Hello, to all dear readers of Habr!
I, Sheptovetsky Alexander, have recently been professionally dealing with various issues of the efficiency of various LPWAN systems of the Internet of Things and would like to speak at this site as an expert in this area.
On the Internet, you can find a lot of various information about LPWAN operation, but, unfortunately, some very important specific features of LPWAN operation are highlighted by the manufacturers themselves, who are interested in showing their technology only in the best light. All systems are declared to have a long operating range, all devices operate on batteries for 10 years, all promise unprecedented safety and system reliability. Independent experts, as a rule, simply reprint advertising information in the form of comparative tables with a set of various parameters, often not understanding what these numbers mean for the consumer.
I want to announce a series of articles in which I will try to clarify the key features of LPWAN systems operation, energy efficiency, range, battery life, bandwidth, security and much more. I will try to be as objective as possible.
The first article will be devoted to the question of what is energy efficiency projected onto NB-IoT solutions, in the next we will discuss energy efficiency of unlicensed solutions, problems with range, bandwidth, security and some other aspects.
How to measure energy efficiency
When describing LPWAN systems, the word energy efficiency is constantly used, what does it mean and can it be measured?
, . LPWAN 10 , ?
, . -T L.1310 , « , ».
LPWAN , , « ». , , .
- , .
, , . , . .
: « , . 2- 3-.».
: « , ».
= Constant
LPWAN 3,6 , - (), , - (). , LoRaWAN, 1,6 20 , 100 2000 . SigFox , 6,2 78 ( Rohde & Schwarz , - 106 , ). , , SigFox 3,8 , LoRaWAN ! ! , , !
. , , Bluetooth . BLE 0dBm 1 7 , . 1000 15 , 470 , 2,1 !
Bluetooth , LoRaWAN SigFox
NB-IoT.
NB-IoT
NB-IoT , NB-IoT - LPWAN LPWAN , , LoRaWAN, SigFox .. , LPWAN - NB-IoT.
3GPP , NB-IoT . , . GPS , NB-IoT , : "NB-IoT , ", 2G , , 2 NB-IoT . NB-IoT 2G 2 . , ?
, . , NB-IoT , LTE, , - , .
NB-IoT , - , - LoRaWAN. ( «Exploring the Performance Boundaries of NB-IoT»).
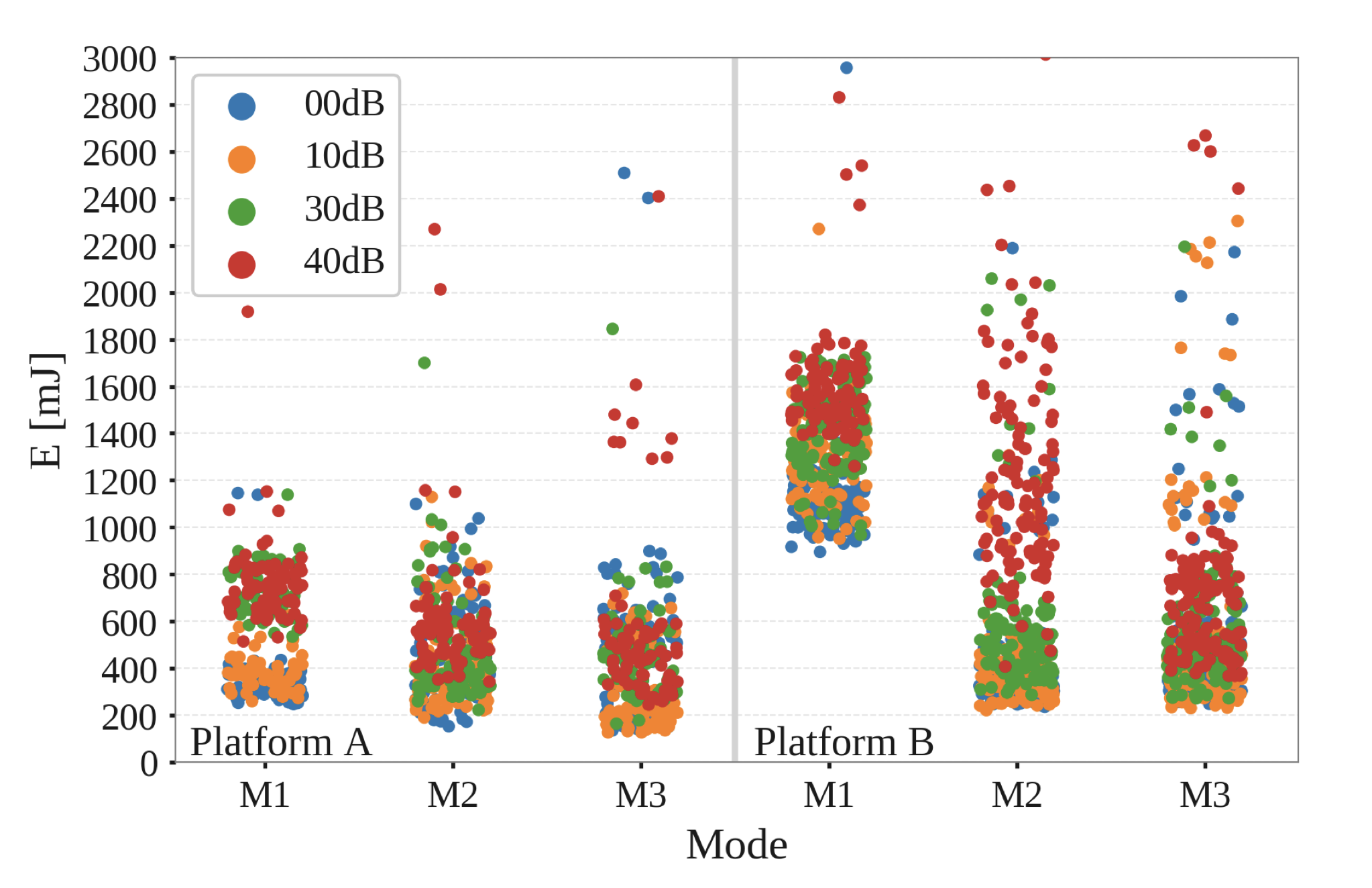
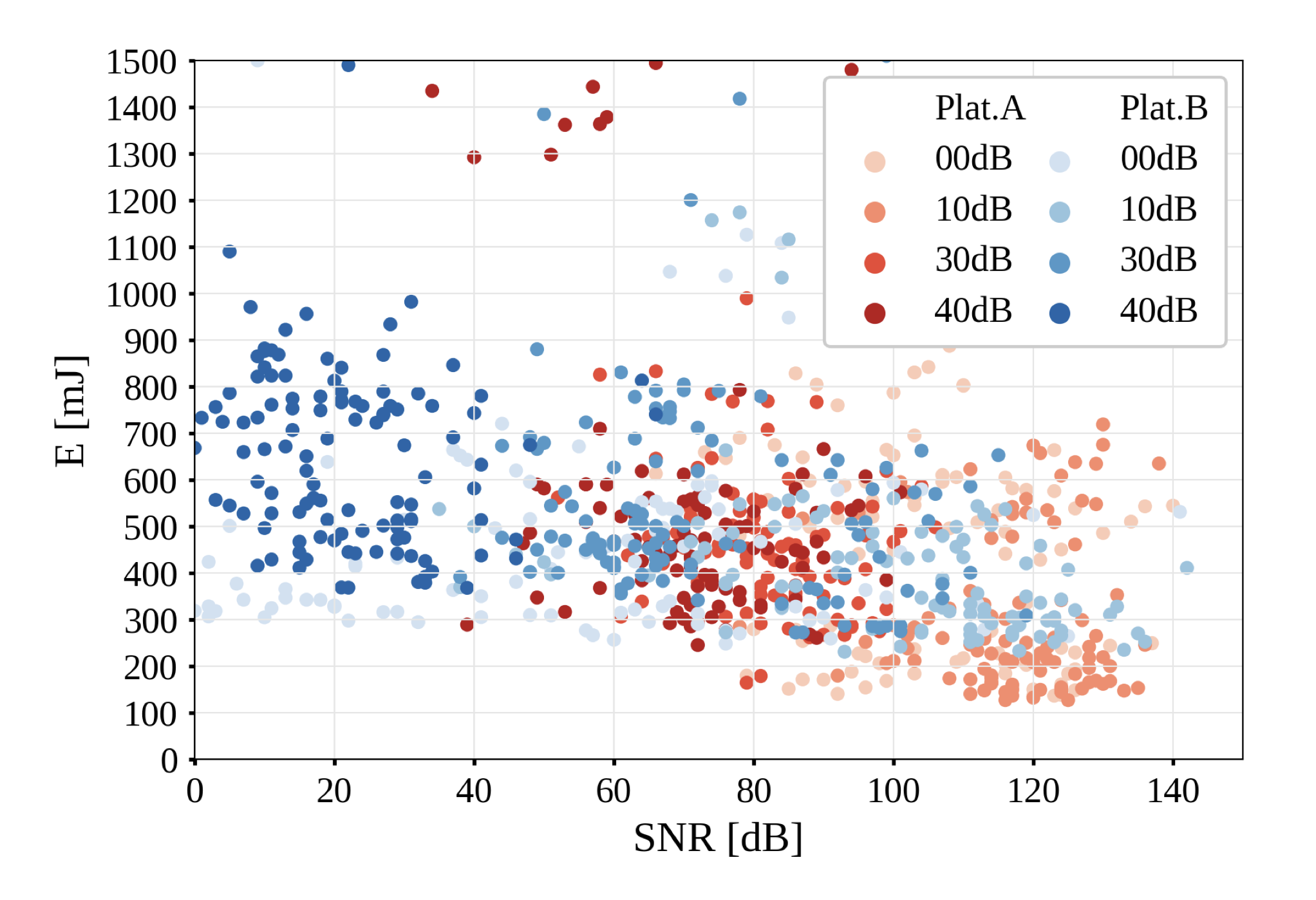
NB-IoT PSM. 2 3 ( «Exploring the Performance Boundaries of NB-IoT») , .
, NB-IoT , , LTE 5G, , .
NB-IoT «Narrowband IoT Device Energy Consumption Characterization and Optimizations».
, NB-IoT, 4G 5G , (SC), .
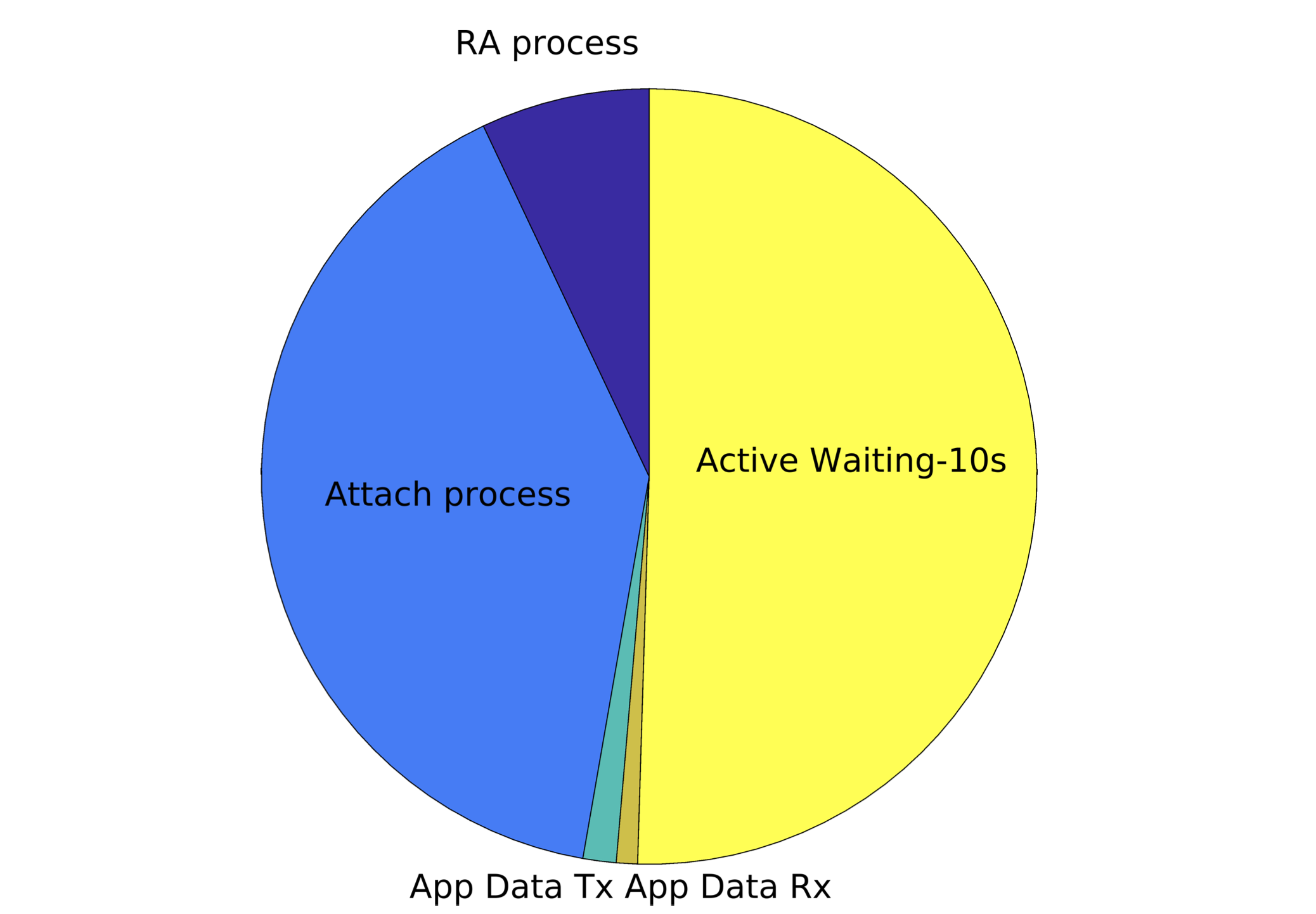
, . SC (, TAU).
NB-IoT : , . PSM 3GPP, . — , (RA), , ( , , / ), IMSI . .
, . , RA, Attach Active Waiting.
, NB-IoT , , , ( 128 2048 ).
5 10 «Narrowband IoTDevice Energy Consumption Characterization and Optimizations». , 1 000 12 .
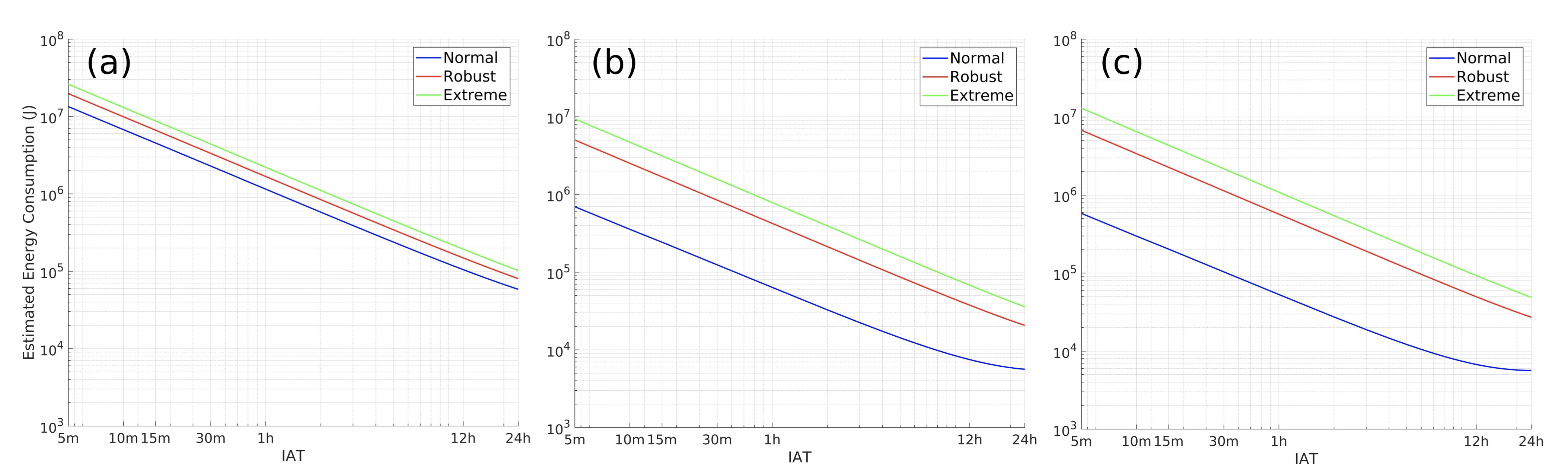
5 NB-IoT . , , 10 5,5 55 - , . 3,6 460 4 600 . , , ! ! 1 700 6 700 . , 10 «» 150 000 .
NB-IoT NB-IoT. : , , , . , :
|
NB-IoT |
LoRaWAN |
SigFox |
2 * |
400 |
29 |
128 |
2 |
5 000 |
70 000 |
15 600 |
10 2 |
1,1 |
1,3 |
3,5 |
2 |
6,8 |
7,8 |
1,8 |
*- NB-IoT «Narrowband IoT Device Energy Consumption Characterization and Optimizations», ( ). , , .
:
LPWAN -, .
LPWAN ( - ).
Sensors based on NB-IoT will have a very wide spread in consumption depending on the manufacturer, operating network and operating conditions. One and the same sensor in some conditions will live for 10 years, and in others it will not last even a couple of months.
It turns out that NB-IoT sensors, despite the fact that they operate at dedicated frequencies, in real conditions of mass use will lose out in the energy sector to low-power LPWAN solutions operating in the license-free frequency range.