Edge Computing - an introduction to the topic
Since the appearance of the first electronic computers (computers) in the 40s of the last century, data processing systems have gone a long way from a separate, unreliable and cumbersome computing device to global distributed systems for processing big data (BigData) obtained in real time. Modern networked computing systems bear the imprint of the previous accumulated many years of experience in their construction and operation.
One of the results of historical development was the emergence of Edge Computing. What is important to know about Edge Computing? This is not a clear definition or specific mechanisms, but a concept in which some of the data processing that is critical to speed is performed at nodes located outside of large data centers and located before the "last mile" or in a minimum number of hops from the end consumer device or data provider ... In the Russian-speaking environment, two designations are common for Edge Computing - "edge computing" and "edge computing".
Consider how the transition from huge machine rooms to edge computing on smartphones came about.
Background - structure and tasks of components of networked computing systems
The task of the earliest operating systems (OS) that appeared in the 50s (for example, GM-HAA) was to coordinate the launch of software packages and output the results. More advanced operating systems (such as Unix, RSX, VMS) appeared in the 70s and received many additional functions, including those related to intercomputer communication. If the first users had to use input / output systems located directly in data processing centers (DC) for work, then with the development of communication systems in the 60s it became possible to connect user terminals via dedicated and dial-up copper telephone lines, and in the late 70s on fiber optic. In the mid-60s, the first commercial satellite channels became available for the organization of communication lines.
. ( 70- Ethernet , 80- SLIP, Token ring, HDSL ..), 80- ( Internet TCP/IP), .
70- . . « » (, Telnet, rlogin ..) FTP.
50- , ( , ) , ( , , ) .
-, 50- 60- ( Cobol, ), 70- SQL.
80- RPC . 80- NFS .
90- , , , :
xDSL.
- ().
VSAT .
(gopher, http ..).
- Archie (90), Wandex (93), Yahoo! (94), Google (96).
PPP , xDSL.
, SMP , () .
-, Web- (Windows 95).
(386BSD, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, Linux ..) .
’ - () , , .
(), (RAID) . .
, 90- « », 2000- . , .
, . , . , , .
, . , .
, , . .
, .
— , :
IaaS – .
PaaS – , , .
SaaS – .
IaaS, .. .
Edge Computing —
— , , (, ) .., . , . Edge Computing.
, Edge Computing — .
:
, . , .
– .
.
IT-.
:
.
.
.
. , , , . IoT ( “ ” - Internet of Things) 5G – , , .
, , , , , . , .
, , . , :
– , , , , , , , , .. endpoint-. , Edge-.
– 1-10 , .
– 10 .
2 3 CDN (Content Delivery Network) - . - CDN .
. « » « » , , , , . – - , , , Ethernet . – , , , .
endpoint- — — , , , CDN . : , .
– , .
(MDC), « » , . . , ( ) , , , . . – . , , . , .
- Edge-.
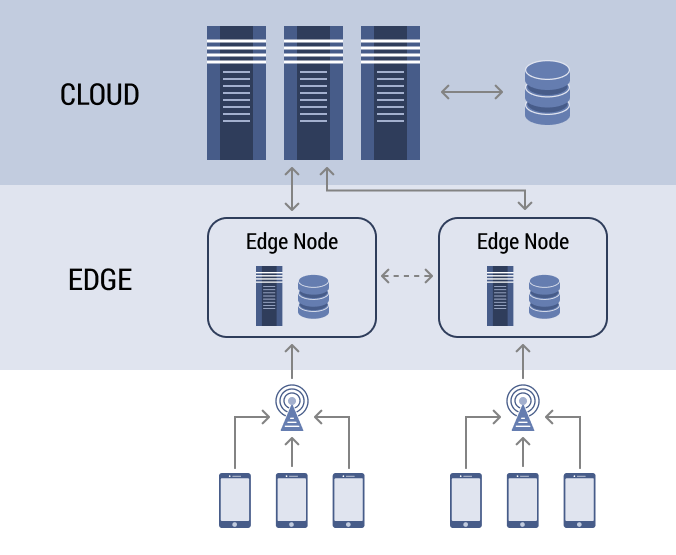
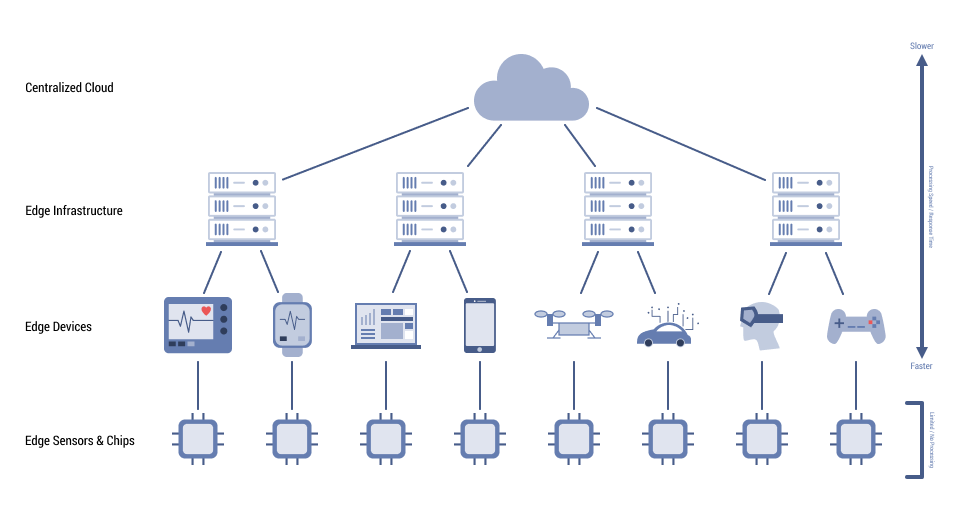
. , Edge-.
IT- . . .
:
.
.
.
.
.
, , ( ), , , , , - .
, – , .
? .
( ) . , . . . .
- . , , . . , / – ( ), ( ). . .
- , . , . , - , .
– , . , - .
?
, , .
, .
«» .
« ».
-.
, -.
.
2018 McKinsey “New demand, new markets: What edge computing means for hardware companies” 100 11 . 2020 .
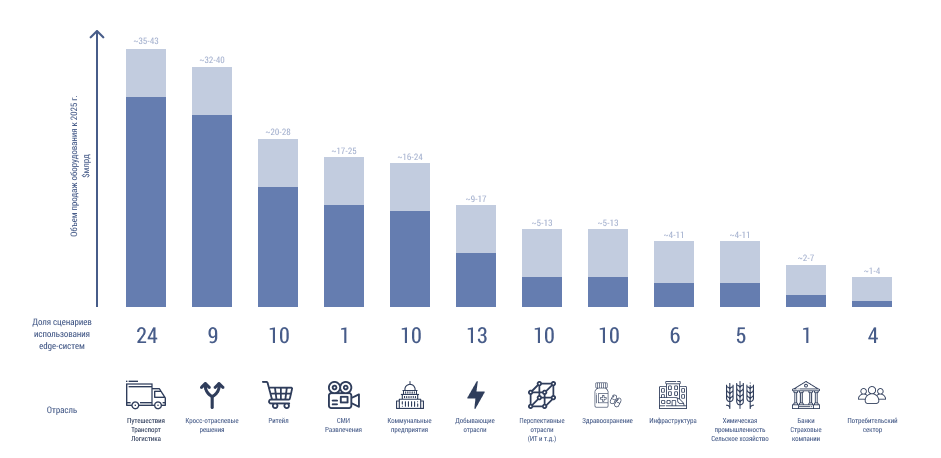
. . - , . CDN .
– , , .
-, -. Forward , edge- endpoint-. Forward BSS/OSS, , . Forward , , , .
OSS , BSS , , ( ERP), ( CRM).
Forward BSS/OSS SaaS, Edge Computing.
, , . - Forward , JavaScript Java.
Forward BSS/OSS . , .
«» . , - . «» . Forward BSS/OSS API .
OSS/BSS . , , , , B2B, B2C B2B2C . - endpoint- .
:
, , , , .
.
edge- endpoint- . , .
, .
, . – , , , , , .. – .
.
, , , .
, 7 . - . , - « : ».
. , , Forward OSS/BSS , - Edge Computing . , , - - - , .
— Prepare yourselves because cyberpunk is coming…