Below is not a tutorial, but only a cheat sheet for developers already familiar with the basics of C # .Net.
The cheat sheet contains only "base" questions. Questions like "how would you design ...", "which application layers ..." are not included in the cheat sheet. As noted in the comments, the questions are more likely for Jun, nevertheless, they are asked at middles interviews.
Code formatting
In the examples, for brevity, the opening parenthesis {is not on a new line. The interviewer may be confused because in C # it is customary to put {on a new line. Therefore, it is better to use common formatting during the interview.
stack and heap, value type and reference type
reference type (example class, interface) are stored in a large heap
value type (example int, struct, references to instances of reference type) are stored in the fast stack
when assigning (passing to a method) value types are copied, reference types are passed by reference (see the struct section below)
struct
value type => when assigned (passed to the method) all fields and properties are copied, cannot be null
no inheritance
supports interfaces
if there is a constructor, all fields and properties must be set in it
interface IMyInterface {
int Property { get; set; }
}
struct MyStruc : IMyInterface {
public int Field;
public int Property { get; set; }
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
var ms = new MyStruc {
Field = 1,
Property = 2
};
// value type ,
//
TryChange(ms);
Console.WriteLine(ms.Property);
// ==> ms.Property = 2;
// boxing ( )
IMyInterface msInterface = new MyStruc {
Field = 1,
Property = 2
};
// object (reference type)
// , msInterface
TryChange(msInterface);
Console.WriteLine(msInterface.Property);
// ==> ms.Property = 3;
}
static void TryChange(IMyInterface myStruc) {
myStruc.Property = 3;
}
}
DateTime is a struct, so it's pointless to check fields of type DateTime for null:
class MyClass {
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
}
var mc = new MyClass();
// false,
// .. DateTime struct (value type) null
var isDate = mc.Date == null;
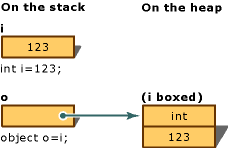
boxing / unboxing
// boxing (value type, stack -> object, heap)
int i = 123;
object o = i;
// unboxing (object, heap -> value type, stack)
object o = 123;
var i = (int)o;
// boxing
int i = 123;
object o = i;
i = 456;
// ==> .. i, o
// i = 456
// o = 123
// boxing
IMyInterface myInterface = new MyStruct(2);
// boxing i
int i = 2;
string s = "str" + i;
// .. String.Concat(object? arg0, object? arg1)
// unboxing, .. Session Dictionary<string, object>
int i = (int)Session["key"];
string
heap reference type
( ) value type
string a = "hello";
string b = "hello";
// string value type
// ( == )
Console.WriteLine(a == b);
// ==> true
var mc1 = new MyClass { Property = 1 };
var mc2 = new MyClass { Property = 2 };
// reference type
// heap
Console.WriteLine(mc1 == mc2);
// ==> false
const vs readonly
const - =>
readonly -
class MyClass {
public const string Const = "some1";
public readonly string Field = "some2";
}
var cl = new MyClass();
Console.WriteLine(MyClass.Const);
Console.WriteLine(cl.Field);
- dll , :
ref out
ref out new class struct
out ref, ,
struct MyStruc {
public int Field;
}
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
var ms = new MyStruc { Field = 1 };
createNew(ms);
Console.WriteLine(ms.Field);
// ==> ms.Field = 1
var ms2 = new MyStruc { Field = 1 };
createNew2(ref ms2);
Console.WriteLine(ms2.Field);
// ==> ms2.Field = 2
}
static void createNew(MyStruc myStruc) {
myStruc = new MyStruc { Field = 2 };
}
static void createNew2(ref MyStruc myStruc) {
myStruc = new MyStruc { Field = 2 };
}
static void createNew3(out MyStruc myStruc) {
// ,
// myStruc = new
}
}
generic-.
interface IAnimal { }
class Cat : IAnimal {
public void Meow() { }
}
class Dog : IAnimal {
public void Woof() { }
}
// , List -
// , List Add,
// ( . )
List<IAnimal> animals = new List<Cat>();
// , IEnumerable -
// IEnumerable
IEnumerable<IAnimal> lst = new List<Cat>();
Add List:
//
List<Cat> cats = new List<Cat>();
cats.Add(new Cat());
List<Cat> animals = cats;
animals.Add(new Cat());
foreach (var cat in cats) {
cat.Meow(); // cats 2
}
//
List<Cat> cats = new List<Cat>();
cats.Add(new Cat());
List<IAnimal> animals = cats;
animals.Add(new Dog()); // , :
//
foreach (var cat in cats) {
cat.Meow(); // cats 1 1 , Meow()
}
Object
ToString
GetType
Equals
GetHashCode
ToString GetType .
Equals GetHashCode , linq, . , .. .Net. hash .
GetHashCode .
,
class MyClass {
public event Action<string> Evt;
public void FireEvt() {
if (Evt != null)
Evt("hello");
// Evt("hello") -
//
//foreach (var ev in Evt.GetInvocationList())
// ev.DynamicInvoke("hello");
}
public void ClearEvt() {
// MyClass
Evt = null;
}
}
var cl = new MyClass();
//
cl.Evt += (msg) => Console.WriteLine($"1 {msg}");
cl.Evt += (msg) => Console.WriteLine($"2 {msg}");
//
Action<string> handler = (msg) => Console.WriteLine($"3 {msg}");
cl.Evt += handler;
cl.Evt -= handler;
cl.FireEvt();
// ==>
// 1 hello
// 2 hello
//
// "+=" "-="
// MyClass
cl.Evt = null;
Finalizer (destructor) ~
garbage collector
.Net,
struct
finalizer: IDisposable. Dispose finalizer, Dispose. finalizer .
throw vs "throw ex"
try {
...
} catch (Exception ex) {
// , .. CallStack
throw;
// CallStack
throw ex;
}
Garbage collector
. heap , , . Garbage collector. :
( ) -
heap
(Generation 0) - , . Generation 0.
- Generation 1.
Generation 0 , . - Generation 1.
, 2 - Generation 2.
Derived.Static.Fields
Derived.Static.Constructor
Derived.Instance.Fields
Base.Static.Fields
Base.Static.Constructor
Base.Instance.Fields
Base.Instance.Constructor
Derived.Instance.Constructor
class Parent {
public Parent() {
// virtual
//
//
DoSomething();
}
protected virtual void DoSomething() {
}
}
class Child : Parent {
private string foo;
public Child() {
foo = "HELLO";
}
protected override void DoSomething() {
Console.WriteLine(foo.ToLower()); //NullReferenceException
}
}
( , ), . (, , ) - . vs vs .
-
-
- , , )
-
SOLID
Single responsibility - , , God-object
Open closed principle -
Liskov substitution -
Interface segregation principle -
Dependency inversion principle - , ,
3
(: )
(: )
(: )
IDisposable, try, catch, finally
singleton ( lock)
(mutex, semaphore ..)
/ . : . , . . ? ( )?
SQL , HAVING
Stack and heap – .NET data structures
Boxing and Unboxing (C# Programming Guide)
Built-in reference types (C # reference)
Covariance and contravariance in generics
C # variance problem: Assigning List as List
Finalizers (C # Programming Guide)
Destructors in real world applications?
Virtual member call in a constructor
Inheritance vs Composition vs Aggregation
Fundamentals of garbage collection