The complete acceptance of the essence of what is happening for us was the passage of a certification audit in accordance with ISO 27001 and obtaining the coveted certificate. Today we are completing a series of articles. At the end of the material, you will find links to previous articles.

When preparing for the audit, first of all, take care of the formal details of the auditor's office visit. This is necessary for the process to be as effective and painless as possible.
- Agree with the certifying authority on the dates of the audit
Usually the month of the audit is discussed in advance, during the negotiation of the contract with the certifying authority. Closer to the date of the audit, the certifying authority will most likely offer a choice of visit intervals and you will need to align them with the schedule of key personnel who will be involved in the audit. If you certify several sites in different cities, carefully think over the logistics and coordinate with the audit team.
- Non-obvious point - clarify the composition and background of the audit team
This item can be useful from a business security point of view. Of course, controlling the independence of the audit team is, first of all, the task of the certification body. However, mistakes happen to everyone, so it will not be superfluous to check the biographies of potential auditors at least on LinkedIn.
For example, we have thus found out that one of the auditors is an active employee of our direct competitor. Fortunately, this was discovered before the start of the audit and everything worked out as he was excluded from the team. But the potential business risks in this situation would be significant.
- Agree with the audit team on the audit plan
This is necessary to understand which employees and departments will be involved in the audit, and on what days of the audit this will take place.
Typically, the plan specifies the schedule for each day of audit by the hour, indicating which parts of the information security management system and which services will be audited at one time or another.
- Book the time of colleagues who will take part in the audit
Once you know the approximate schedule of the audit team's visit, you can plan the time of your colleagues. Typically, auditors want to hold meetings with the top management of the company, with the information security department (obviously) and with those who are responsible for the operation of the areas to be certified.
For example, in our area of certification, 5 main services were declared and the auditor interviewed the heads of each of the departments responsible for the provision of these services. It is important to provide for a replacement for department heads for interviews (in case of illness, business trip, vacation, etc.).
- Conduct training and knowledge control for all employees
The point seems complicated, but it's actually not that bad. All employees should be involved in one way or another in the information security management system and comply with the rules established by the policies. However, the level of responsibility of employees for information security depends on the position and specifics of the work. We have implemented this as follows: all employees, depending on their positions, can have one or more roles in the field of information security. Each role has its own requirements for the employee, but absolutely all employees of the company have the base role "User". Training and further control of knowledge should be focused on this role.
We use testing to control the knowledge of our employees. There are many systems of this kind on the market, but we used the functionality built into the corporate portal. In our experience, auditors do check test results and can ask employees control questions from tests.
- Conduct a separate training for colleagues who will participate in the audit
By this time, a general training should have already been conducted for all employees (so that they know why and why changes are taking place in the processes in the company). However, special attention should be paid to those colleagues who will be directly involved in the audit. It is worth warning that during the audit nothing criminal will happen - they just have to tell the audit team about their daily work and, if necessary, answer specific questions.
- Take care of all required passes and permits for the audit team
Remember that the audit will begin even before the certification authority team is in your meeting room. The entrance to the business center is the first "line of defense". Here, auditors assess how seriously the physical security of the offices is ensured. If you are renting office space, then auditors will probably want to look at contracts with landlords to determine the delineation of the parties' responsibilities for physical security. And if the reality differs from what is written in the contract, problems may arise. In some cases, it is necessary to work separately with the security service of the business center.
For example, our auditor noticed that there is a clause in the contract with the business center that every visitor is issued a pass, but he was not given any pass at the entrance to the business center. To which we replied that the agreement does not mention the issue of a pass "on hand" - accordingly, the pass was issued, but not issued :)
If the certification perimeter includes data centers, take care of issuing special passes for auditors in advance. In addition, we advise you to discuss the upcoming visit with the contact persons from the data centers and clarify which of the employees will answer the auditors' questions about the physical security of the data centers.
Technical training
Technical preparation for an audit is one of the most important and difficult points. Before the first audit, our IT team had to sweat a lot. Let's start with physical security.
Of course, most of the physical security will be assigned to the security service of the business center: this is access to the building, security and fire alarms, video surveillance, etc. Well, from our side it was necessary to conduct an "audit" of measures to ensure physical security in offices:
- Replace or add access control systems (ACS) in several offices.
- Check the reliability of the safes and the quality of their installation (whether they are bolted to the floor).
- Carry out an audit of filing cabinets (are there locks, markings).
- , , .
- . , .. . , , ( , , Wi-Fi ..).
Next, let's talk about standardization - one of the most important steps towards fast modernization and ease of further maintenance. This approach saved a lot of preparation time. For example, we have upgraded the OS (operating systems) on the users' work computers. Despite the cost of the process, this update was necessary to encrypt computer disks, as well as optimize our services, hardware and policies for a specific OS.
Of course, in matters of encryption, there were some pitfalls: if workstations have classic HDDs (not SSD or M2), then working at such a computer becomes torment. Therefore, we also had to upgrade part of the office hardware. The second difficulty is that hard drives on computers have become much less “live”. Well, and the third nuance - it became necessary to enter the bitlocker password when loading. At that time, we had not yet had time to configure network unblocking, and TPM was not everywhere, and enabling work with TPM without network unlocking is pointless from the point of view of information security.
As mentioned above, we have moved the main server capacity to a dedicated data center. We had a small equipped server room, but, in most cases, "our own" server rooms lose in terms of physical security to specialized sites.
Note that the choice of data centers for Co-Location is quite large: moreover, there are data centers on the market that are certified according to ISO 27001. In our case, a data center was chosen that was not officially certified according to ISO27001 or TIER III, but at the same time it had all the necessary technical solutions and competent specialists. Some of the risks associated with the main data center were covered by the backup data center. As a result, two “simpler” data centers cost less than a data center with all certificates.
Working with server hardware has become a separate chapter in the certification epic. We had to seriously update the OS on the servers, which required a lot of time from the team. many of the services are open source. Yes, we also use Microsoft services, but certification pushed us to transfer all possible services to open source software. Thus, we began to actively implement the infrastructure as code approach. One of the significant benefits that we have experienced is space savings due to the failure to back up a number of services.
The main proof of anything in an audit is a record, in the broadest sense of the word. From a technical point of view, these are various logs. In preparation for the audit, we spent a lot of time working with logs using the ELK log recording system. This system has become a kind of "magic wand", eliminating the need to collect logs manually. Thanks to ELK, IT staff can save a tremendous amount of time while investigating incidents. Additionally, thanks to the system, the issue of logs backup is solved.
These are just the main jobs in terms of technical training. However, let's move on and move on to day X - the audit of the company's ISMS .
How is the audit going
The main document that the examiner studies in the framework of a certification audit is the Statement of Applicability (hereinafter - SoA). It should indicate 114 controls from the ISO 27001 standard, their applicability / inapplicability to the company and the means by which these controls are implemented. In fact, this document is a reflection of many months of work on the implementation of this standard.
As a rule, in front of each SoA clause there should be a link to a document (policy), which describes how the company implements this or that control. The auditor verifies that everything written in the SoA is true.
To do this, he looks:
- How well your ISMS policies / documents comply with ISO 27001;
- , .
«» – , , - .. – , , , .
If in internal policies you refer to, or mention a third party standard, then it must be attached to the policies (that is, an official copy must be purchased). Thus, at the first stage, the auditor works with documents, and at the second, he “goes to the fields”.
The second stage, it seems to us, is the most insidious, but also the most interesting. Paradoxically, the internal team that was preparing for the audit had a lot of positive emotions. What is the reason for this? This is probably a topic for a separate article.
At the second stage, there is a "physical" check of offices and data centers (everything that is stated in the certification perimeter).
When preparing for the auditor's visit to the data center, you must first agree with the data center on the allocation of a person to meet with the auditor. Moreover, such an employee must have a high level of training and knowledge regarding the work of data centers. Auditors will be comprehensively interested in the security of the data center: air conditioning systems, communication channels, power supply systems, generators, physical access, etc.
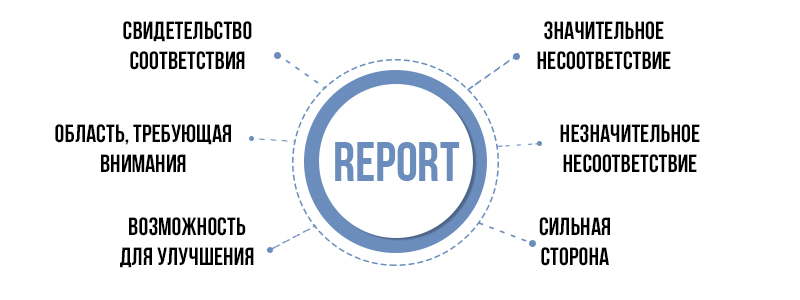
As part of the audit at all sites, the auditor usually records the following in the report:
- Conformity evidence
This is evidence of compliance with the standard, which the auditor found during the audit.
- Major Nonconformity
This is something that the company should avoid in every possible way - a mismatch that jeopardizes the effectiveness of the entire ISMS. Corrective action must always be taken for such a discrepancy. The certificate cannot be issued until the significant non-compliance is closed. Therefore, another visit of the auditor will be required to verify the closure of this non-compliance. As a rule, the company is given 90 days for this. It should also be remembered that the additional visit of the auditor will be charged separately.
- Minor Nonconformity (minor nonconformity)
Minor inconsistencies do not pose a big problem for the company - based on the results of the audit, it will be enough to fill out a form where you describe how and in what time frame it is planned to eliminate the inconsistency. Their presence does not affect the issuance of a certificate. However, if not eliminated before the next audit, they will become material nonconformities.
- Area of Concern (area requiring attention)
These are elements of the management system (usually affecting its performance) that can prevent a company from meeting the requirements of the standard in the foreseeable future. Are not inconsistencies, but require company attention. It is best to eliminate them whenever possible.
- Opportunity for Improvement
These are opportunities for the development of the company's ISMS, which the auditor was able to identify during the audit. These are tips from the series "how to make the system work even better."
- Strong Point (strong point)
Here, the auditor notes the elements of your ISMS that are “best practice,” that is, particularly effective. You could say that this is open praise for what you did really well.
Based on the results of the audit, you will receive a report with a detailed description of all the identified above points, which should be used in preparation for the next audit.
How to live on?
When you finally received the long-awaited certificate, do not relax: you need to confirm compliance with the company's standard annually. From now on, the audit will become a regular item in the company's budget.
The main task of the certified company is to maintain the information security management system in working order and to accumulate records confirming the functioning of the controls from the statement of applicability.
But there is good news: a full audit takes place every three years. Within two years after the certification audit, less significant checks are carried out - inspection audits. They differ in the scope of verification: during an inspection audit, the controls from the applicability application are checked selectively, and the auditor may not visit all sites. That is, these visits are usually faster and easier.
Conclusion
ISO 27001 certification is a useful measure both for the functioning of the business itself and for the satisfaction of its customers. Despite the fact that the volume of time and financial costs seems enormous, these are investments that pay off in difficult times from the point of view of information security. We hope that our series of articles will help everyone who has embarked on the exciting path of obtaining a certificate.
Read the previous materials from the cycle:
5 stages of inevitable adoption of ISO / IEC 27001 certification. Denial of
5 stages of inevitability of ISO / IEC 27001 certification. Anger
5 stages of inevitable adoption of ISO / IEC 27001 certification. Bargaining
5 stages of the inevitability of the adoption of ISO / IEC 27001 certification. Depression