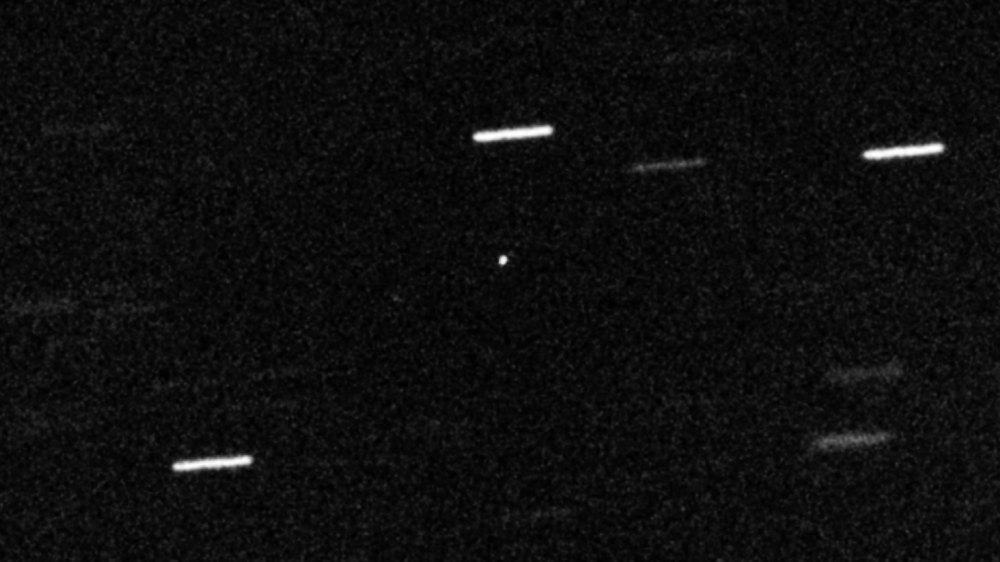

Oumuamua through a telescope, photo NASA / Alan Fitzsimmons (Isaac Newton Group)
1I / Oumuamua was discovered on October 17, 2017, when it had already passed the point of closest approach to the Sun and was moving away from us. The determination of the orbit from the observational data led to a sensational conclusion - the object was moving with hyperbolic speed, which means that it is a guest from interstellar space and leaves us forever. As a result, everything that mankind has managed to learn - the object had dimensions from 100x35 to 1000x167 meters, a reddish tint typical for objects in the outer solar system, rotated at a speed typical for asteroids (7-8 revolutions per hour) and changed its brightness by 10 times, which led to the conclusion that it most likely resembles a cigar in shape. Also, he was found to have a typical non-gravitational acceleration for comets, but without any traces of visible coma (evaporating matter).

, ESO/M. Kornmesser
Harvard astrophysicist Avi Loeb was a proponent of the artificial origin of Oumumua almost immediately. Back in 2018, he published a scientific article in which he argued that non-gravitational acceleration can be explained if the object is a very thin disk, that is, in fact, a solar sail. And the low probability of stumbling upon such an object may indicate that a civilization deliberately sent a probe on a solar sail into our solar system. In January of this year, he published his book Extraterrestrial: The First Sign of Intelligent Life Beyond Earth, in which Avi is inclined to believe that Oumuamua is the man-made garbage of an advanced civilization: “Buoy, grid of communication blocks, road sign, launchers for probes. Broken equipment of another civilization or man-made garbage. These are plausible explanations for the mystery of Oumuamua, plausible because humanity is already doing the same, albeit on a smaller scale, and we will think about repeating them if and when we start exploring interstellar space . "
Of course, the idea of the artificial origin of an object flying past us is very attractive. But it requires very strong evidence - after decades of space exploration, many spent stages, booster blocks, broken satellites, and even such a crazy object as a mannequin in a spacesuit in an electric car fly around the Earth, but there are still much more natural asteroids both in number and in mass. ... In 2019, Nature published an article by the Swiss International Institute of Space Sciences (ISSI), in which the peculiarities of our interstellar guest are explained by its natural origin. For example, Oumuamua could throw out unusually large dust particles that are much less visible to telescopes. In the solar system, comet 2P / Encke sometimes, for some unknown reason, does this. The general conclusion of the article is an unusual comet,but not enough to seriously think about its artificial origin. Talking about this article in his book, Avi comes to a sharp criticism of "scientific institutions engaged in groupthink ”, writes that he was ridiculed in the material of the Boston Globe (although in the article he was called talented), and scientists because of prejudice are looking for extraterrestrial life in the wrong place and wrong.

Changes in brightness of Oumuamua according to telescope data for three days, ESO / K image. Meech et al
Dust ball
In the English language there is an established expression "dust bunny" (literally "rabbit from the dust"), which has no idiomatic analogue in Russian. These are lumps of dust that form under furniture and in other hard-to-reach places in the apartment. Jane Luu, at the University of Oslo, Norway, built another modelthe formation of 1I / Oumuamua. In the inner coma of a comet, located behind the Oort cloud of an unknown star, a fractal dust aggregate (in simple terms, a lump of dust) could form. Then, under the influence of hydrodynamic forces, he broke away from the parent comet and went to wander through interstellar space, thrown out of his home planetary system by the solar wind of his star, and after a journey of unknown how many millions of years he accidentally visited our solar system.
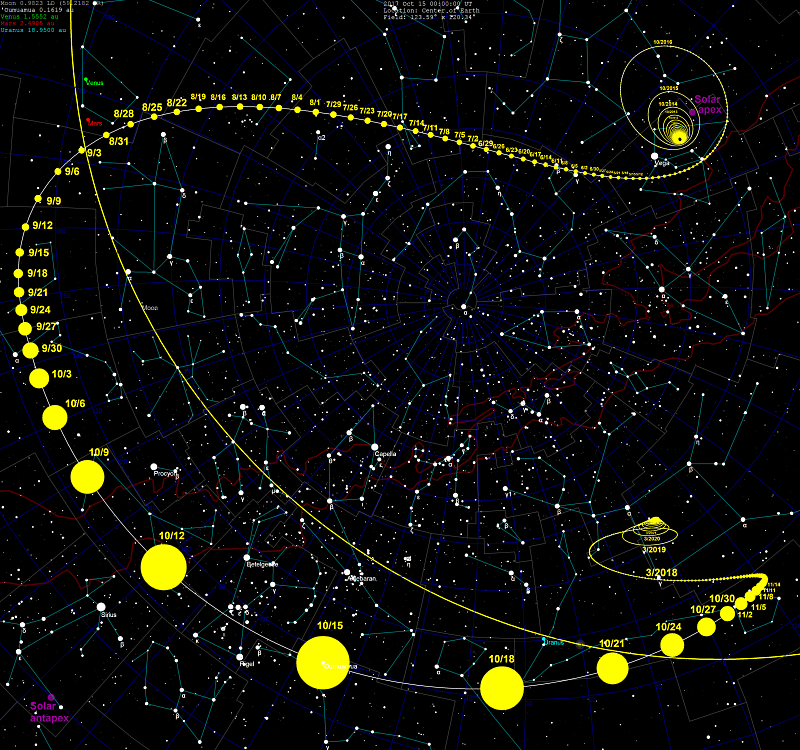
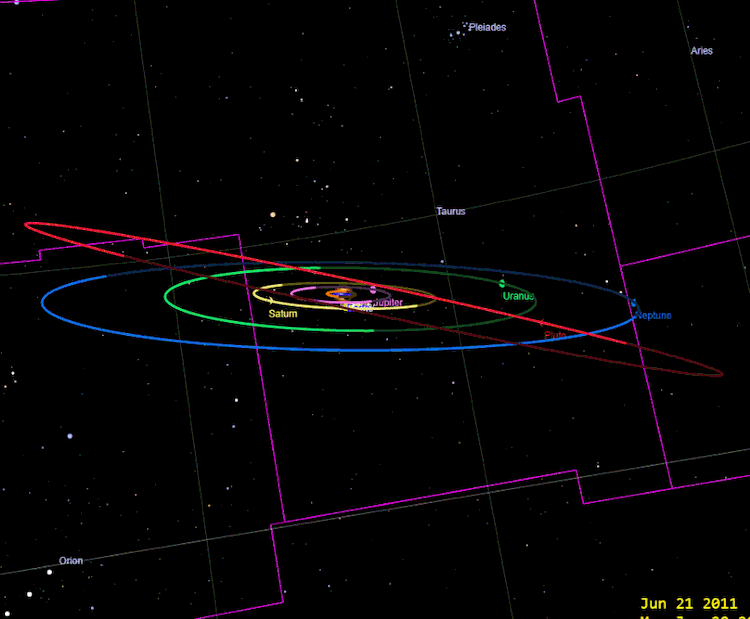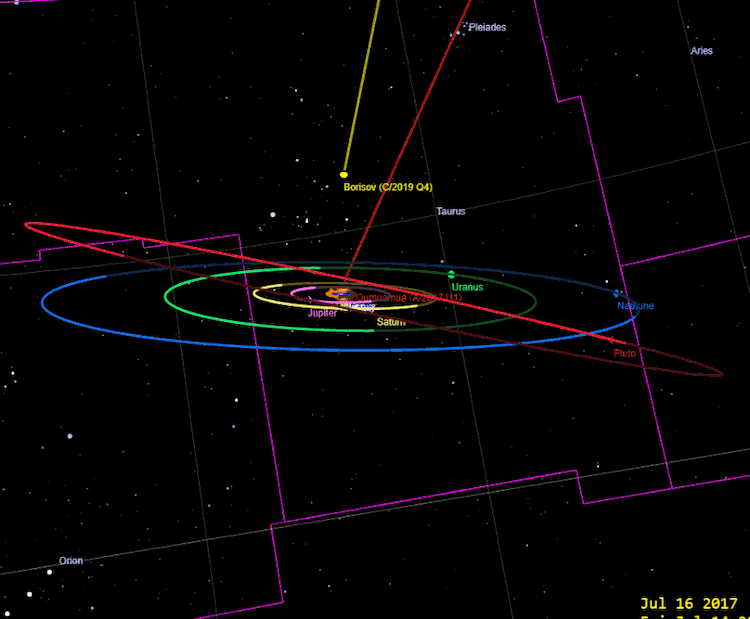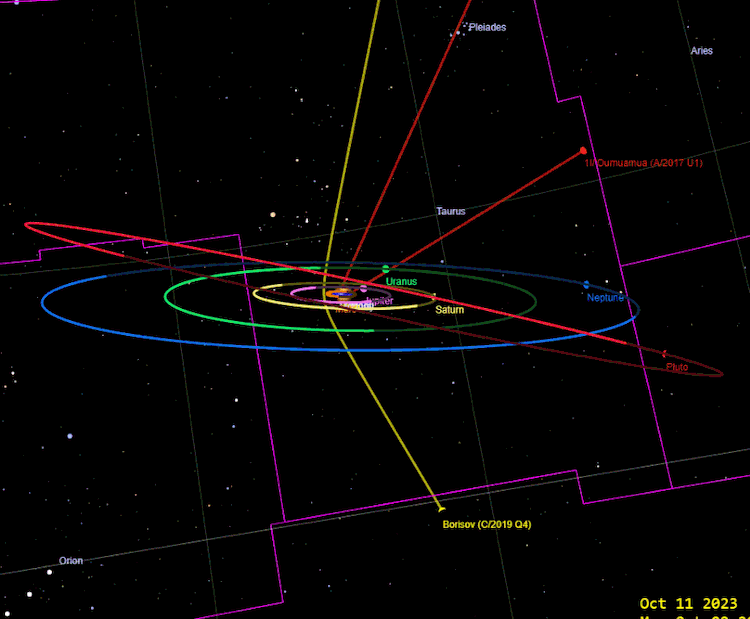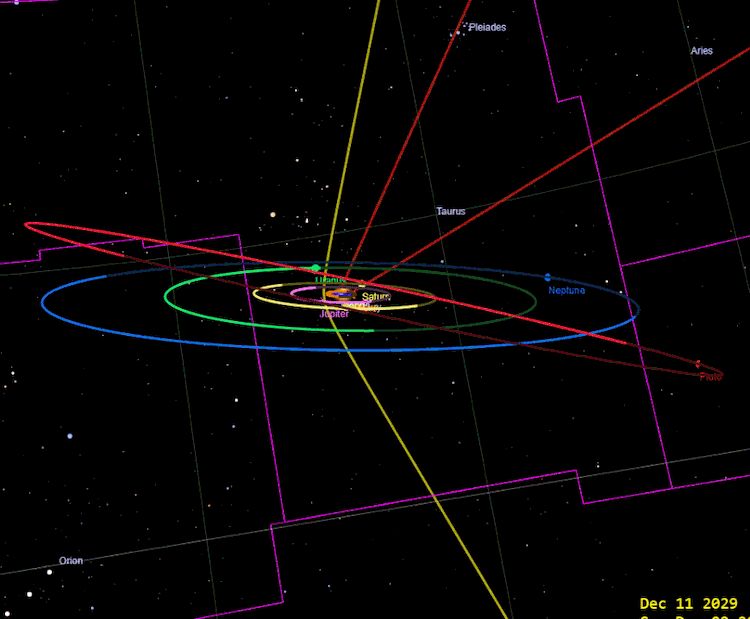
Trajectory 1I / Oumuamua for a terrestrial observer, image by Tomruen / Wikimedia Commons
Hydrogen snowdrift
Another option to explain the non-gravitational (due to the Sun) acceleration 1I / Oumuamua is that it contained ice from molecular hydrogen. Greg Laughlin of Yale University and Daryl Seligman, now at the University of Chicago, say that the coldest regions of molecular clouds, the nursery where stars are born, could be conditions for hydrogen snow to form. Despite the fact that hydrogen is the most abundant element in the Universe, we practically do not observe it in solid form, because inside our solar system it is too warm for this. But a guest from the cosmic cold could theoretically have such an unusual composition. When moving through the solar system, the heat of our star began to evaporate hydrogen snow, and as a result, a "remnant" of an unusual shape was obtained,accelerating from emissions of hydrogen invisible to telescopes.
1I / Oumuamua and 2I / Borisov, image Tony873004 / Wikimedia Commons
Alas, Oumuamua flew away never to return, and it is not a fact that the collected data will be enough to unambiguously determine which hypothesis is correct. Most remarkable, in my opinion, is that the second interstellar object, Comet 2I / Borisov, was discovered just two years later. There is a hope that guests fly into our solar system much more often than it might seem, and as mankind creates ever more vigilant instruments, we will learn more and more about each new guest from the interstellar abyss.