The first scientific theory, the purpose of which was the analysis and optimization of work processes, is "Scientific management". At the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, through the efforts of the American researcher Frederick Taylor and his associates, the theory of classical management was created. It is based on the premise that there is a “best way” to do any given job, and the problem of low productivity can be solved by using a method called “scientific timing”. The essence of the method is to divide the work into a sequence of elementary operations, which are timed and recorded with the participation of workers. As a result, this allows you to get accurate information about the time required to complete a particular job.

Thus, more than 120 years ago, such a simple step gave rise to a scientific approach to the study of processes. With the development of society and technology, approaches to the analysis and optimization of processes evolve and improve: there is a transition to "mass production", which is based on specialization with the possibilities of optimizing assembly, computerization and analysis of statistics.
Modern Process Mining is an evolution of this approach with big data in mind.
Evolution
In the late 80s, the well-known Taichi Ono made a breakthrough by developing and implementing an approach called "Lean Manufacturing" at Toyota. The approach is based on constant work with all types of losses that arise in the process. Eliminating losses a priori increases efficiency.
The next qualitative step in the field of process optimization is the development and implementation of the "DMAIC cycle" tool, and the use of Six sigma statistical process control methods, which also need no introduction. The key characteristics of the stage are - entering KPIs and dealing with deviations, focusing on the customer and ensuring continuous improvement of processes.
These approaches, which worked well 5-10 years ago and relied on manual tools such as gemba, timing, customer and expert surveys, and design sessions, nowadays, in an era of ever-increasing complexity and acceleration of processes, do not provide a complete picture.
Today, the ubiquitous development of digital technologies, robotization and automation, the Internet of things, global networks and mass digitalization provide the basis for a qualitatively new stage of research and optimization of processes, the implementation of ML and AI capabilities.
Process Mining is such an AI transformation tool.
What exactly is this approach needed for?
Invented by Professor Wiel van der Aalst at the beginning of the last decade, Process Mining technology has rapidly gained popularity in both scientific and corporate environments. Today, with the growth of the volume of information and the speed of changes in business, it is replacing the classical methods of describing and manually modeling processes.
By restoring business process diagrams as they actually occur, Process Mining provides insights - objective knowledge necessary to eliminate bottlenecks, optimize imperfections, and improve organizational performance. Thus, using the Process Mining toolkit, the company solves both compliance issues and process performance issues.
Visualization of insights (bottlenecks, returns, loops, great variability) on the process graph:
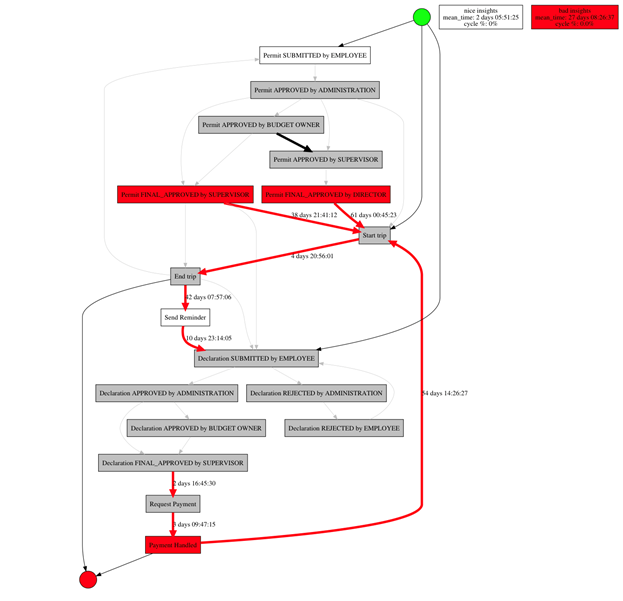
Digital transformation is one of the main drivers of modern business. Its prerequisites, or mandatory conditions, are traditionally considered transparency and openness, which Process Mining directly helps to achieve. In fact, he makes an "X-ray" of the processes occurring in the company, providing a comprehensive, and most importantly reliable picture of the entire chain of events, and not individual steps, thereby eliminating barriers between various departments and divisions. The resulting assessment of the company's current operating efficiency is objective, and therefore can be used to identify optimization opportunities, track changes and respond quickly. Process Mining, by erasing organizational boundaries, provides insights for any level of detail. The value of these insights lies inthat they give the company a foundation and direction for further actions to improve and digitalize processes in all divisions.
Thus, Process Mining provides process owners with full analytics in order to make management decisions to improve the process on objective data.
How is the implementation going
The basis for the application of Process Mining is formed by event logs. Information systems automatically record all activities performed during one process. In addition to activities, event logs contain start and end timestamps, a unique case ID, and other attributes of the event: performers, text of correspondence, deal decision, territorial attributes, and so on.
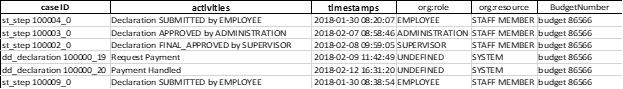
Log files, providing reliable and detailed information about the course of the execution of a business process, make it more transparent. With this information, you can visualize and analyze a model of a real, not an intended process. This is important because it is this gap that makes Process Mining very efficient for large companies. However, it is not limited to restoring business process models from log files. By comparing log data and process diagrams, Process Mining allows you to identify deviations and bottlenecks in the process, study the duration of each stage, detect unnecessary or skipped stages, and identify potential optimization and, therefore, efficiency gains.
One of the key tasks is to extract insights from the data available in corporate IT systems. Having digital information about all the actions performed within the process, using the Process Mining technology, the company is able to reproduce the actually executable business process. And the construction of its visual scheme allows not only to get a complete picture of the chain of events, but also to investigate the current state of the process at any level of detail. By analyzing the model of the reconstructed process together with data on the duration and features of its execution, it is possible to identify delays in the implementation of individual actions, the relationship between users, looping in the process, ineffective performers, as well as hidden shortcomings and problems in the processes, due to which it can significantly decrease the productivity of an entire organization.In addition, Process Mining allows you to see the process in dynamics, which means the ability to track changes that occur as a result of the introduction of certain improvement measures. So, Process Mining plays a key role in providing valuable and objective information necessary to improve the efficiency of solutions to optimize business processes. The main advantages of a process-oriented analysis are as follows:The main advantages of a process-oriented analysis are as follows:The main advantages of a process-oriented analysis are as follows:
- Increase in productivity;
- Faster and more efficient collaboration;
- Reduced time for administrative work;
- Transparency;
- Reducing costs.
Together, this ensures the stable growth of the company.
Of course, Process Mining is of great value for business process owners, as it identifies unwanted changes and deviations, bottlenecks and other risks in the process, thereby showing exactly where problems and vulnerabilities exist in the system and how they affect overall performance. However, the question "Why?" Is much more interesting. - what is the cause of these problems and deviations? Machine learning can help answer this question.
What did Sberbank do?
To implement intellectual analysis of processes, the R&D Process Mining team of Sberbank has developed a special library.
The Python library includes all the analysis methods you need, and are now easily accessible for experimentation. The first version of the Open Source solution includes features that allow you to:
- reconstruct process graphs with various algorithms;
- convert process graphs to bpmn notation;
- calculate various process metrics;
- do clustering and find the main paths of processes.
- , k-means, , . , .
- — . , LOF, Isolation Forest , Process Mining , , , . , . , .
Revealing the main paths of the process:

Heatmap of the process throughput:
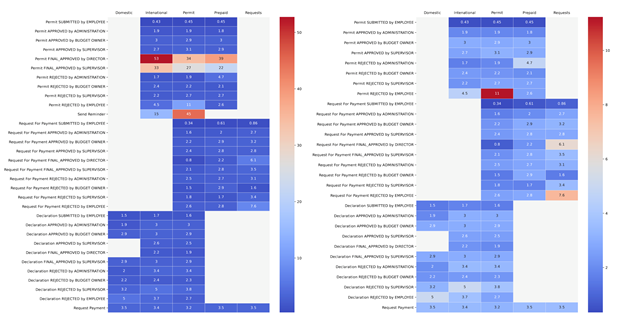
Plot of variables:

Automatic search for insights:
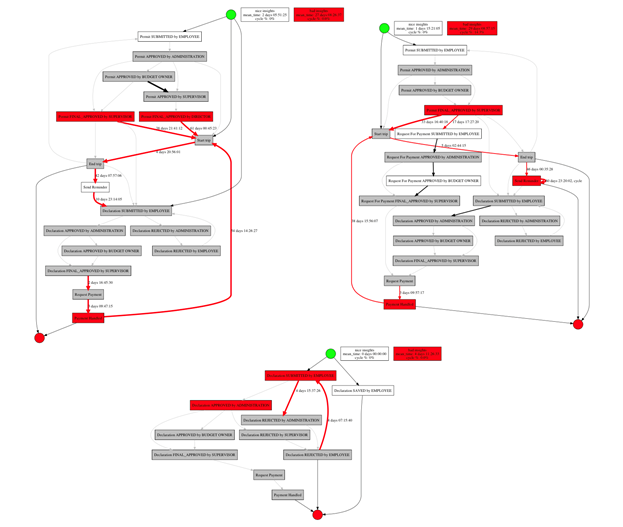
Machine learning algorithms are used in the library to implement automatic root cause analysis (Root Cause Analysis), as a result of which critical weaknesses of the process are identified and the starting points for its optimization are determined ... In addition, Root Cause Analysis allows you to establish the most likely influencing factors and causes of problems, that is, it helps to answer the questions of when and why deviations occurred in the process.
Thus, Process Mining is, first of all, visualization and analysis of business processes. On the basis of the logs stored in information systems, it is possible to restore the actual (visual) scheme of the process execution in the form of how it actually takes place. Machine learning, in turn, allows you to determine root causes and thereby understand why the process proceeds in this way.
How we apply Process Mining ourselves
We have more than 12 thousand offices in Russia, subsidiaries and banks outside the Russian Federation, ecosystem companies. Process Mining allows you to “reach” the processes in regional banks, to colleagues from Sberbank International: we already have experience, we have seen the processes of Kazakhstan, Belarus; to our subsidiaries: SberLeasing, SberFactoring, etc.
We started using the technology in 2019. The first and very successful end-2-end study was the analysis of the lending process. Lending is a huge cross-functional process, which at that time involved several thousand employees and several automated systems.
We collected and glued event-logs from several systems, thanks to which we received detailed information about the duration of the process at each stage, reconstructed real versions of the process paths, and compared them with normative ones. The process turned out to be overloaded with a variety of paths and variations of the passage of individual stages, loops, returns from stage to stage, and this is all a waste of time and, ultimately, money. Found inefficiencies, loops, ping-pong between performers and bounces. We built a performance heatmap by territory, which showed the differences in the organization of the process and the speed of decision-making on the application.
Performers' comments have become a valuable source of information. The ML-module for text analysis made it possible to automatically, without a training sample, cluster the texts of correspondence and get the TOP reasons why the application returns to the previous stages, why the process is slow.
All this gave us the answers where we need to "treat" the process.
Process Mining is effective on any processes that leave a digital footprint: whether it is a business process "issuing a loan" or an internal one that ensures "approval of a business contract".
The technology has become widespread in Sberbank in digital audit. For internal audit, process analysis is a subject area. Process Mining allows you to get a completely different kind of high-quality results, because:
- Digital data is used for 100% of process instances. Accordingly, the output is a 100% objective picture, which is difficult to argue with: the process owners can always verify the data. From an audit point of view, this approach is very good.
- Algorithms provide insights that cannot be obtained by standard audit methods.
- A big plus of digital technology is contactlessness; in a pandemic, there are no other audit options. It makes it possible to fulfill the plan of inspections and work when everyone is in conditions of remote work.
The SberPM Python library is available on GitHub at the link . Each Data Scientist can install Sberbank's solution and start analyzing processes with Process Mining technology.