Low-cost broadband satellite internet is the dream of millions of people living in remote regions. In most of these places, you will not be able to connect to a regular highway, and all other methods are either unavailable or very expensive. Therefore, satellite Internet is now being developed by three companies at once - Elon Musk's Starlink, OneWeb and Project Kuiper from Amazon.
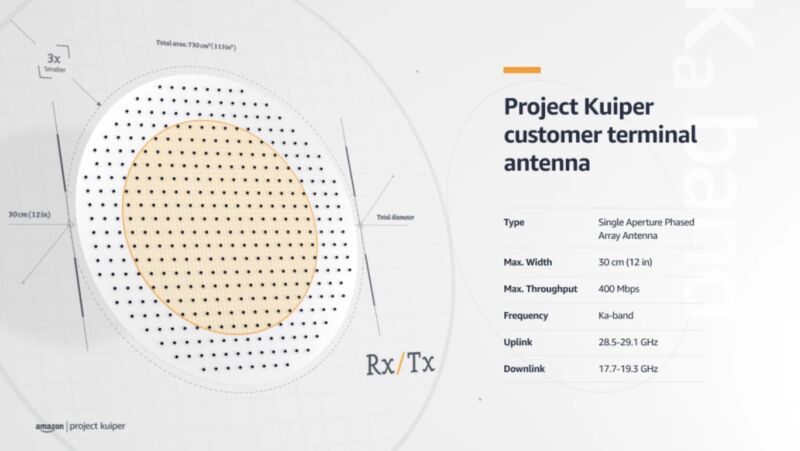
The other day, Amazon said the completion of the creation of a low-cost antenna for the satellite user terminal. According to the developers, the basis of the antenna design is a new architecture, which made the system small and lightweight. At the same time, it provides channel bandwidth up to 400Mbps.
What is this antenna?
It is designed to work in the Ka-spectrum. To keep production costs down, Amazon needed to reduce the size, weight, and complexity of the antenna. In a normal situation, everything would have been solved easily and simply, but here the company was dealing precisely with the Ka-spectrum, where physical separation of the receiving and transmitting antennas is required in order to avoid interference and communication problems. Usually, the receiving and transmitting antennas are installed in different places. But this requires additional space, plus the cost of production increases.
Amazon managed to develop a system where both antennas are layered on top of each other - the structural elements overlap, and so as not to interfere with the reception or transmission of data. The design includes a combination of digital and analog components. This arrangement made it possible to create an antenna with a diameter of only 12 inches, which provides bandwidth up to 400Mbps.
“The key achievement was the integration of the transmitting and receiving phased array antennas in one aperture. This can be done in other frequency bands, but Project Kuiper plans to operate in the Ka-band, where the transmit and receive frequencies are far apart, ”the company said in a statement.

Phased arrays are a class of radiating systems in which several antennas - there may be two, maybe thousands - are located at the same aperture, creating a focused beam of radio waves.
The main task was not only to create an efficient antenna, but also to make it available for mass production, with a low cost for the end user.
Amazon will use the 17.7-18.6 GHz and 18.8-20.2 GHz spectrum for space-to-Earth and 27.5-30.0 GHz for Earth-to-space communications.
The testing phase has already been passed
The company said that the prototype has already been tested, all test elements have been completed successfully, so next is the stage of practical implementation. The tests were carried out in the field, and the conditions were different - both weather and all others. As it turned out, the bandwidth of the channel is enough to provide 4K video transmission.

Amazon is now hiring employees to scale up the project. That is, it is entering the practical phase and people, new employees are needed.
Priority is on downloading content
The company tried to balance the speed of receiving and transmitting data, but still the priority was given to downloading. The developers believe that they have created several innovative elements at once, which make it possible to create new types of antennas. They are very different from what is widely used today.
One of the achievements is the dissipation of heat in the satellites themselves. The problem is that there is no air in space that can remove heat. Therefore, it was necessary to develop not only powerful systems capable of providing a reliable signal, but also to think about reducing the energy consumption of these systems. The project participants say that they had to puzzle over this problem, but in the end they managed to solve it.
Unfortunately, having told about such details, the project participants kept silent about the fact that Kuiper will become available to end users. The FCC gave Amazon 6 years to deploy the satellite system - during this time at least 50% of the devices should be in orbit. All others should be launched by July 30, 2029.
The company previously said that the network will become available as soon as 578 satellites are in orbit. In total, the FCC has given permission to launch 3,236 vehicles.
The main competitor to Amazon's satellite network, SpaceX's Starlink, has already provided test access to several hundred subscribers. Available speed - from 50 to 150 Mbps with delays from 20 to 40 ms. By 2021, the company promises to significantly improve all network performance metrics.
