Table of contents
Calculation of the footage and area of production (some matrices)
Expenses
Dumping data with PyODBC
Uploading Data Using MsSQL Library SL
Calculation of the footage and area of production (some matrices)
The matrix of the footage of manufactured products by profiles and formats is a two-dimensional array A 6 * 6, which is subdivided into a two-dimensional array B p * f, where p = 5 is the corrugation profile, f = 5 is the format, and one-dimensional Z p is the sum of the produced meters by corrugation profiles and Z f is the sum of produced meters by formats. Correspondingly, the matrix Zp is a one-dimensional matrix of 5 elements, it is the sum of the columns of the matrix A, Zf is a one-dimensional matrix of 5 elements, it is the sum of the rows of the matrix A. There is one element not filled in - a66, this cell will be the total length of the produced products.
It also took 2 more one-dimensional matrices: Sp - the area of products manufactured by profiles and Sf - the area of products manufactured by formats and a constant matrix F - a one-dimensional matrix of 5 elements - a list of raw materials formats.


Deal with filling! Now algebra begins.
The sum for formats and profiles is calculated by adding rows and columns, respectively, of the original matrix A.
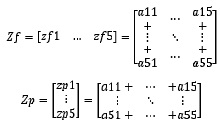
The calculation of areas by format is very simple, we simply multiply 2 matrices A and F

or
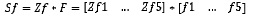
Area by corrugation profiles:
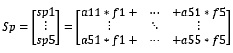
Function block listing
FUNCTION_BLOCK Format_math
VAR_INPUT
EN:BOOL;
imp:BOOL;
END_VAR
VAR_INPUT RETAIN
f:INT := 1;
p:INT := 1;
END_VAR
VAR_INPUT
l_roll:REAL;
k_imp:INT;
res:BOOL;
res_month:BOOL;
END_VAR
VAR_OUTPUT
// [f,p], f=6 - , p=6 -
length_f:ARRAY[1..6, 1..6] OF REAL;
wS_f:ARRAY [1..5] OF WORD;
wS_p:ARRAY [1..5] OF WORD;
END_VAR
VAR_OUTPUT RETAIN
S_f:ARRAY [1..5] OF REAL;
S_p:ARRAY [1..5] OF REAL;
END_VAR
VAR_OUTPUT
S_f_month:ARRAY [1..5] OF REAL;
S_p_month:ARRAY [1..5] OF REAL;
END_VAR
VAR
imp_old:BOOL;
f_b: ARRAY [1..5] OF BOOL;
p_b: ARRAY [1..5] OF BOOL;
length_f_old:ARRAY[1..6, 1..6] OF REAL;
i:BYTE;
j: BYTE;
k:REAL;
END_VAR
BEGIN
k:=l_roll/(k_imp*1000);
IF EN AND not imp AND imp_old THEN
length_f[f,p]:=length_f[f,p]+k;
//length_p[p]:=length_p[p]+(l_roll/(k_imp*1000));
END_IF
FOR i:=1 TO 5 DO
length_f[i,6]:=0;
length_f[6,i]:=0;
FOR j:=1 TO 5 DO
length_f[i,6]:=length_f[i,6]+length_f[i,j];
length_f[6,i]:=length_f[6,i]+length_f[j,i];
END_FOR
END_FOR
CASE f OF
1: S_f[f]:=length_f[f,6]*1.050/1000;
2: S_f[f]:=length_f[f,6]*1.250/1000;
3: S_f[f]:=length_f[f,6]*1.400/1000;
4: S_f[f]:=length_f[f,6]*1.575/1000;
5: S_f[f]:=length_f[f,6]*1.600/1000;
END_CASE
FOR i:=1 TO 5 DO
S_p[i]:=length_f[1,i]*1.05/1000+length_f[2,i]*1.25/1000+length_f[3,i]*1.4/1000+length_f[4,i]*1.575/1000+length_f[5,i]*1.6/1000;
wS_p[i]:=REAL_TO_WORD(S_p[i]*10);
wS_f[i]:=REAL_TO_WORD(S_f[i]*10);
END_FOR
IF res THEN
FOR i:=1 TO 6 DO
FOR j:=1 TO 6 DO
length_f_old[i,j]:=length_f[i,j];
length_f[i,j]:=0;
END_FOR
END_FOR
FOR i:=1 TO 5 DO
S_f_month[i]:=S_f_month[i]+S_f[i];
S_f[i]:=0;
S_p_month[i]:=S_p_month[i]+S_p[i];
S_p[i]:=0;
END_FOR
END_IF
IF res_month THEN
FOR i:=1 TO 5 DO
S_f_month[i]:=0;
S_p_month[i]:=0;
END_FOR
END_IF
FOR i:=1 TO 5 DO f_b[i]:=0; END_FOR
FOR i:=1 TO 5 DO p_b[i]:=0; END_FOR
f_b[f]:=TRUE;
p_b[p]:=TRUE;
imp_old:=imp;
END
Expenses
RPI 3 model B for 4 thousand rubles (on AliExpress 3 thousand rubles). It was possible to get by with a cheaper RPI zero (2 thousand rubles), but the framework of the system was initially blurred by the non-existent TK (let's do this first, and then we'll see if we need something else ... then ... and then ...);
24/5 AliExpress 300 . ( );
CODESYS Control for Raspberry Pi SL 50 . - RealTime 2 , ;
PyODBC
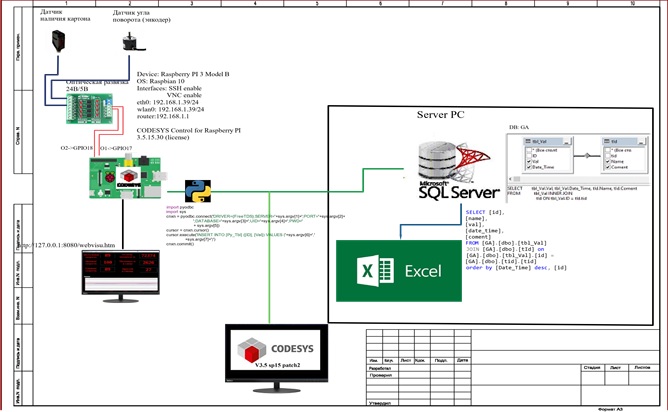
ODBC Raspberry
:
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo apt-get install python3-dev unixodbc-dev git
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ git clone https://github.com/mkleehammer/pyodbc
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ cd pythodbc
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ import pyodbc
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ python3 setup.py
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ cd /home/pi/pyodbc
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo python3 setup.py build
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo apt-get update
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo apt-get install g++
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo apt-get install unixodbc-dev
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ pip install pyodbc
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ odbcinst -j
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ cat /etc/odbcinst.ini
[FreeTDS]
Description=FreeTDS Driver v0.91
Driver=/usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf/odbc/libtdsodbc.so
Setup=/usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf/odbc/libtdsS.so
fileusage=1
dontdlclose=1
UsageCount=1
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ cat /etc/odbc.ini
Driver = FreeTDS
Description = My Test Server
Trace = No
ServerName = mssql
#Port = port
instance = MSSQLSERVER #(whatever is the service u r runningcould be SQLEXPRESS)
Database = database_name
TDS_Version = 4.2
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo nano /etc/freetds/freetds.conf
[egServer70]
host = ntmachine.domain.com
port = 1433
tds version = 7.0
[mssql]
host = server_ip_adress
instance = MSSQLSERVER
#Port = port
tds version = 4.2
.
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo python3
>>> server = '192.168.1.2'
>>> port = '1433'
>>> database = 'GA'
>>> username = 'plc'
>>> password = '123456'
>>> cnxn = pyodbc.connect('DRIVER={FreeTDS};SERVER='+server+';PORT='+port+';DATABASE='+database+';UID='+username+';PWD='+ password)
>>> cursor = cnxn.cursor()
>>> cursor.execute('select top 10 ID,Val,Date_Time from tbl_Val')
#cursor.execute('INSERT INTO tbl_Val (ID, Val) VALUES (15, 20)')
>>> rows=cursor.fetchall()
>>> for row in rows: print(row.ID, row.Val)
/home/pi/pyodbc/ “query.py”. , .
import pyodbc
import sys
cnxn = pyodbc.connect('DRIVER={FreeTDS};SERVER='+sys.argv[1]+';PORT='+sys.argv[2]+
';DATABASE='+sys.argv[3]+';UID='+sys.argv[4]+';PWD='
+ sys.argv[5])
cursor = cnxn.cursor()
cursor.execute('INSERT INTO [Py_Tbl] ([ID], [Val]) VALUES ('+sys.argv[6]+','
+sys.argv[7]+')')
cnxn.commit()
5 2 , :
IP ;
( MSSQL 1433);
;
;
;
ID ;
.
SQL_Insert
FUNCTION_BLOCK SQL_Insert
VAR_INPUT
xExecuteScript: BOOL;
Server:STRING := '192.168.1.2';
PORT:INT := 1433;
DB_Name:STRING := 'GA';
login:STRING := 'plc';
password:STRING := '123456';
ID: INT;
Val: REAL;
END_VAR
VAR
pResult: POINTER TO SysProcess.SysTypes.RTS_IEC_RESULT;
Text: string;
END_VAR
BEGIN
IF xExecuteScript THEN
text:='sudo python /home/pi/pyodbc/query.py ';
text:=concat(text,Server);
text:=concat(text,' ');
text:=concat(text,INT_TO_STRING(Port));
text:=concat(text,' ');
text:=concat(text,DB_Name);
text:=concat(text,' ');
text:=concat(text,login);
text:=concat(text,' ');
text:=concat(text,password);
text:=concat(text,' ');
text:=concat(text,INT_TO_STRING(id));
text:=concat(text,' ');
text:=concat(text,REAL_TO_STRING(Val));
SysProcess.SysProcessExecuteCommand(text,pResult);
xExecuteScript:=FALSE;
END_IF
END
query.py . :
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo python /home/pi/pyodbc/query.py server port DB_name login pass id Value
DB_send , ID 10 integer Val 10 real.
FUNCTION_BLOCK DB_Send
VAR_INPUT
id:ARRAY[1..10] OF INT;
val:ARRAY[1..10] OF REAL;
Time_send:TIME :=T#60S;
END_VAR
VAR
SQL_Ins: SQL_Insert;
TONInst: TON;
i: int;
END_VAR
BEGIN
TONInst(IN := NOT(TONInst.Q), PT:= Time_send);
IF TONinst.Q THEN
FOR i:=1 TO 10 DO
IF id[i]<>0 THEN
sql_ins(xExecuteScript:=true, ID:=id[i], val:=val[i]);
END_IF
END_FOR
END_IF
END
? DB_Send , , ID->Val SQL_Inset Python . pyodbc.connect cursor.execute SQL- INSERT… .
MsSQL Library SL

3S-Smart Software Solutions GmbH MsSQL Library SL – (200€) , MsSQL OPC-. TDS . - 2 , , , , 2 , , PyODBC.
:
SELECT
INSERT
UPDATE
DELETE
Execute Stored procedures
5 SQL IEC:
BOOL
DINT
REAL
STRING
DATETIME
4- :
fbMsSQL_compact
fbMsSQL for database communication
fbPing to check the availability of a remote host
fbFIFOQuery to handle more SQL queries over time
Has 4 default rendering templates
login credentials
login procedure
query window
response window
Download and install the package from store.codesys.com. After installing the MsSQL Library SL package in the .. \ CODESYS MsSQL SL Library \ V1.4.0.5 \ Examples \ Raspberry Pi target directory, an illustrative example of using the library is unpacked.
The page for connecting to the database and displaying data.
