
Recently I wool Habr and came across a comment from Inskin:

I first met in Windows Admin Center when it only had a file management counter and nothing else. Now all the tools from RSAT are slowly moving to Windows Admin Center.
So far I have not seen a single sensible Russian article about setting up Windows Admin Center and decided to write it myself. Below the cut is a detailed review, two hidden high-end WAC chips, as well as instructions for installing and configuring.
What features are currently implemented?
A little over a year ago, WAC was practically unused, the preview version contained only a beautiful dashboard and process management.
Now, you can do a full deployment of new servers directly from the browser.
- Task Manager
- Certificate management
- Device management
- View events
- Conductor
- Firewall
- Add or remove programs and services and roles
- Regedit
- Task Manager
WAC can also serve as a gateway for WinRM and RDP.
By the way, to connect, Windows Admin Center uses WinRM and a common runspace together with WSMan, so if you have network drives connected, you can connect to the servers that host these drives without entering a username and password.
Try to make Enter-PSSession without specifying Credentials, if the command does not ask for a username or password, then it will be possible to enter through WAC without entering a username and password.
What you might be missing:
Some of the functionality is still hidden behind plugins, so you might have missed two very cool features and one not very cool one.
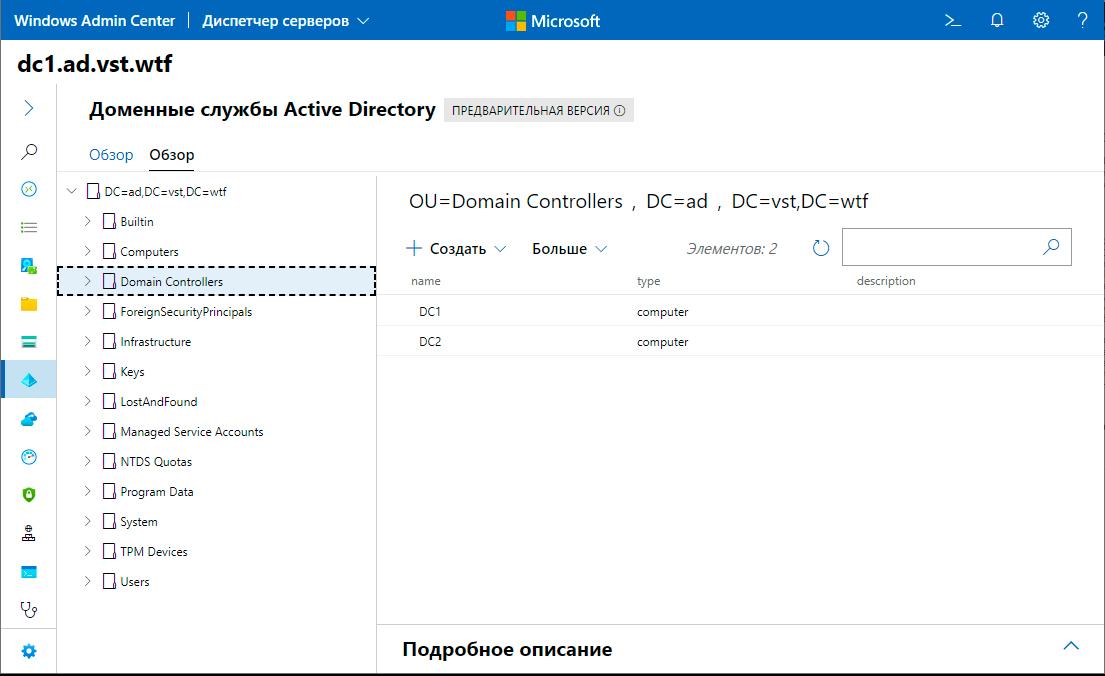
AD Management (preview):
The Active Directory controls are like something between ADAC and ADDC. It's good that they rethought the interface, in general it looks even more convenient than through RSAT. In one more question, you can go entirely to WAC.
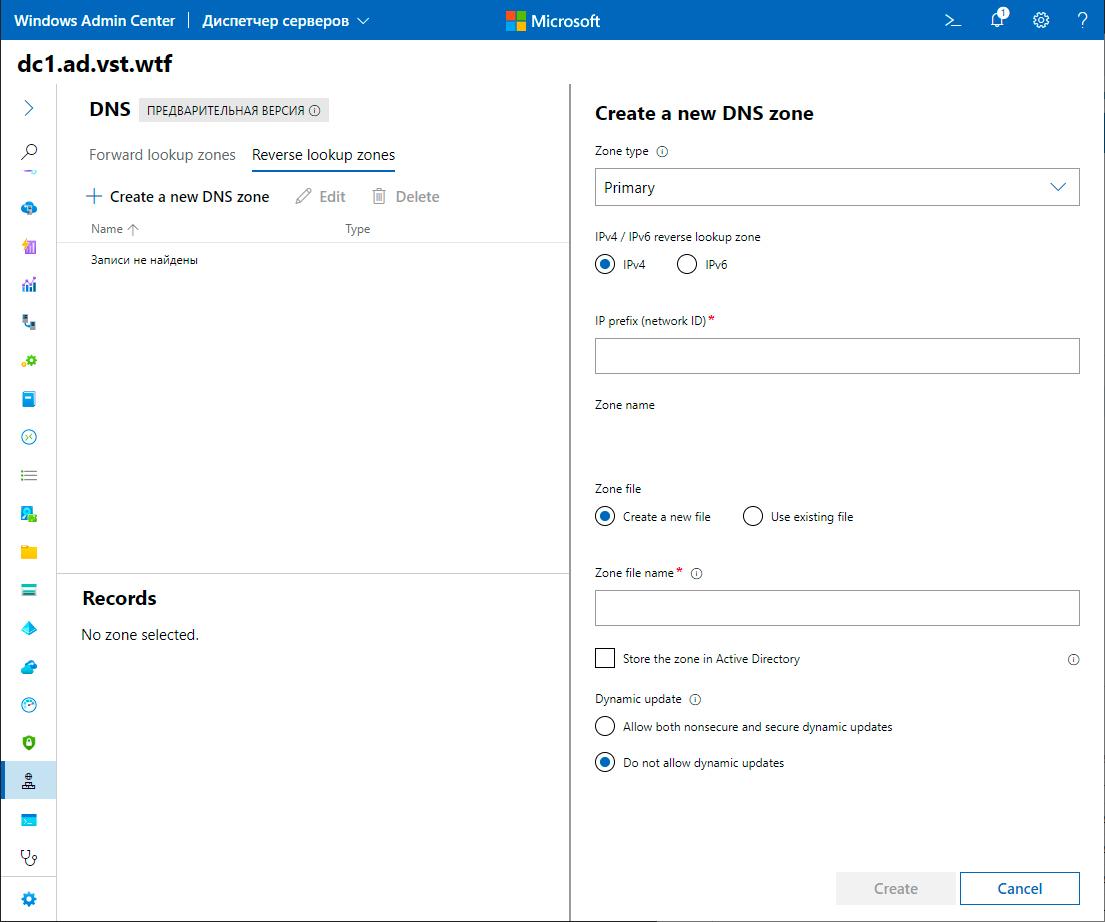
DNS management (preview):
Fully DNS management functionality has been moved to WAC. Creating new zones, PTR records, all of this is now available through the Windows Admin Center.
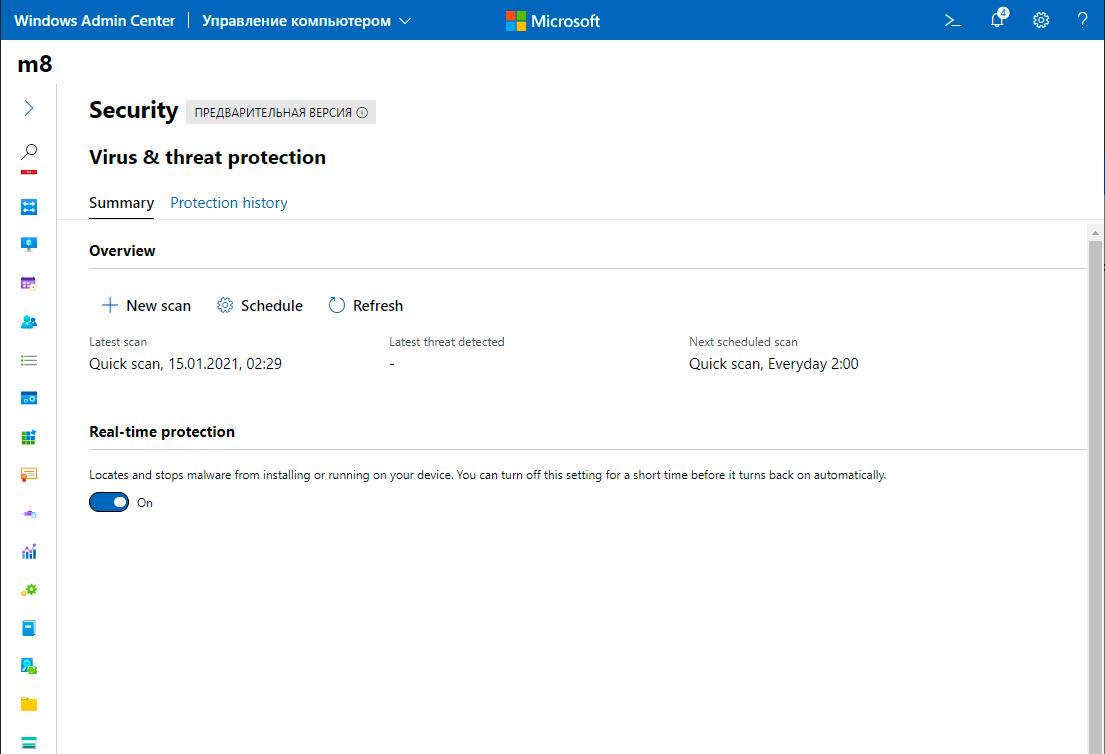
Windows Defender Management (preview):
So far, you can only manage scans and disable real-time protection. All the defender's points are missing, plus you cannot manage protection against ransomware.
Installation on Windows Server / Windows 10
In my opinion, the most correct installation is installation on a local computer. First, you need to download the installation file from the link:
http://aka.ms/WACDownload
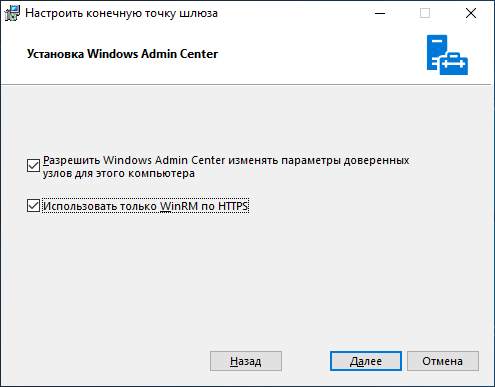
Installation is very simple, "next, next, done", but you need to give a couple of recommendations. Be sure to select the item about automatic WAC update, I guarantee it will come in handy for you, but for some unknown reason, this item is disabled by default.

WinRM works over the HTTP protocol, so to prevent Windows Admin Center from connecting to remote servers over HTTP, be sure to enable this item. It is also disabled by default.
If you are using WAC on a home system, I recommend leaving the self-signed certificate. It is automatically added to the trusted ones and does not cause any inconvenience, but if you have your own certificate and want to use it, then enter its fingerprint in the column in the column, as shown below:
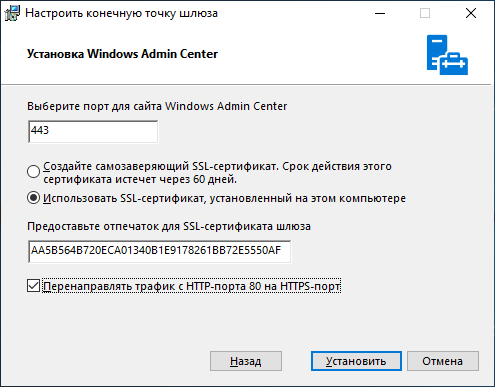
You can go to certmgr -> Personal -> Certificates, go to the properties of the certificate and find its thumbprint.
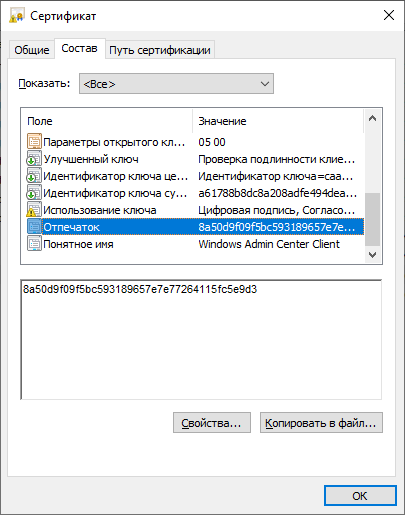
Ditto with PowerShell:
Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:LocalMachine\MY | Select-Object FriendlyName, Thumbprint
Installation on Server Core

A VPS with Windows Server Core can be taken directly from the marketplace
To use Windows Admin Center as a control node, you need an Active Directory. You can log into Windows Admin Center deployed on Server Core only under an administrative role in AD.
Download WAC:
Start-BitsTransfer -Source http://aka.ms/WACDownload
-Destination C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\wac.msi
Install with a self-signed certificate:
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\wac.msi" -ArgumentList " /qn SSL_CERTIFICATE_OPTION=generate"
If you have a purchased certificate or certificate from Let's Encrypt installed in the system certificate store, then write it Thumbprint in the installer arguments.
You can get the certificate fingerprint like this:
Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:LocalMachine\MY | Select-Object FriendlyName, Thumbprint
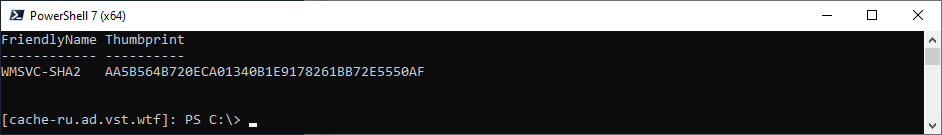
You need to inscribe the fingerprint after SME_THUMBPRINT, as in the example:
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\wac.msi" -ArgumentList " /qn SME_THUMBPRINT=AA5B564B720ECA01340B1E9178261BB72E5550AF SSL_CERTIFICATE_OPTION=installed"
To change the certificate, you will need to run the installer again, writing in the fingerprint of the new certificate.
conclusions
With each new version, Windows Admin Center becomes more functional and functional.
To complete happiness, you need only to complete all the managers related to AD, add support for RRAS, IIS, transfer the entire explorer along with normal SMB and Bitlocker management, group policy management and normal Windows Defender, and so that all the managers that work with files can open and choose paths from the disk of the machine to which you are connected. And also so that when you close WAC, you need it to close the PSSession and free memory on the server, it would still be nice to be able to install on Server Core without the mandatory presence of AD, and when finished, you can go to MS SQL Server.
But in general, very good, I highly recommend reading.
