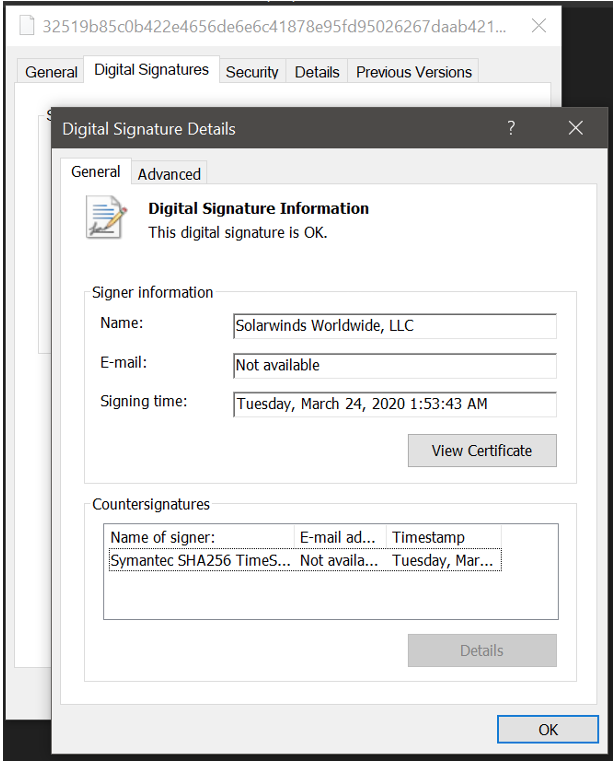
The validity of the digital signature on the DLL with built backdoor
virtually all core media was the news of the burglary SolarWinds software in the global cyber-espionage campaign. Here you need to understand the scale of the attack: this software for monitoring IT infrastructure (CPU, RAM, network) is used by thousands of private companies and government agencies, including the NSA, Pentagon, State Department, etc. A total of 300,000 customers worldwide (this page has already been removed from the official SolarWinds website, the link is a copy from the web archive).
The most interesting in this attack: 1) the introduction of a backdoor inside SolarWinds updates and 2) the original mechanism of hiding data in the service HTTP traffic of the SolarWinds program. In a nutshell, we will tell you about the steganography (covert signaling) method that was used here.
Some details about the attack were published by FireEye in a report dated December 13, 2020. This American company must protect its customers' networks from such sabotage, but in the end it itself suffered from hacking along with them.
Some of SolarWinds' customers:

Key facts
- The backdoor was discovered seven months after the attack began and was codenamed SUNBURST. Considering the scale of the infection, this is a serious failure of antivirus companies.
- DLL SolarWinds Orion, .
SolarWinds Orion
The backdoor was found in the SolarWinds.Orion.Core.BusinessLayer.dll library , which is signed with a valid digital signature from SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC (screenshot above).
In particular, a number of updates to the SolarWinds Orion program for March-May 2020 were infected, which were distributed with a valid digital signature.
It was a standard Windows Installer Patch file with all the usual resources, including the infected SolarWinds.Orion.Core.BusinessLayer.dll library . After installation, the library was normally loaded into memory by the regular SolarWinds.BusinessLayerHost.exe executable .
Microsoft explained that the attackers “used [on-premises compromise] to gain access to the trusted SAML token signing certificate of the organization [SolarWinds]. This allowed them to spoof SAML tokens for all existing users and accounts of the organization, including highly privileged ones. " Apparently, we are talking about physical penetration into the company's office (on-premises compromise).
Unique features
- Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA) for generating subdomains and modifying DNS queries. The Trojan sent a request for a resolution of the avsvmcloud [.] Com subdomain , and the DNS response contained a CNAME record indicating the command server.
- All traffic was masqueraded as network traffic using the Orion Improvement Program (OIP) service protocol through the SolarWinds API. Thus, antiviruses and firewalls could not distinguish between backdoor activity and actual SolarWinds activity.
- The backdoor code was embedded in standard software components.
Steganography
And here's the most interesting part - how exactly the backdoor masked packets in normal network traffic:
HTTP GET HTTP HEAD, — HTTP PUT HTTP POST. PUT , 10000 ; POST. HTTP- If-None-Match userID, , .
JSON HTTP POST PUT userId, sessionId steps. DEFLATE XOR. Base64.
HTTP- XML, .NET. GUID HEX. HTTP- hex- :\{[0-9a-f-]{36}\}"|"[0-9a-f]{32}"|"[0-9a-f]{16}
. , GUID HEX. -HEX, HEX. DWORD , , . XOR , DEFLATE. — ASCII, JobEngine , .
In the case of such advanced attacks, it is impossible to identify the developers of the program. Researchers make assumptions based on the coincidence of the code with previously discovered hacking tools, as well as on the basis of who exactly was the victim of espionage.
For example, Iranian uranium enrichment facilities were damaged in 2010 . The very advanced Stuxnet malware slightly changed the rotation speed of the installations - and eventually disabled them. Accordingly, it is logical to assume that the customers and developers of the malware were the US and Israeli special services , since these countries are systematically trying to prevent the manufacture of nuclear weapons in Iran, not always acting diplomatically.
As for the SUNBURST backdoor, it is more likely attributed to Russian hackers from the APT29 (Cozy Bear) group , based on the ingenuity of the techniques used, the choice of targets and physical penetration into the victim's office. Although the customer and the contractor are not known for certain.
Snort's rules for detecting and blocking SUNBURST traffic are publicly available .
