
A simple explanation of the principles of parameter passing in Java.
Many programmers often confuse which parameters in Java are passed by value and which by reference. Let's visualize this process, and then you will see how simple everything is.
Let's start with the basics.
Data is passed between methods via parameters. There are two ways to pass parameters:
(by value). . . , .
(by reference). () . , . , , , .
Java :
, , .
— (heap).
: ?
Java
, .
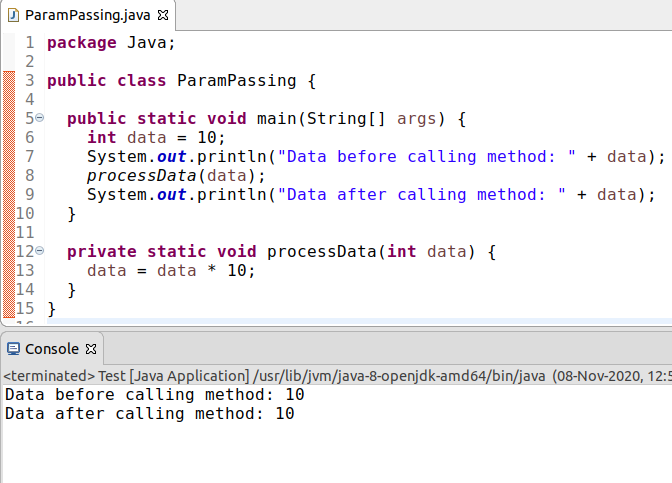
Java , processData
. , ( main
) .
:
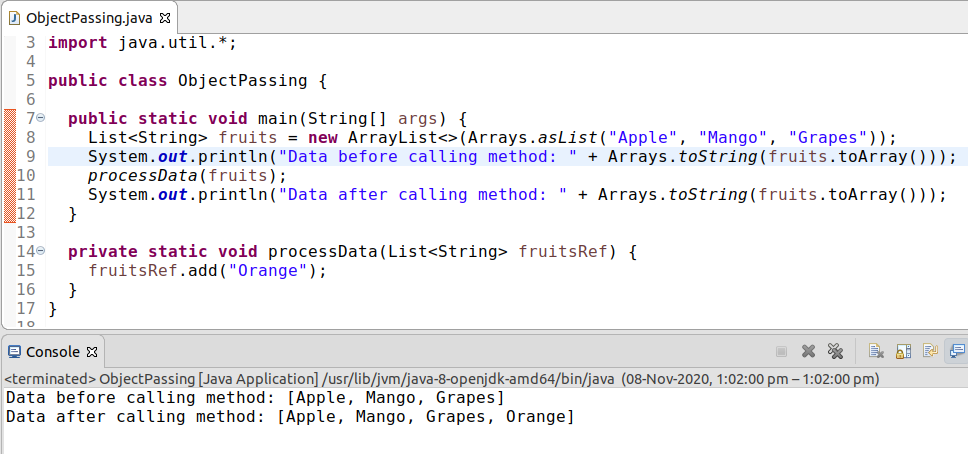
? Java , ? , Java - ? , . : "Java ".
, .

, , fruits
processData
. fruitRef
— fruit
. fruits
fruitsRef
. . , . , , , .
:
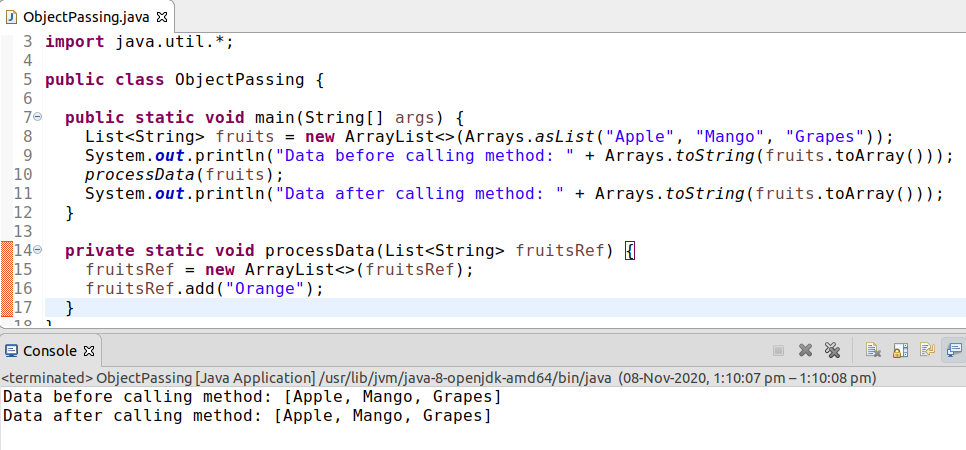

fruitRef
new
. fruitRef
, , , , , .
, Java . .
.
, .
:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d){
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
public static Node push(Node head, int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
public static void deleteNode(Node head, int position) {
// List is empty
if (head == null){
return;
}
// If position is 1st, removing head node
if (position == 1) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
Node prevNode = head;
int i = 2;
while (prevNode != null && i != position) {
prevNode = prevNode.next;
i++;
}
// When position is more than number of node
if (prevNode == null || prevNode.next == null) {
return;
}
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node currNode = head;
while (currNode != null) {
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 5);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 3);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 1);
System.out.println("Created Linked list is: ");
printList(head);
// Delete node at position 2
deleteNode(head, 2);
System.out.println("\nLinked List after Deletion at position 2: ");
printList(head);
}
}
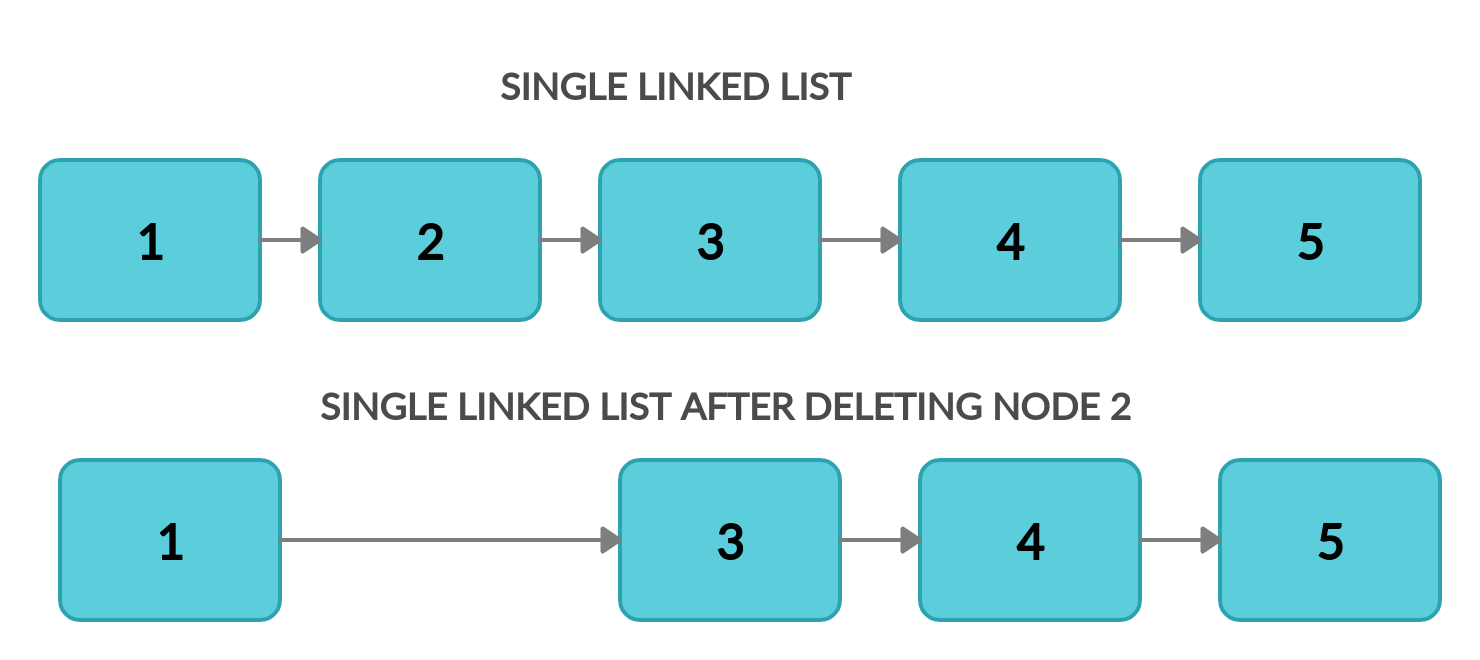
, — (Position = 1
). , ? , .

:
public static Node deleteNode(Node head, int position) {
// List is empty
if (head == null){
return head;
}
// If position is 1st, removing head node
if (position == 1) {
head = head.next;
return head;
}
Node prevNode = head;
int i = 2;
while (prevNode != null && i != position) {
prevNode = prevNode.next;
i++;
}
// When position is more than number of node
if (prevNode == null || prevNode.next == null) {
return head;
}
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
return head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 5);
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 3);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 1);
System.out.println("Created Linked list is: ");
printList(head);
// Delete node at position 2
head = deleteNode(head, 2);
System.out.println("\nLinked List after Deletion at position 2: ");
printList(head);
}
//Rest of the code remains same
, Java: .
" Oracle Java Programmer (OCAJP)".
, 15 .