
Hello, friends! Today, my article will be devoted to cysts of the small salivary glands.
Today I will tell you about the most common retention cyst of the lower lip (or "mucocele").
ATTENTION! -Uwaga! -Pažnju! -Attention! -Achtung! -Attenzione! -WARNING! -Uwaga! -Pažnju!
Photos taken during the operation will be presented below! With types of teeth, gums, blood anddissection. For the faint of heart, please refuse to read this article.
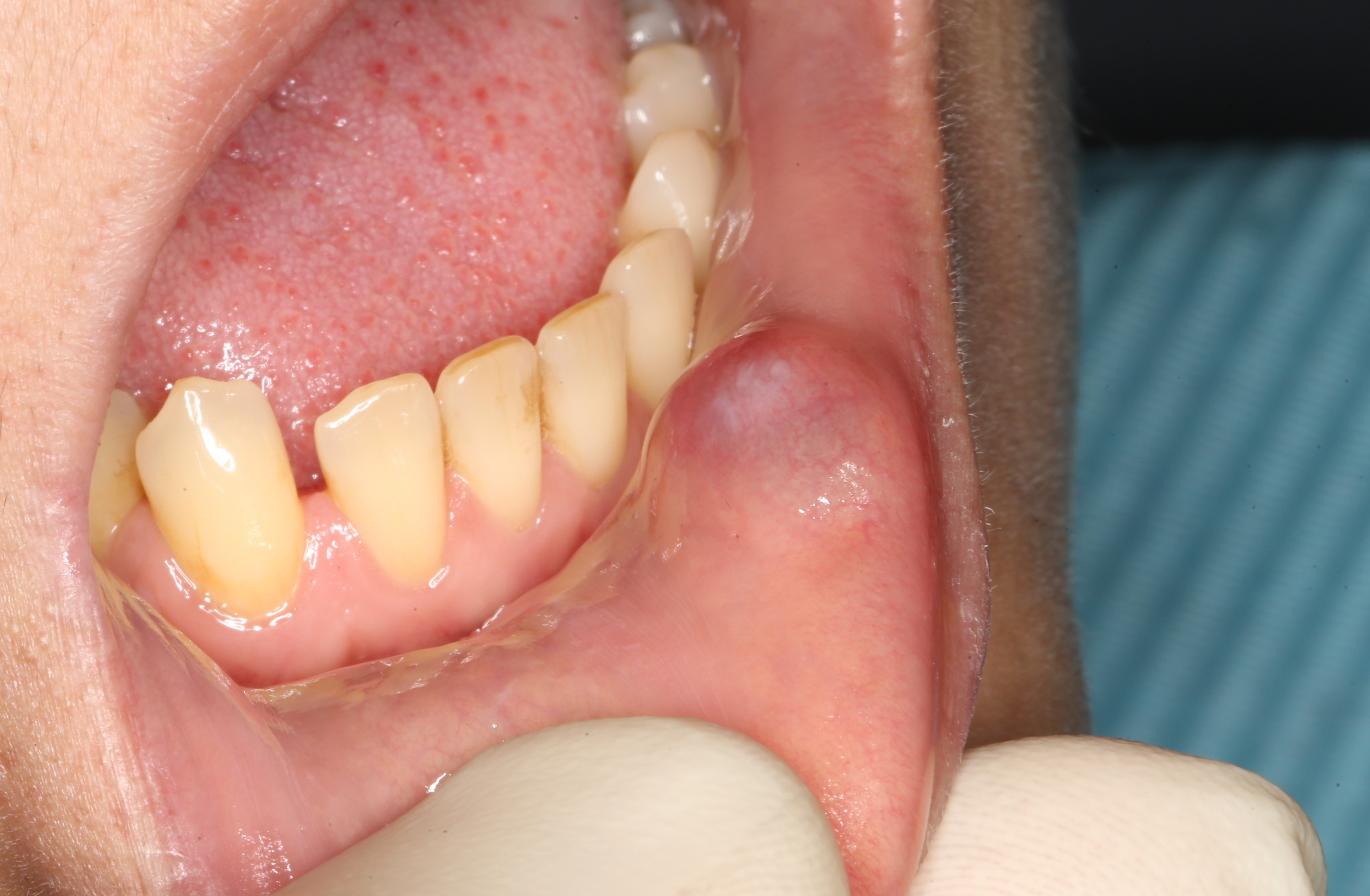
A retention cyst is a consequence of trauma to the salivary gland, most often due to biting when chewing. The duct of this gland is damaged, the release of saliva stops and a cyst containing thick mucus is formed. It looks like a hemispherical tubercle with clear boundaries, absolutely painless, but causing discomfort when talking and eating.
This “bubo” on the lip is the cyst:

The photo below clearly shows that it is in this place that the patient permanently

bites her lip: It often happens that patients bite through this cyst, its contents flow out, and it collapses. This makes it difficult to remove. If this happens, you need to wait until it swells again, and then proceed to the operation.
To begin with, anesthesia is performed.
I beg your pardon right away, I used the following couple of pictures and paragraphs in my previous articles. But given the fact that many stumbled upon my works for the first time, most will be interested in what exactly pain relief is.
In order to minimize all the discomfort associated with the injection, the so-called application anesthesia is used .
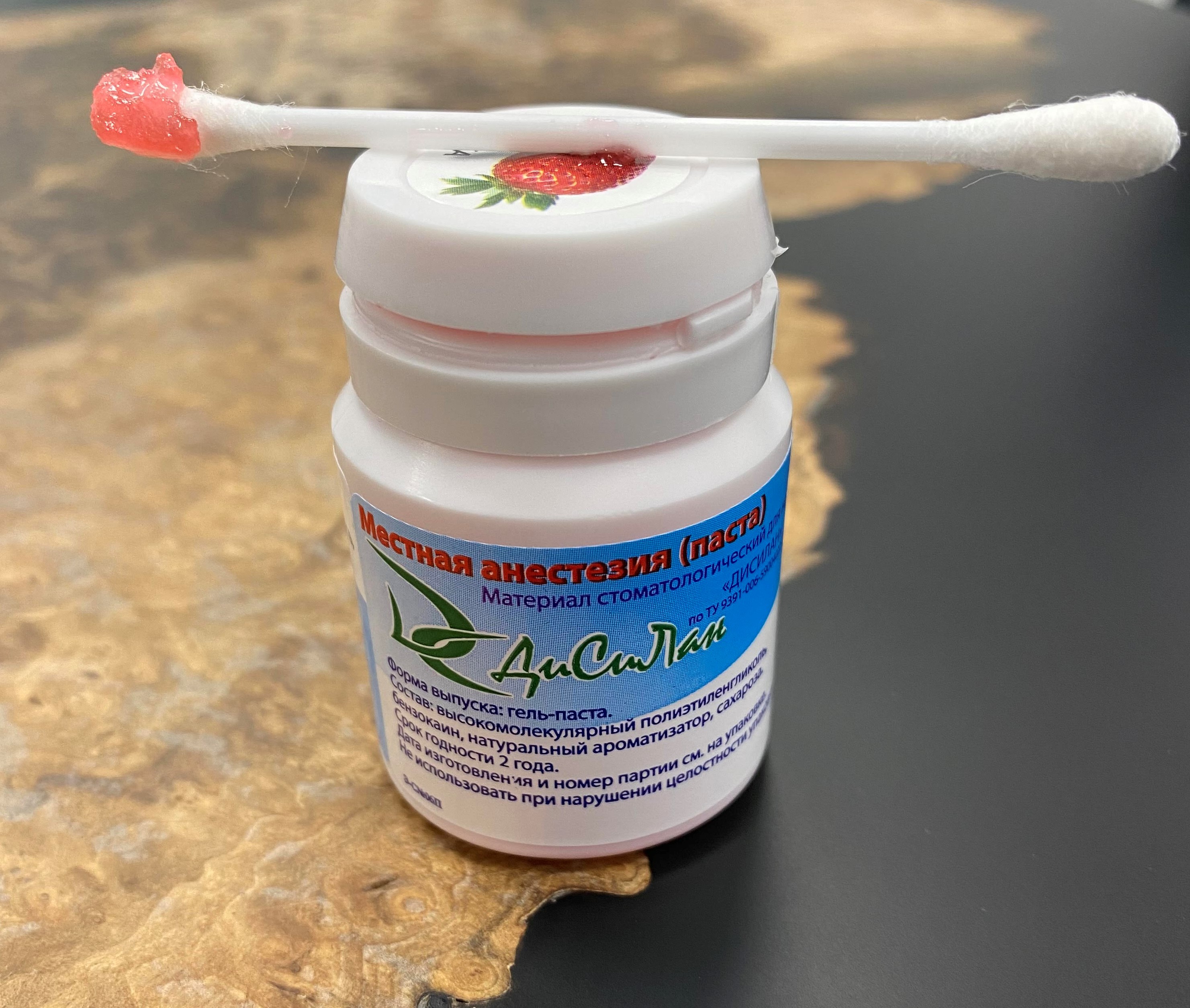

Gel-paste based on polyethylene glycol and benzocaine.
The gums were "lubricated", she was slightly numb. And now you can proceed to the injection ( infiltration anesthesia ).
In modern dentistry, the main active ingredient of the anesthetic is " Articaine " in one concentration or another.
The photo below shows a reusable cartridge syringe, two disposable needles of different lengths and two cartridges with an anesthetic.
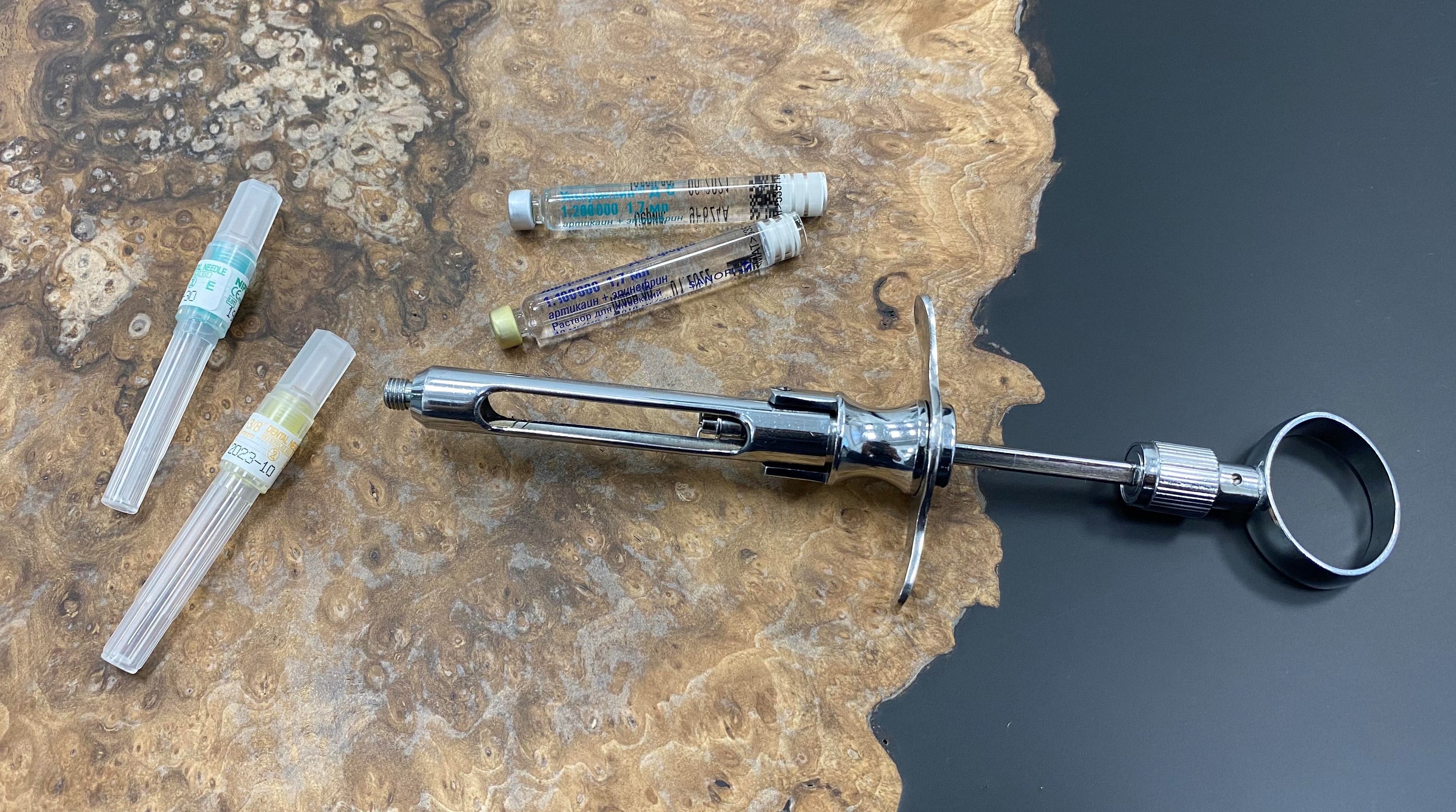
In this case, Ultracaine is represented . The ratio of adrenaline and active substance (Articaine ) in the blue carpool is 1: 100,000 (1 mg of adrenaline per 100 ml), and in the green one - 1: 200,000 (0.5 mg of adrenaline per 100 ml). Consequently, the anesthetic in the blue cartridge lasts a little longer than in the green one. I rarely use this dosage - only when a more prolonged effect of anesthesia is needed, or in acute purulent inflammation.
After the anesthesia has been carried out, a

With the help of a scalpel, two incisions bordering the cyst are made:

Next, carefully pull the cyst with tweezers, and with the same scalpel we continue to highlight the neoplasm, trying not to pierce the cyst shell. Otherwise, the contents will spill.
Like that:
Well, of course not so impressive. The shell will collapse, making it difficult to remove.

It looks kryvy, but in fact everything is not as scary as it seems.

In just a couple of minutes, the cyst was removed:

As you understand, the process itself is quite straightforward and, if done correctly, it is relatively quick.
The photo above is not what you thought, but the small salivary glands, which also need to be removed. Why? But because if you leave them, then there is a chance of relapse.

The wound only looks large, but in fact it is not:

Well, the cyst has been removed, it's time to suture.
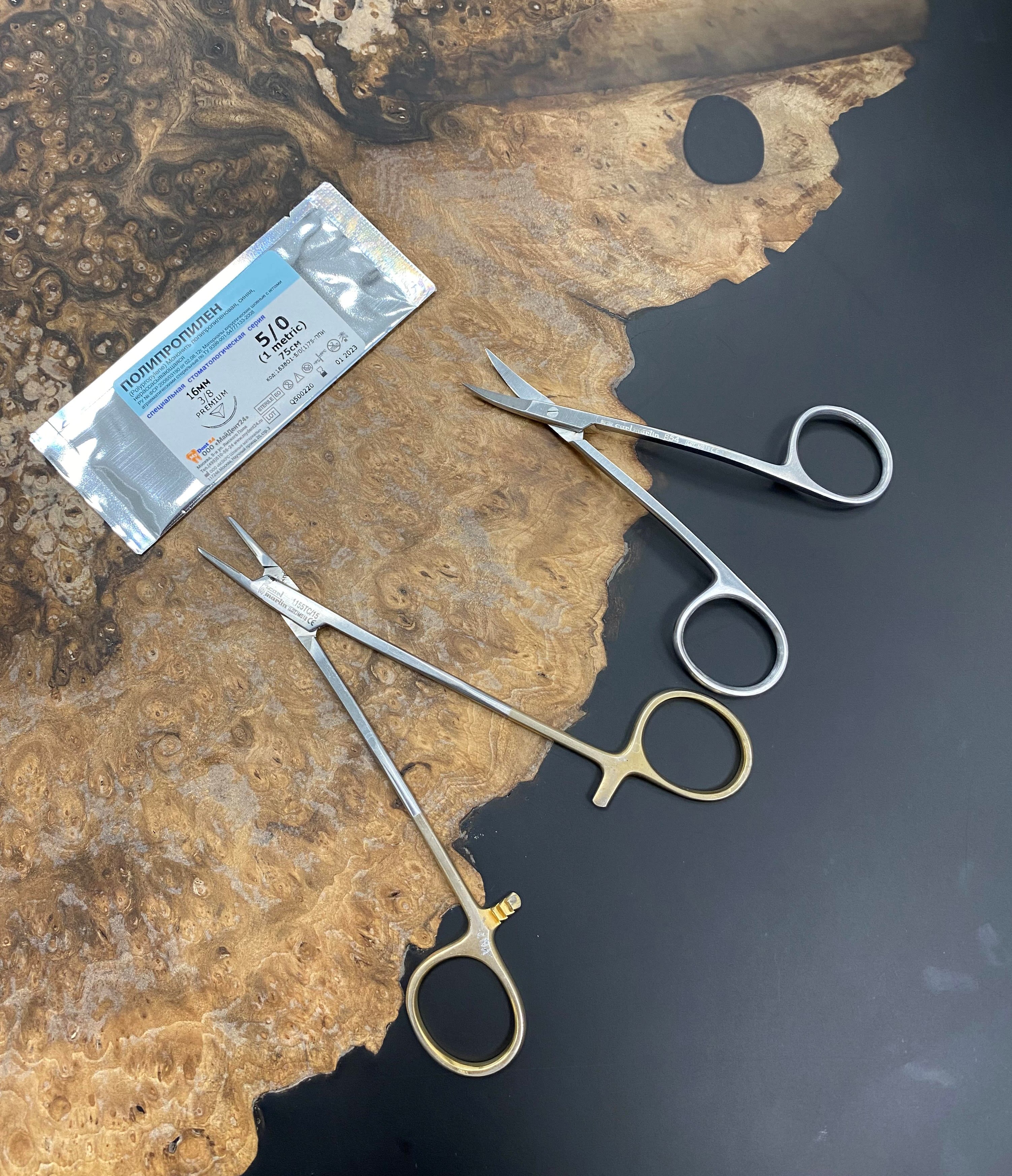

Suture material is used - monofilament. Non-absorbable thread, like a fishing line.
Unlike absorbable sutures, this thread does not accumulate plaque and food debris, which is especially important in the case of surgeries.

The lip after removal of the cyst looks something like this:

The most unpleasant thing in the postoperative period is a slight swelling and bruising. In general, there is no pain. It worries you as if some ill-mannered comrade slapped you on the lip.
After a couple of weeks, the stitches can be removed.

The dent that has formed after removal will smooth out within a month after the operation.
Everything will look like nothing happened.
The small scar that you can see in the photo will also disappear over time.
That is, in fact, the whole operation.
Py. Sy.
Bonus!
Are you wondering what a cyst looks like?
This little friend:

And inside is the following:

Usually, any neoplasms are sent for histological examination in order to verify the cyst. But there was no doubt that it was a mucocele, therefore, there was no point in overpaying for a laboratory test.
That's it for today, stay tuned!
Best regards, Andrey Dashkov
What else to read?
About dental implantation and bone grafting:
- Installation of an implant: how is it done?
- Sinus lifting: how is it done?
- Splitting in dentistry: how is it done?
- Bone block transplant: how is it done?
- Sinus lifting and instantaneous implantation
- Implantation in the absence of teeth, as a result of untimely access to the dentist
- Total prosthetics on implants
About wisdom teeth and their removal:
- Wisdom teeth: you cannot leave them
- Consequences of untimely removal of wisdom teeth
- Removal of wisdom teeth. How it's done?
- ChLH or not ChLH? That is the question ...
- Numbness after wisdom tooth extraction
- Wisdom teeth: Pull-pull!
About professional oral hygiene:
- Professional oral hygiene. Part I. Introduction
- Professional oral hygiene. Part II. How it's done?
And, of course:
- Tooth extraction, "inexpensive" ... consequences
- Dentistry: expectation and reality
- Recommendations after the appointment of a dental surgeon
- The naked truth (article on the formation of the cost of treatment in a dental clinic)