
Our wiki defines a gyro locomotive as a locomotive with a mechanical energy storage (flywheel), designed to transport trains of trolleys along the tracks of horizontal mine workings, which are dangerous due to gas or dust explosion.

The locomotive is equipped with a massive flywheel weighing more than 1.5 tons, to which an air motor is connected on one side of the shaft.
When compressed air is supplied to this engine under high pressure, it begins to spin the flywheel to a speed of about 3 thousand revolutions per minute.
, .
— , .
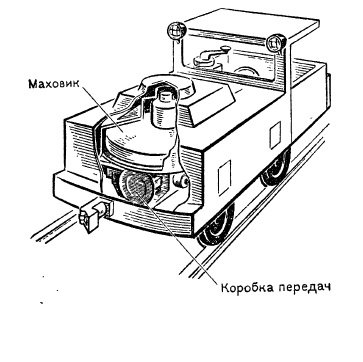
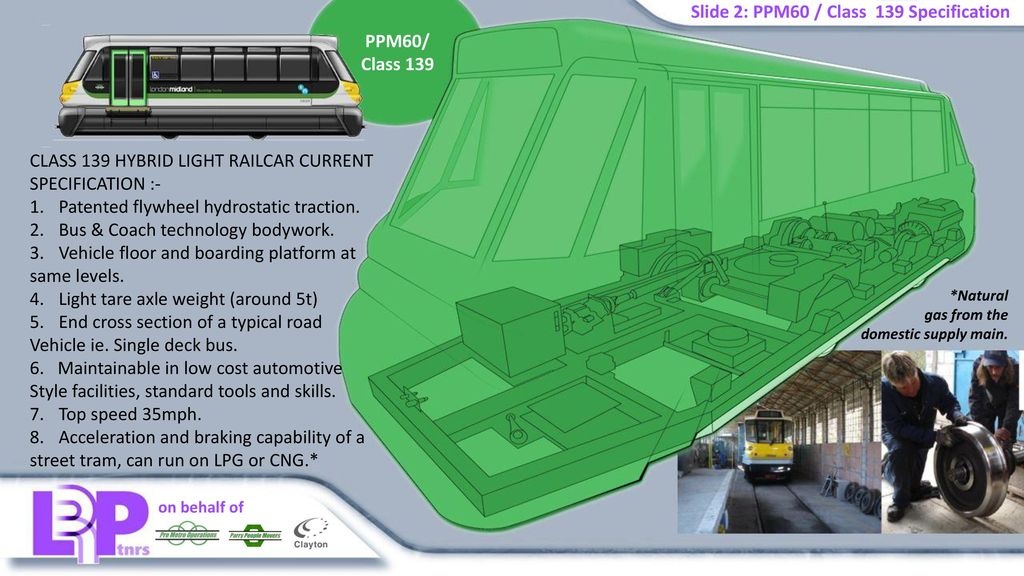
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
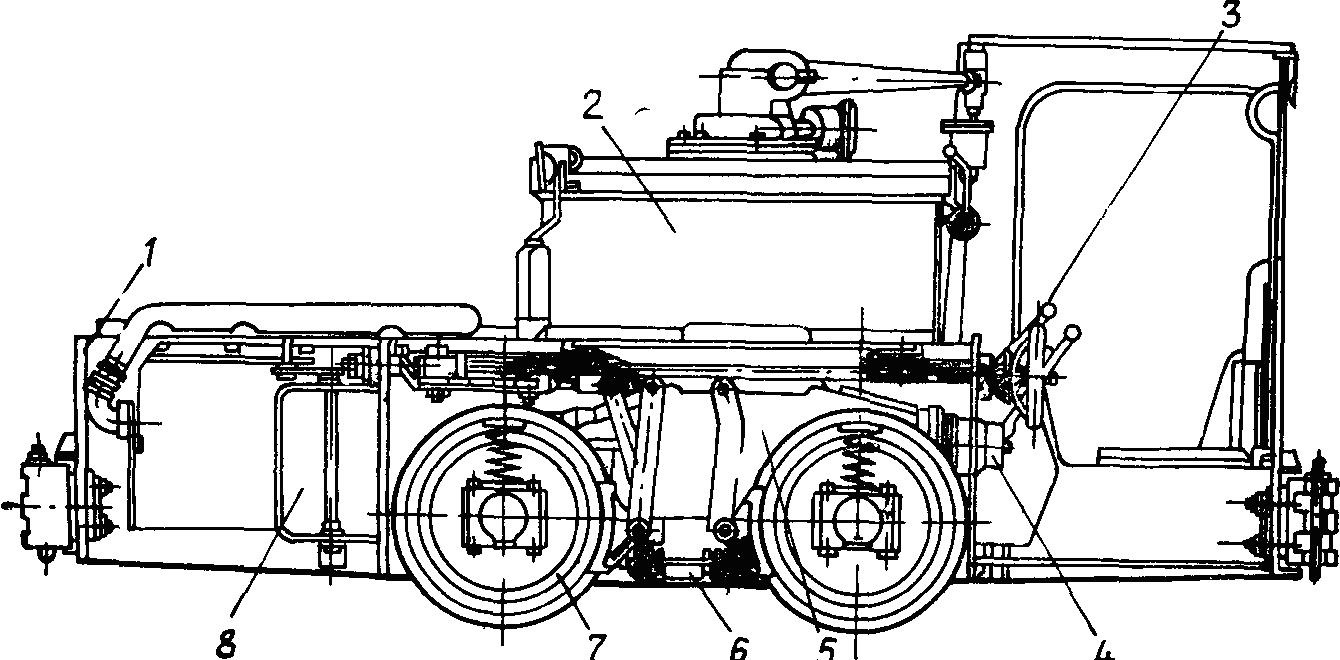
, , , , , .
, , .
, , .
, , .
, .

, , - , .
, , .

, ?
1940- .
«».
.
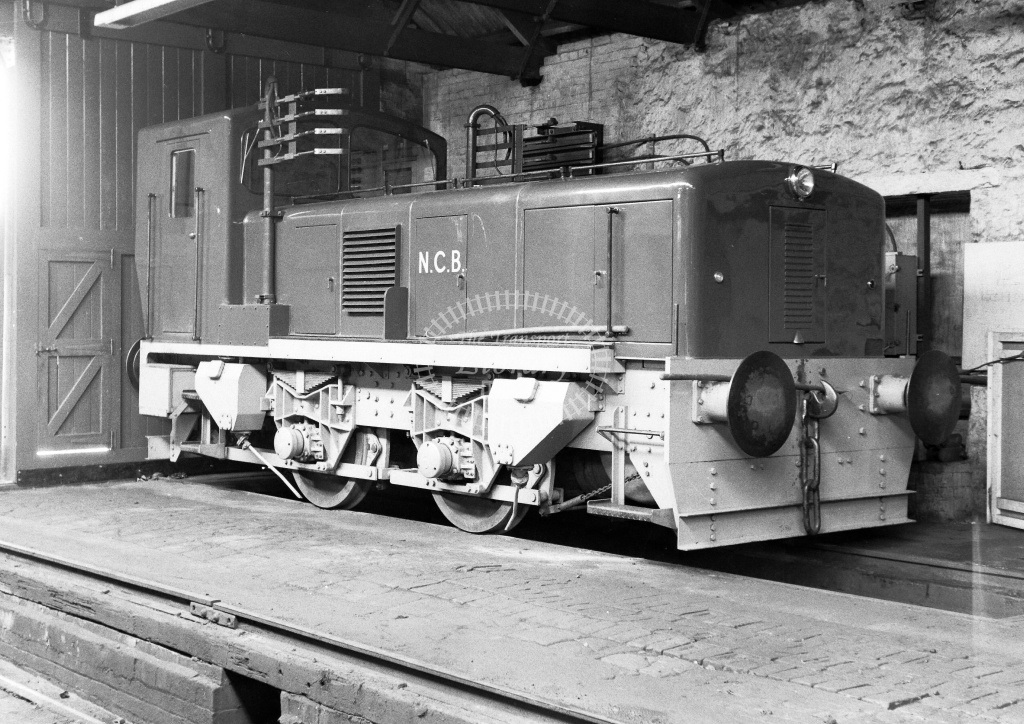

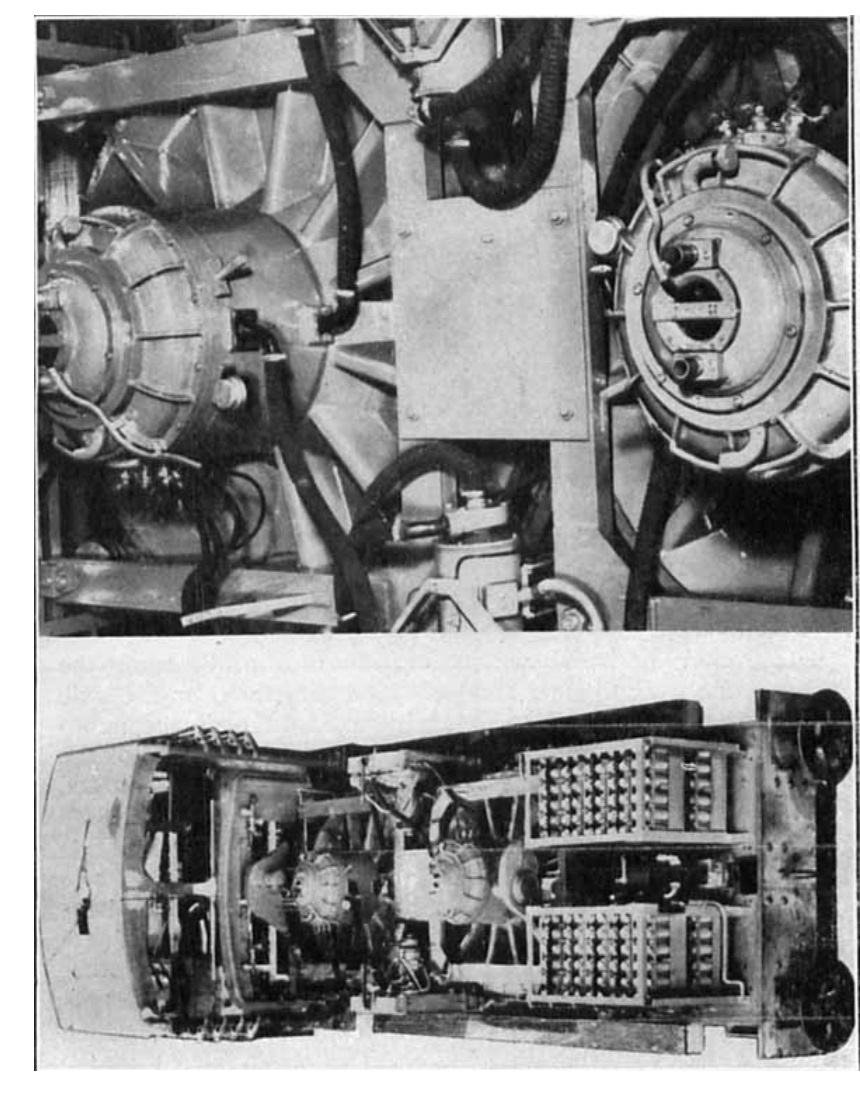
200 .. (150 ), .
3- , , .
.

, , .
, .
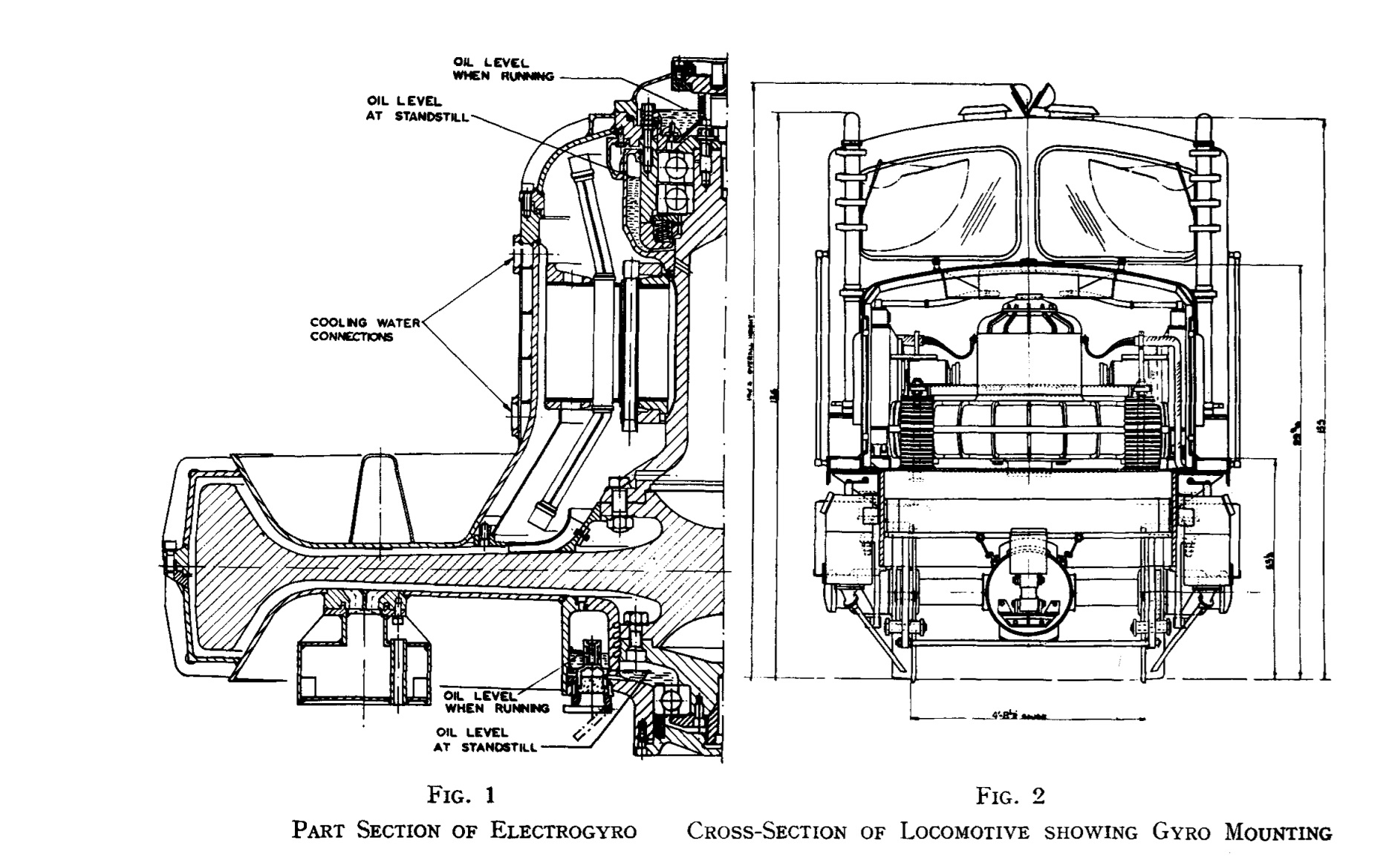
3000 / «».
, 2,5 30 .
34 24 / .
1958 , 1965 .
, , British Rail Class 70 , , .
, .
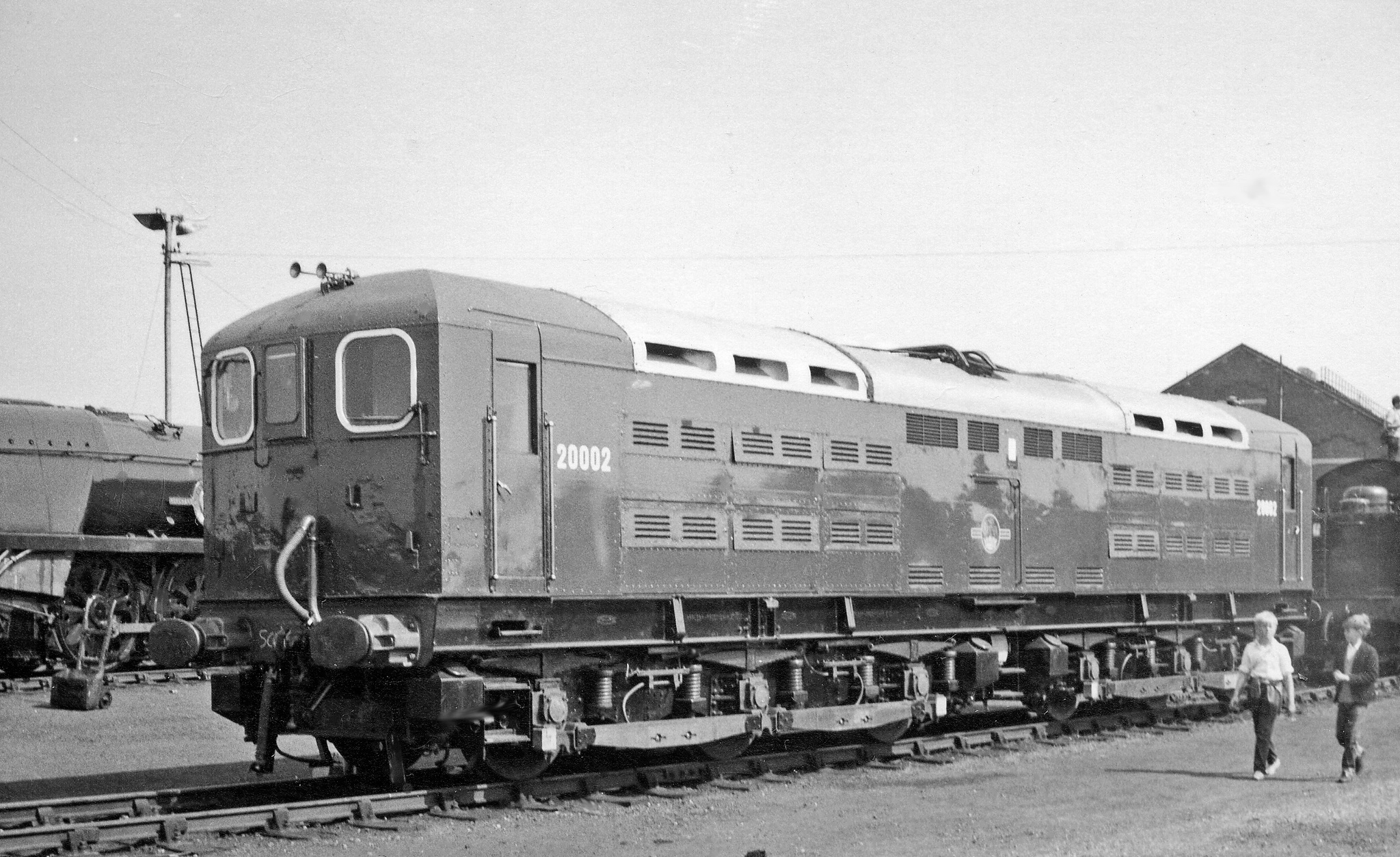

.
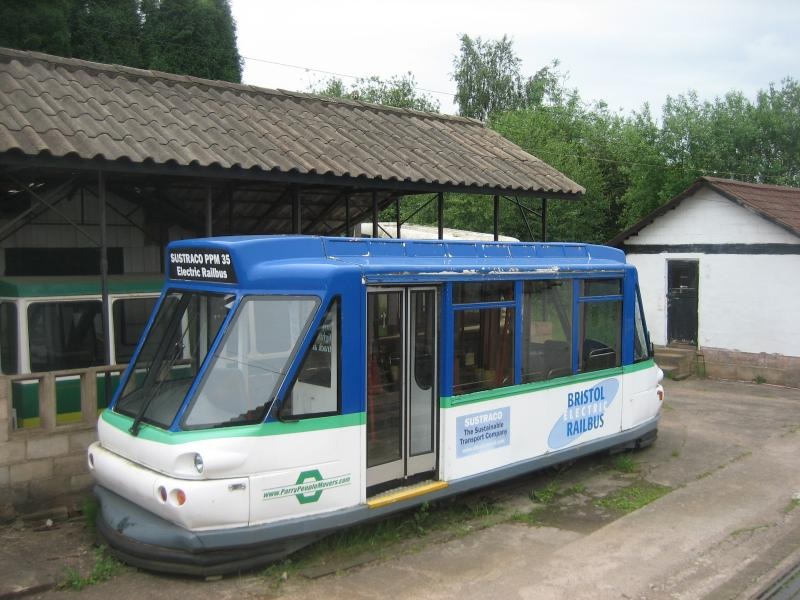
Parry People Movers Ltd. (PPM) - , , (FES) .
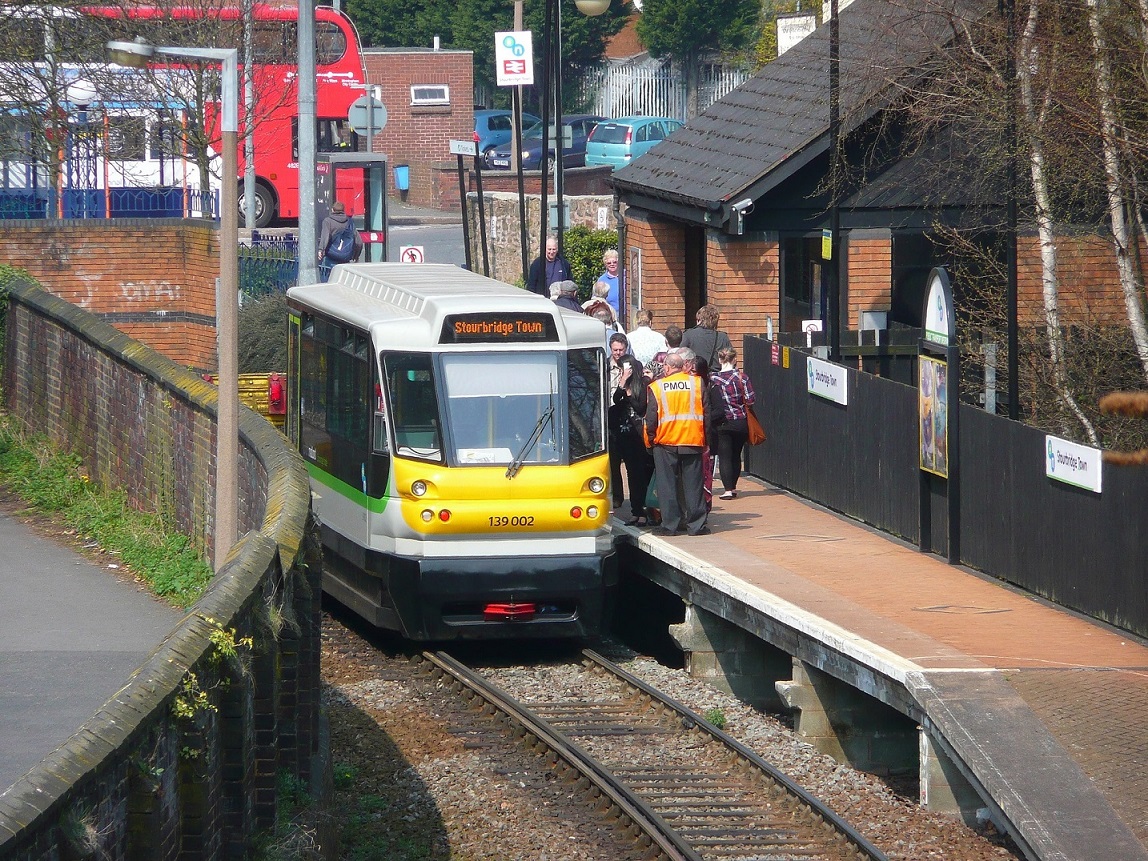

PPM 1 500 , 2500 / .
.
.
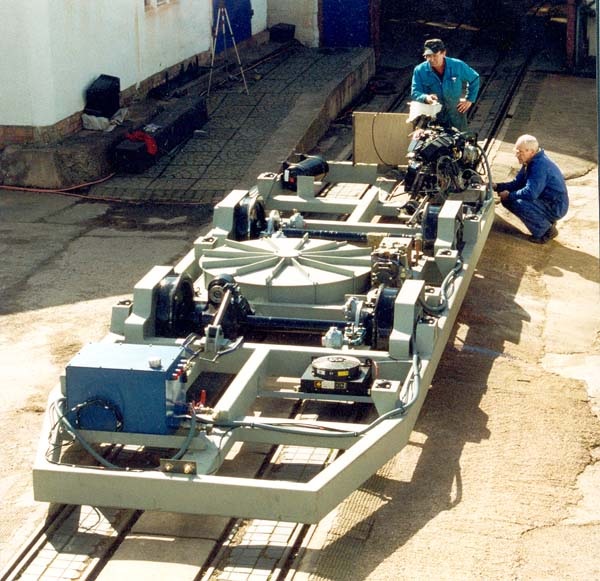

( ) ( ).
, .
– .
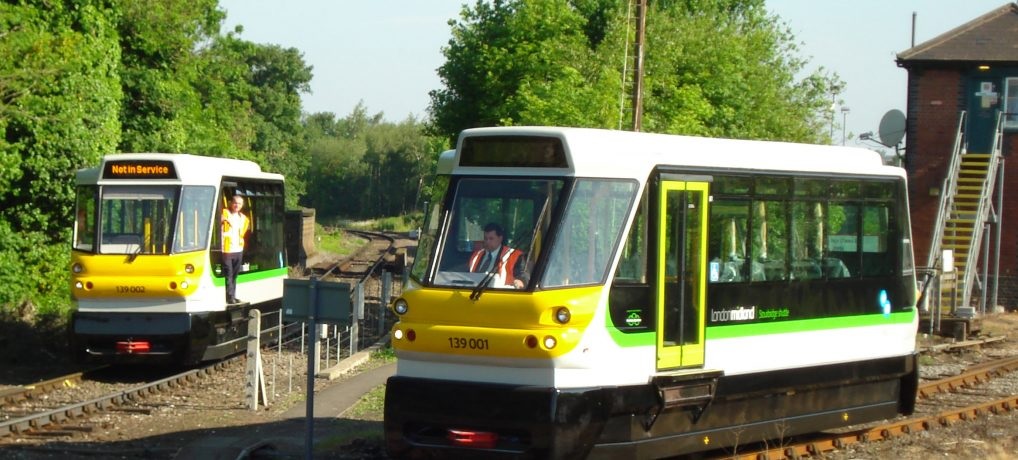


, , – .

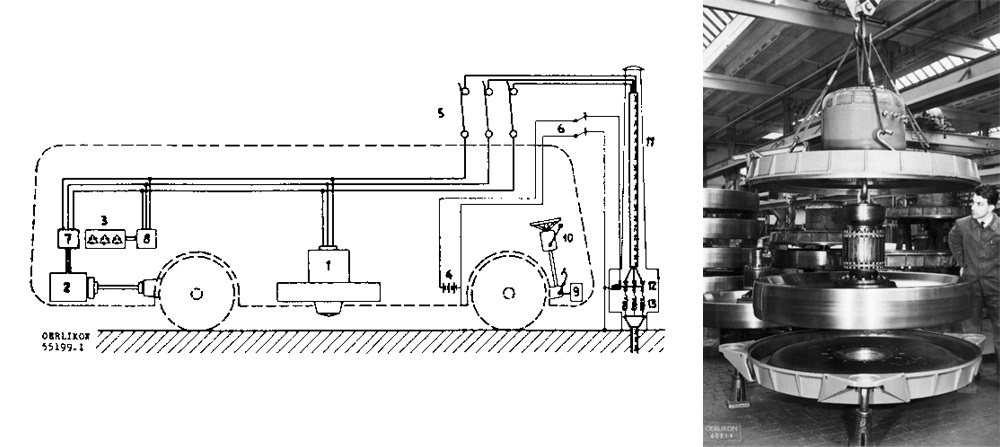
.

, — .

Interestingly, it is difficult to control a gyrobus, since its flywheel has the properties of a gyroscope (it seeks to maintain a constant position in space).
Disadvantages: heavy weight - a gyrobus designed to transport 20 people for 20 kilometers must have a flywheel weighing 3 tons.
A flywheel rotating at a speed of 3000 rpm requires special safety measures (the linear speed of the flywheel rim reaches 900 kilometers per hour).
And finally, there are space programs related to the accumulation of energy in the flywheel.

But this is, most likely, not just a flywheel, but a super flywheel — a topic for another conversation :).