
Today, when astronomy has returned to the school curriculum, any high school student (well, in theory, anyone) should know: the distance from our planet to the Sun is approximately 149.5 million kilometers. This distance is also called an astronomical unit.
But, it is clear that this answer somehow had to be obtained, and astronomers took several steps, stretching for more than one millennium. Below - more about each step.
Step one - the atheist Aristarchus and Luna
Aristarchus of Samos lived in the 3rd century BC and was a truly outstanding astronomer. Long before Copernicus, he built a heliocentric model of the structure of the world. Quite accurately determined the length of the year at 365 + (1/4) + (1/1623) days. Improved the sundial. He also attempted to measure the distance from the Earth to the Sun and Moon. Aristarchus dedicated a whole treatise to this (by the way, the only written work of this author that has come down to us).
With the Moon, he got pretty close to the correct answer: 486,400 km (according to Aristarchus's calculations), 380,000 km (average distance according to modern data). A hundred years later, another ancient astronomer Hipparchus, by the way, clarified these figures. But with the Sun, Aristarchus turned out to be a sickly bobble.
But first, how did the ancient Greek astronomer measure this distance. It is known that sometimes the Sun and the Moon can be observed simultaneously. Moreover, there are times when the Sun illuminates exactly half of the Moon. Then the angle "Earth-Moon-Sun" is a straight line, and by measuring the angle "Moon-Earth-Sun", using trigonometric relations, knowing the Earth-Moon distance, find the Earth-Sun distance.
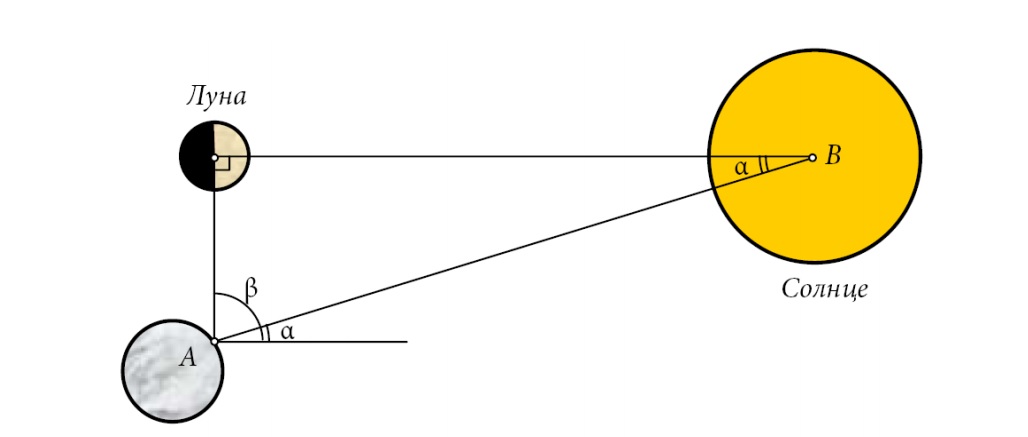
But "it was smooth on paper." First, Aristarchus had to catch the moment when exactly half of the moon was illuminated, and it was almost impossible to do this without a telescope. And secondly, again, without serious measuring equipment, to accurately measure all parameters. It is not surprising that the Greek was mistaken, and very much: the angle α turned out to be as much as three degrees (in reality it is equal to 10 minutes), and the distance to the Sun is only 7.5 million kilometers. Based on this distance, Aristarchus came to the conclusion that the Sun is much larger than the Earth. This became the main argument of his heliocentrism (the largest object should be in the center of the universe).
However, the error in determining the distance did not play a large role in science; Aristarchus's calculations did not receive wide popularity at all (even among the educated part of the population of ancient cities). The reason was rather political; the whole point is in his heliocentric model of the universe. It ran counter to the geocentric model followed by the then scientific consensus. And there are mentions that they even tried to bring him to trial as an atheist. Some time later, at first, Hipparchus criticized his views, and later Ptolemy (whose geocentric model successfully survived to Copernicus) completely ignored the results of Aristarchus, contributing to their oblivion for a long time.
Step two - look at Venus (Kepler and Horrocks)
It took humanity almost two thousand years to take this next step towards an answer, but let's be fair, it was not an easy time and there were plenty of other problems.
And to begin with, it was necessary to choose another object on which to rely in their calculations. In 1626, the famous German astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler proposed Venus as a candidate. By that time, astronomers already knew about one rather rare astronomical phenomenon - the passage of Venus across the disk of the Sun, moreover, it happens twice with a difference of several years, and then there is a significant break. The method proposed by Kepler was as follows: it is necessary to measure the transit time of Venus across the disk of the Sun from different points on the Earth. And comparing these times, you can find the distance from Earth to Venus and to the Sun.

However, it just sounds simple. At the very least, it was necessary to wait for this phenomenon. It was succeeded by the British astronomer Jeremy Horox, who corresponded with Kepler and knew about his method. First, the Briton specified the frequency of this phenomenon: a "double" happens with a difference of eight years every one and a half centuries. And the next one was supposed to take place in 1639. Horrocks prepared for the event, watching the skies from his home in Mach Hole, near Preston, and his friend doing the same from Salford, near Manchester. At first, it seemed that luck had turned away from them, since there was heavy cloudiness that day, but half an hour before sunset, the clouds parted and a couple of astronomers managed to carry out their plan. Based on observations, Horrocks calculated that our planet is separated from the Sun by 95.6 million km. This was already much closer to the truth, but still incorrect.
– ()
Until the next Venusian "double" it was necessary to wait a century and a half, and while time passed, astronomers spent it looking for other ways to calculate the desired distance. And the French astronomer of Italian origin Giovanni Domenico Cassini succeeded. He was generally noted in astronomy as a talented observer (for example, he was the first to see the Great Red Spot on Jupiter). By that time, astronomers had already appreciated the possibilities offered by the simultaneous observation of the same object from distant places. In 1672, Cassini, together with another French astronomer Jean Richet, carried out such a project: the first remained in Paris, and the second went to South Africa, where France had its own colonies. They simultaneously observed Mars and, calculating parallax, determined its distance from Earth. Parallax, if anyone does not know,it is the displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed on two different lines of sight. Well, they knew how to calculate the distance to an object using parallax for a long time.
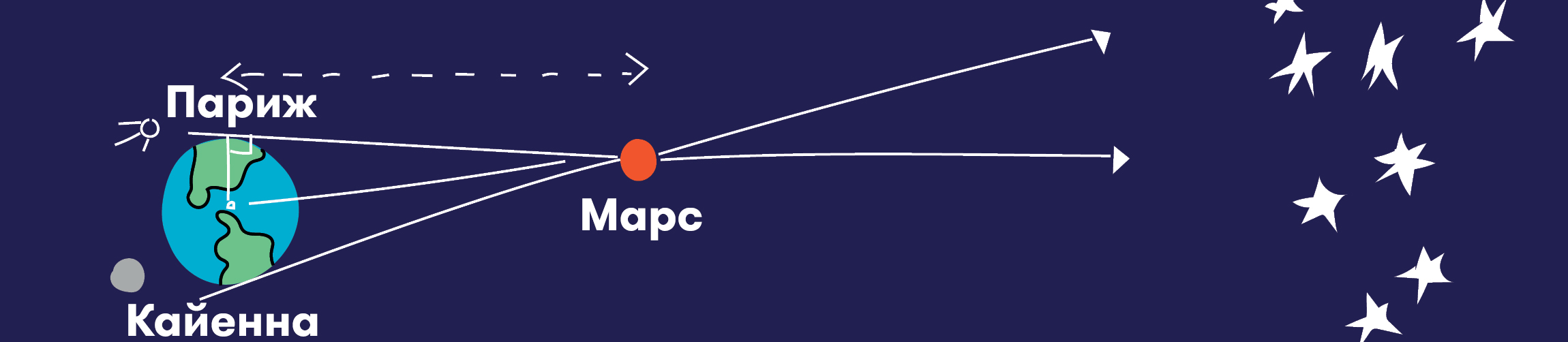
And since the relative ratios of the various distances between the Sun and the planets were already known from geometry, by calculating the parallax distance to Mars, Cassini was able to do the same for the Sun. Its result - 146 million km - was already very close to modern estimates. Interestingly, at the time when Cassini carried out these calculations, he was an adherent of the geocentric system, that is, he received distances close to the correct ones, but he built a map of the solar system in the old fashioned way, with the Earth in the center. He later admitted that Copernicus was right, but to a limited extent.
Step four - again Venus and astronomers around the world
Meanwhile, another Venusian "double" was approaching (in 1761 and 1769) and astronomers were going to squeeze the maximum out of this event. In order not to depend on weather conditions and collect data from different points on Earth, a large international project was organized (it is considered almost the first in history) under the auspices of the French Academy of Sciences. Scientific expeditions to the observation sites were prepared and sent in advance. Not everything ended smoothly - the expedition sent to New Guinea went missing in the jungle.
But overall, the project was a success.
By the way, Russia also actively participated in it. In our country, he was led by a man of extraordinary talents and energy - Mikhailo Lomonosov (it was he, by the way, who discovered the atmosphere on Venus).
Lomonosov managed to get an audience with Empress Catherine II and convince her of the importance of this work both for science and for state prestige. Having received the support of the treasury, Lomonosov was able to deploy 40 observation posts on the territory of the Russian Empire. Catherine herself came to one of them, near St. Petersburg, and looked with interest through a telescope.
As a result of this great work of astronomers around the world, the number that is included in textbooks today was obtained. But there is no limit to perfection, and after another one hundred and fifty years, on December 8, 1874 and December 6, 1882, the next passage of Venus across the disk of the Sun was again observed by scientific expeditions around the world, refining the data obtained. And then again in 2004 and 2012. However, in the course of these observations, other useful data were obtained, but this is another topic.