kaggle». , data science, , , Kaggle, . . - , . !
1.
. , (features) . , .
, , , :
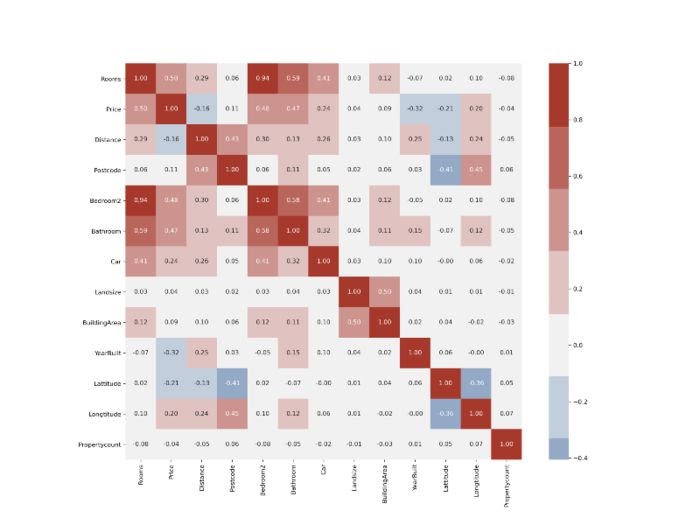
, . , . . , :
houses = pd.read_csv('data/melb_data.csv')
# Calculate pairwise-correlation
matrix = houses.corr()
# Create a mask
mask = np.triu(np.ones_like(matrix, dtype=bool))
# Create a custom diverging palette
cmap = sns.diverging_palette(250, 15, s=75, l=40,
n=9, center="light", as_cmap=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12))
sns.heatmap(matrix, mask=mask, center=0, annot=True,
fmt='.2f', square=True, cmap=cmap)
plt.show();

, . , DataFrame .corr
. np.ones_like dtype
, bool, True , DataFrame
:
>>> np.ones_like(matrix, dtype=bool)[:5]
array([[ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True],
[ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True],
[ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True],
[ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True],
[ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True]])
Numpy .triu
, , False . Seaborn heatmap :
sns.heatmap(matrix, mask=mask, center=0, annot=True,
fmt='.2f', square=True, cmap=cmap)
, , , .
2. value_counts
value_counts
, , dropna False:
>>> houses.CouncilArea.value_counts(dropna=False, normalize=True).head()
NaN 0.100810
Moreland 0.085641
Boroondara 0.085420
Moonee Valley 0.073417
Darebin 0.068778
Name: CouncilArea, dtype: float64
, , , . , , value_counts
- . :
>>> missing_props = houses.isna().sum() / len(houses)
>>> missing_props[missing_props > 0].sort_values(ascending=False
BuildingArea 0.474963
YearBuilt 0.395803
CouncilArea 0.100810
Car 0.004566
dtype: float64
, DataFrame
. 0%, .. .
3. Pandas DataFrame Styler
pandas. pandas DataFrame’. .style
DataFrame’ pandas, . , :
>>> diamonds = sns.load_dataset('diamonds')
>>> pd.crosstab(diamonds.cut, diamonds.clarity).\
style.background_gradient(cmap='rocket_r')

Seaborn heatmap. pd.crosstab
. .style.background_gradient
, , . DataFrame
, , - VS2.
, :
>>> pd.crosstab(diamonds.cut, diamonds.clarity,
aggfunc=np.mean, values=diamonds.price).\
style.background_gradient(cmap='flare')
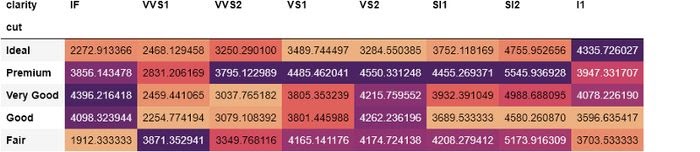
. DataFrame
, VS2 . , , . .style
:
>>> agg_prices = pd.crosstab(diamonds.cut, diamonds.clarity,
aggfunc=np.mean, values=diamonds.price).\
style.background_gradient(cmap='flare')
>>> agg_prices.format('{:.2f}')

.format {:.2f} 2 .
4. Matplotlib
EDA (Exploratory Data Analysis) , Matplotlib . , , , , . .
, . , rcParams Matplotlib :
from matplotlib import rcParams
rcParams
- Python, Matplotlib:

. , , , :
# Remove top and right spines
rcParams['axes.spines.top'] = False
rcParams['axes.spines.right'] = False
# Set fixed figure size
rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12, 9]
# Set dots per inch to 300, very high quality images
rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 300
# Enable autolayout
rcParams['figure.autolayout'] = True
# Set global fontsize
rcParams['font.style'] = 16
# Fontsize of ticklabels
rcParams['xtick.labelsize'] = 10
rcParams['ytick.labelsize'] = 10
, Matplotlib. , rcParams.keys()
.
5. Pandas
Matplotlib, pandas , . , . , pandas 5 , pandas:
get_option()
/set_option()
- / .
reset_option()
- .
description_option()
- .
option_context()
- , .
. pd.get_option
, , , set_option
:
>>> pd.get_option(‘display.max_columns’)
20
, , , DataFrame
. 20 , , .head
, pandas , :
>>> houses.head()

, . :
>>> pd.set_option(‘display.max_columns’, None)
:
>>> houses.head()

:
pd.reset_option(‘display.max_columns’)
, . display.max_rows
5, .head()
:
>>> pd.set_option(‘display.max_rows’, 5)>>> houses

plotly
, pandas. , , .plot
DataFrame’ pandas:
pd.set_option(‘plotting.backend’, ‘plotly’)
, plotly.
, pd.option_context
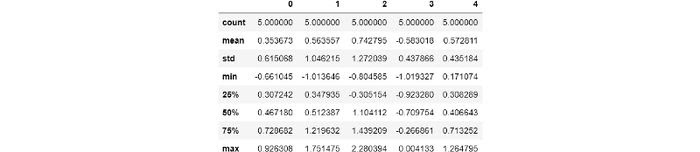
. , . , , pandas . , :
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(5, 5))
>>> pd.reset_option('display.max_rows')
>>> with pd.option_context('float_format', '{:f}'.format):
df.describe()
"Machine Learning. Professional"