
Greetings to the dear reader!
Today I would like to talk about what a hash function is, touch on its main properties, give examples of use and in general outline the modern SHA-3 hashing algorithm, which was published as the US Federal Information Processing Standard in 2015.
General information
A cryptographic hash function is a mathematical algorithm that maps arbitrary-sized data into a fixed-size bitmap.
, -, «-» «», «».
- :
) - ̆, -
b) -
c) ̆ , -
d) ̆ -
e) ,
- SHA3-256.
256 , 256 , .
, 64 . , 256 .
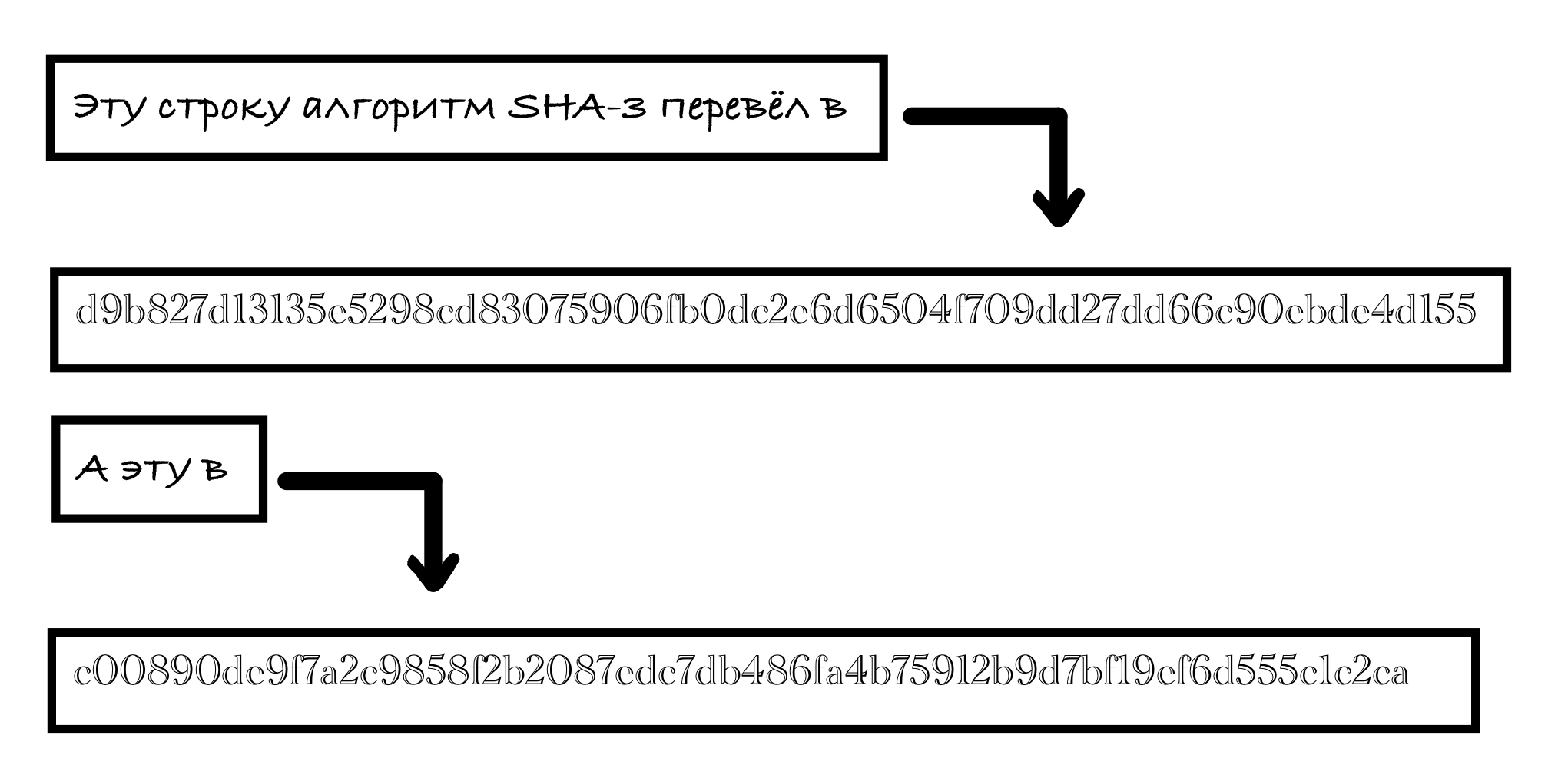
: " , , 256 ?"
: 256 !
, 256 - ,
.
, , :
, , !
.
- .
̆ - ̆:
Pre-image resistance
h, m ,
Second pre-image resistance
, ̆
,
Collision resistance
,
-
.
Collision resistance. , , ̆ . , - ̆̆ , , . , ̆ - ̆ , , . - ̆ , , ̆.
, -̆ ̆ , ̆ .
Pre-image resistance. . - , , , . , . .
Second pre-image resistance. . , - . , , , , . , , ,
,
, . -, , .
, , .
, , , .
, - , .

-
-:
•
- ̆, , , - ̆.
•
. , . , . -, .
•
, , . . , -.
:
, . , , . , ( ). , , , . , -, .
SHA-3.

SHA-3
(NIST) 2007—2012 -, SHA-1 SHA-2.
, :
•
•
,
•
, ISA
5 :
• BLAKE
• Grøstl
• JH
• Keccak
• Skein
SHA-3 Keccak.
Keccak .
Keccak
- ̆ Keccak ̆ , ̆ «» , Z «» .
Keccak
,
̆ , .
SHA-3 Keccak-f[1600],
, .
1600 ,
, .
, , SHA3-256
SHA-3 S
,
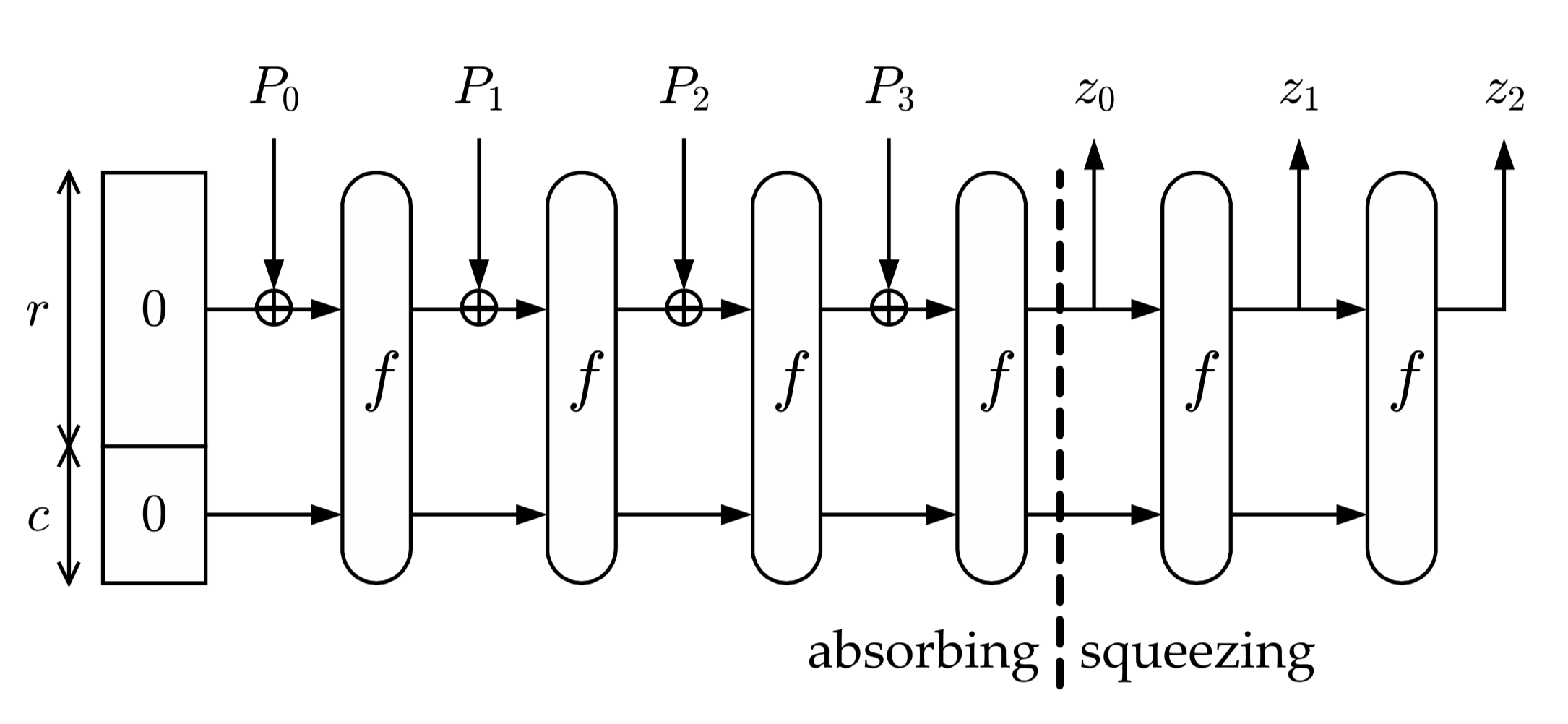
. Keccak
, 2.
- :
• M P ̆ r
• P n
• «»: ̆
(b = r+c) 2
,
, 2
.
0.
• «»:
,
- -,
.
«» ,
.
, :
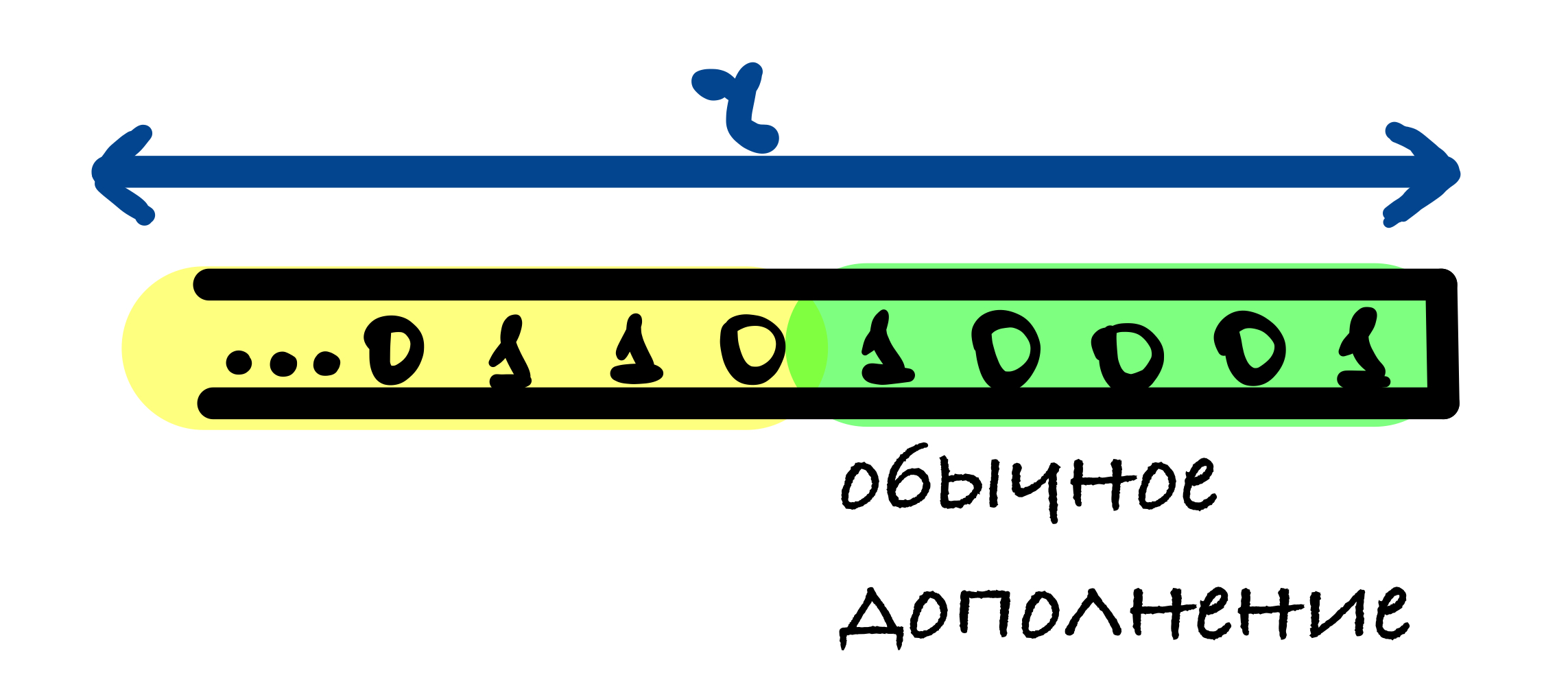
SHA-3 10...1: 1, 0 r - 1 1.
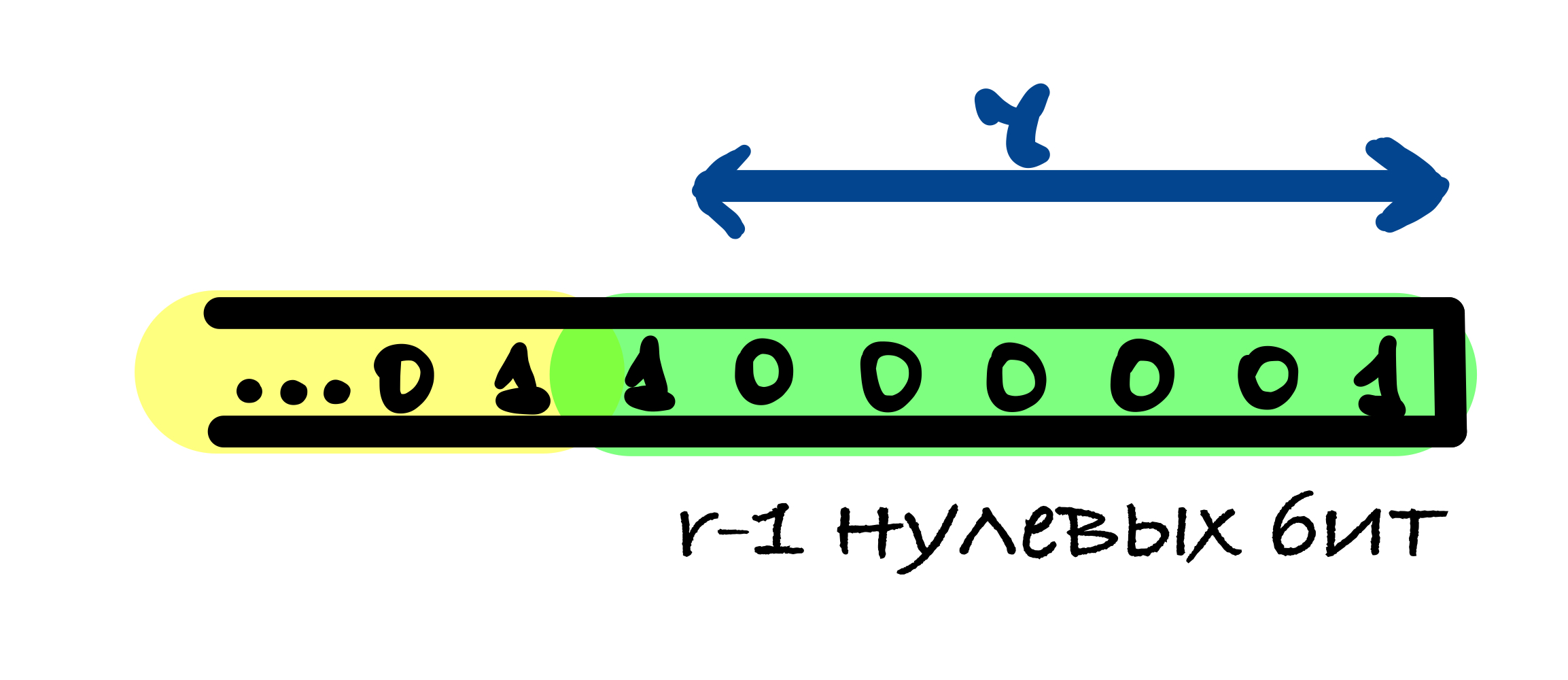
r - 1 , ̆ r - 1 . , r - 1 .
M r, , ̆ ̆ , r - 2 . , , , - .
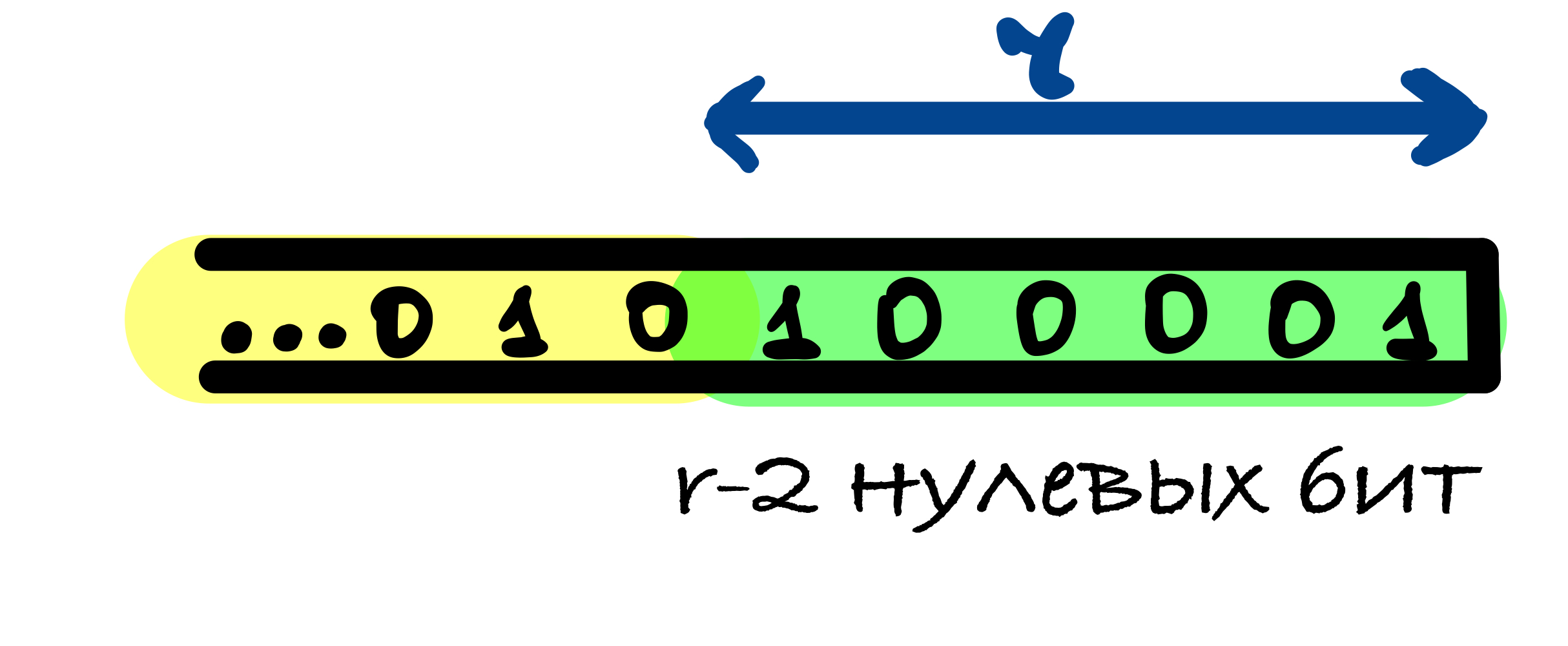
, - ̆, , .
:
, , , ,
:
,
, :
- ,
,
- (64 )
, .
:
:
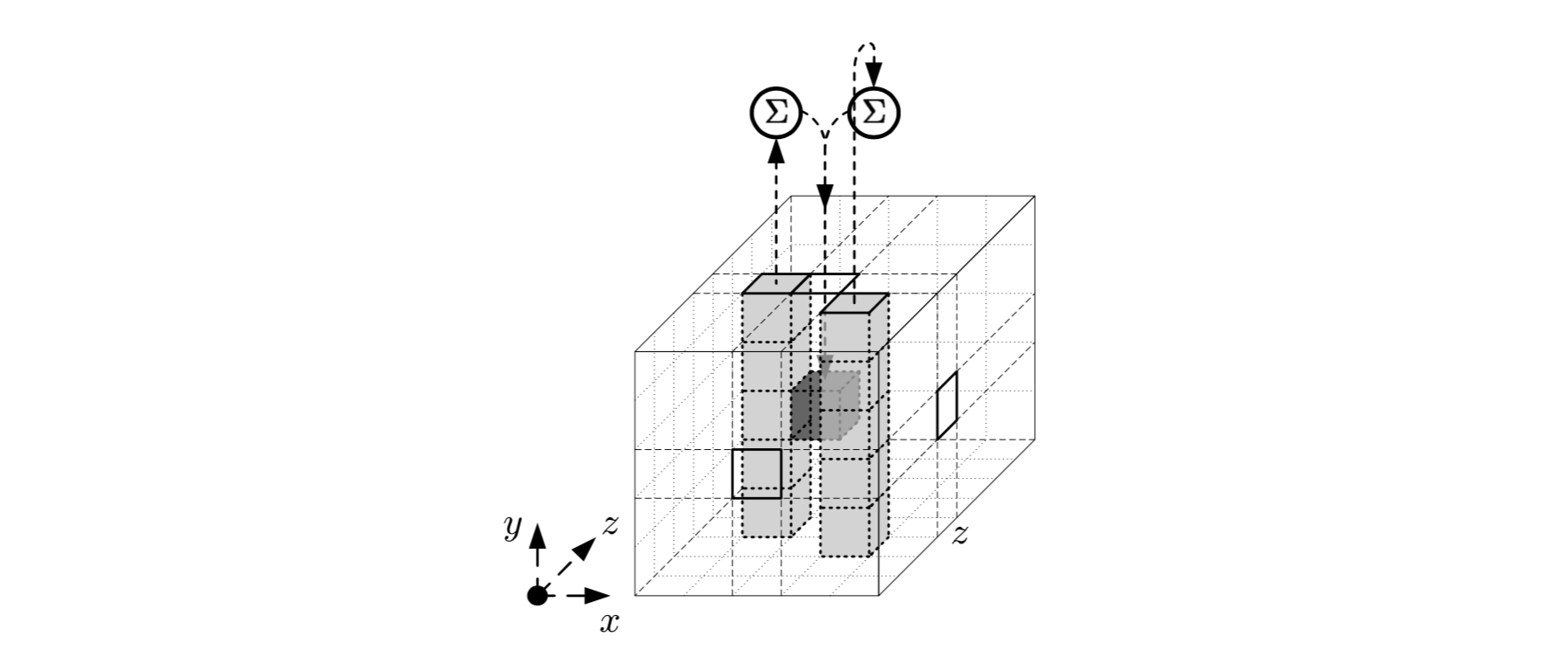
:

( z).
:

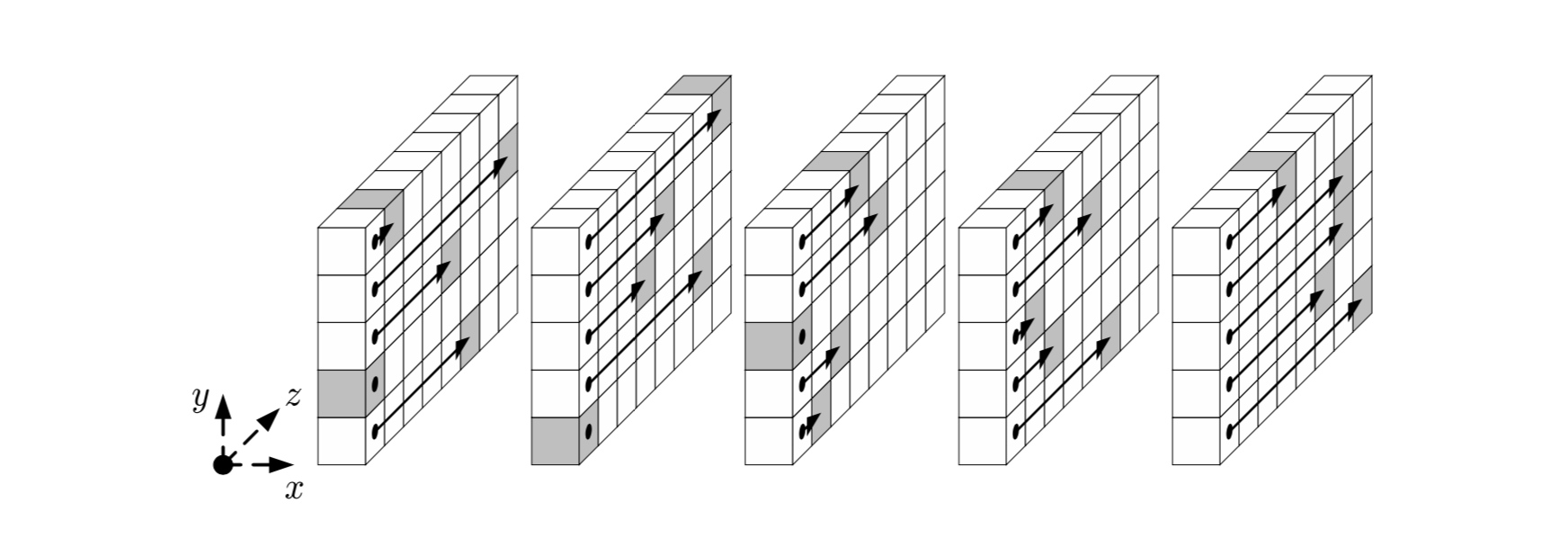
:


:

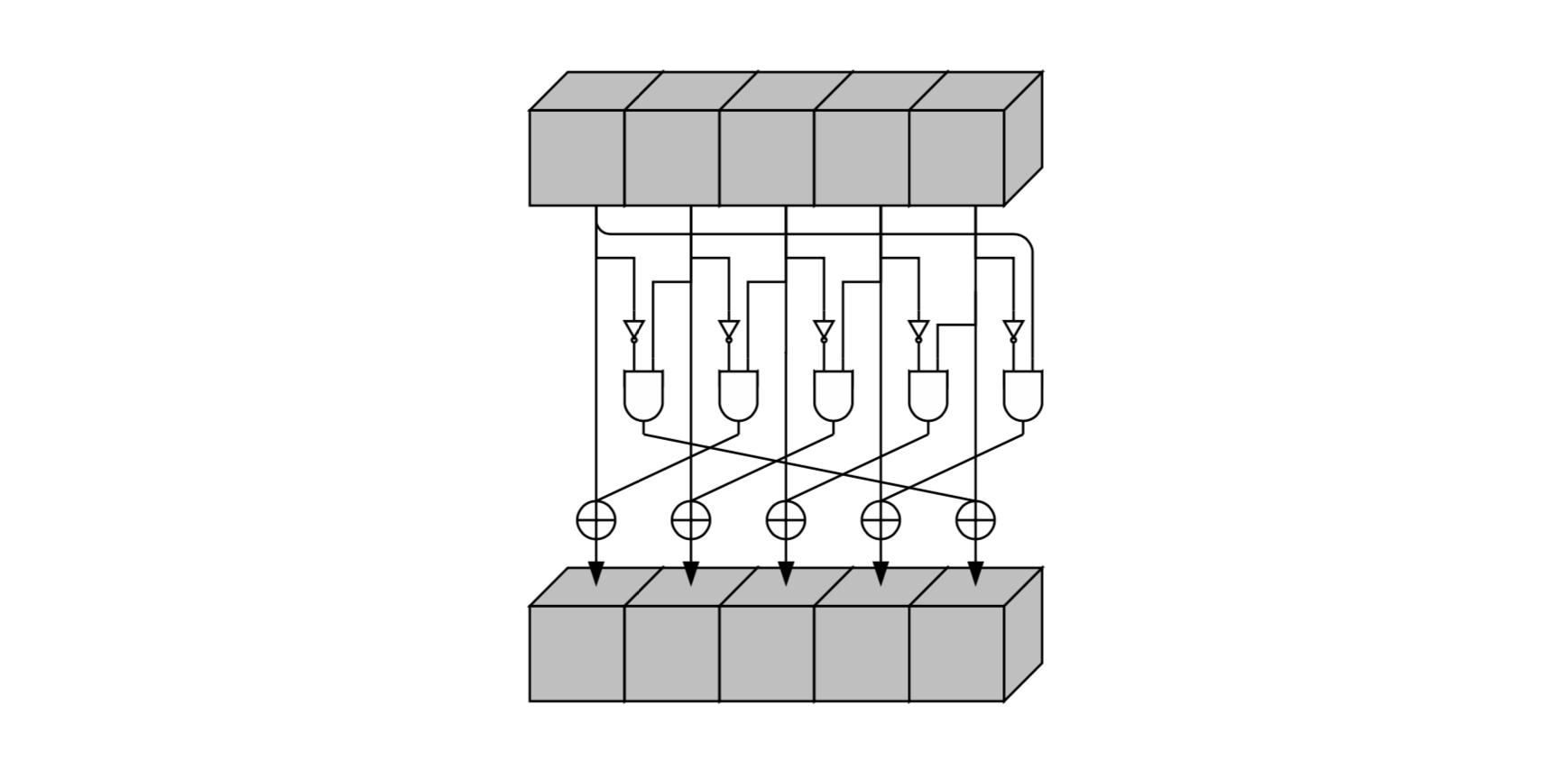
.
, , .
.

:

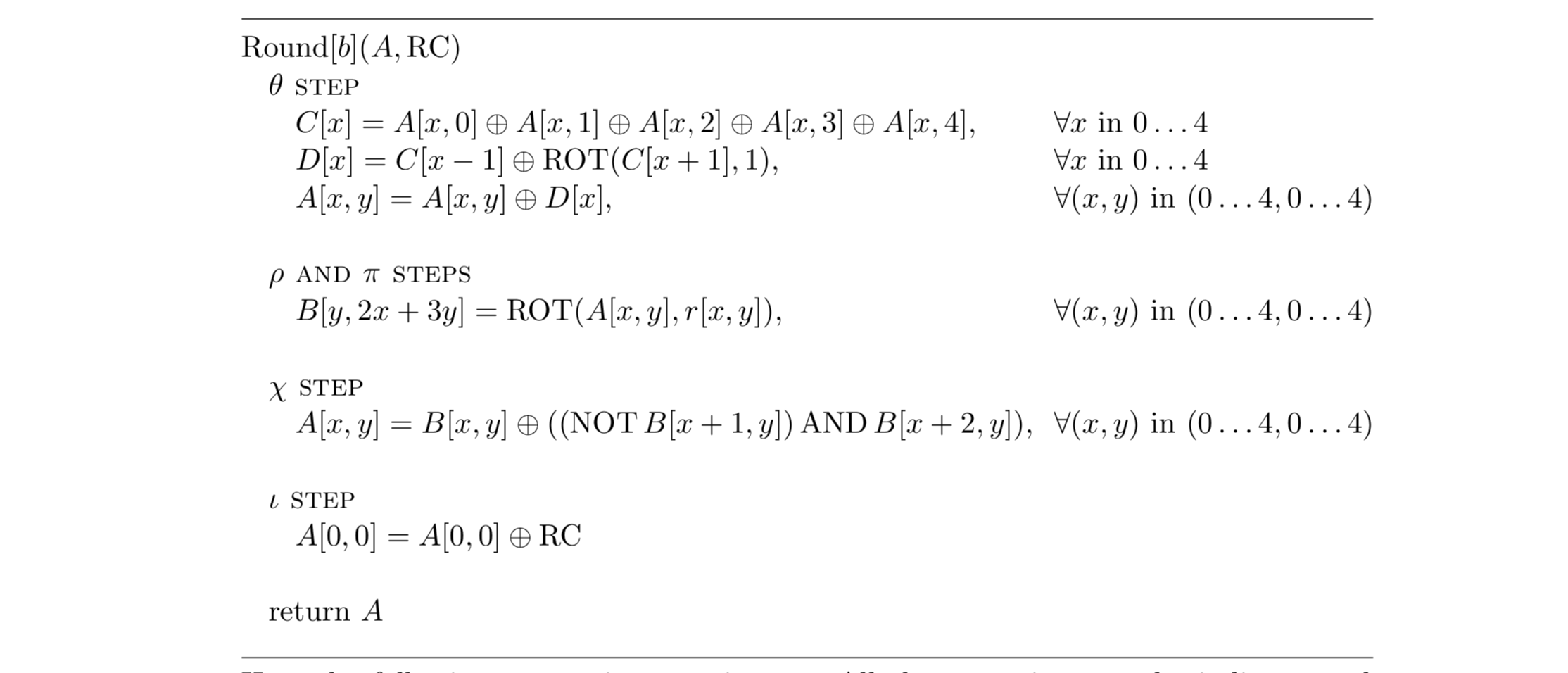
:
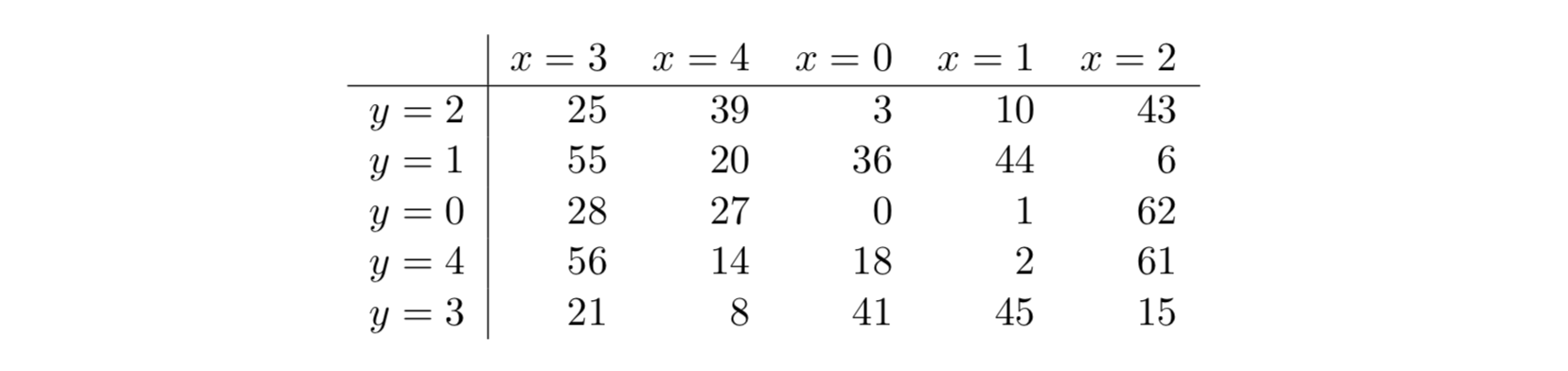
, -
SHA-3 Keccak, Secure Hash Algorithm
I hope everything was clear and interesting
Thank you all for your attention!