I propose to plunge into the jungle of the microarchitecture of the computer and understand how one of the most common technologies for ensuring the hardware integrity of the BIOS boot, Intel Boot Guard, works. The article highlights the prerequisites for the emergence of technology, lists all modes of operation, and also describes the algorithm for each of them. Everything in order.
History and prerequisites for creation
The computer boot process is a chain of events in which control of the executive equipment is transferred from link to link, starting with the user pressing the power button and ending with the application. The problem is that each of these links can be compromised by an attacker. Moreover, the earlier the component is attacked, the more freedom of action the offender gets. There are known cases of attacks in which an attacker replaced the BIOS or Boot loader with his own vulnerable ones and, in fact, turned the computer into a "brick" (which is why this type of attack is called Bricking). In an effort to protect the boot process of a computer, many integrity checkers have been created. However, any program can be successfully replaced by an offender,therefore it is impossible to rely on it one hundred percent. Hence the need arose to create a more reliable hardware technology to ensure the integrity of the boot.
In 2013, Intel integrated Boot Guard technology into the new Haswell microarchitecture as its option for providing hardware protection for the computer's boot. An Authenticated code module (ACM) hardware module was added to the boot process, and hardware manufacturers had to expand the BIOS by adding an initial boot block (IBB). Since then, the computer's boot chain includes ACM, with which the IBB is checked, after which control is transferred to the BIOS, and so on.
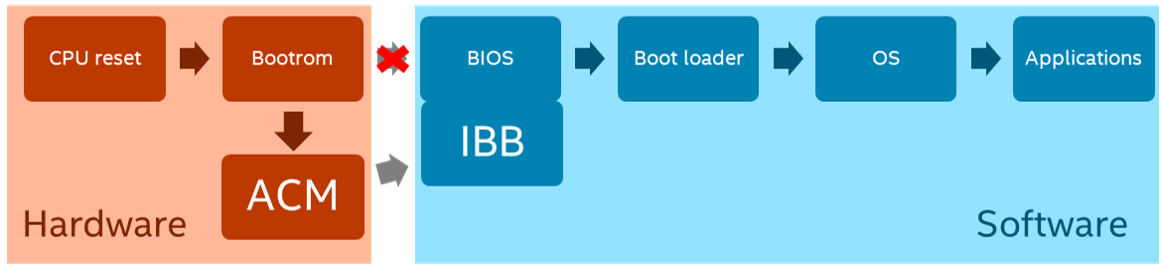
Operating modes
Boot Guard . , ACM IBB. , "" .
Boot Guard :
(Measured boot) , . TPM (Trusted platform module) — , , RSA, RSA.
(Verified boot) , . — , : . , . .
TPM (IBB), IBB. Boot Guard :
TPM
IBB
IBB
IBB
IBB
, —
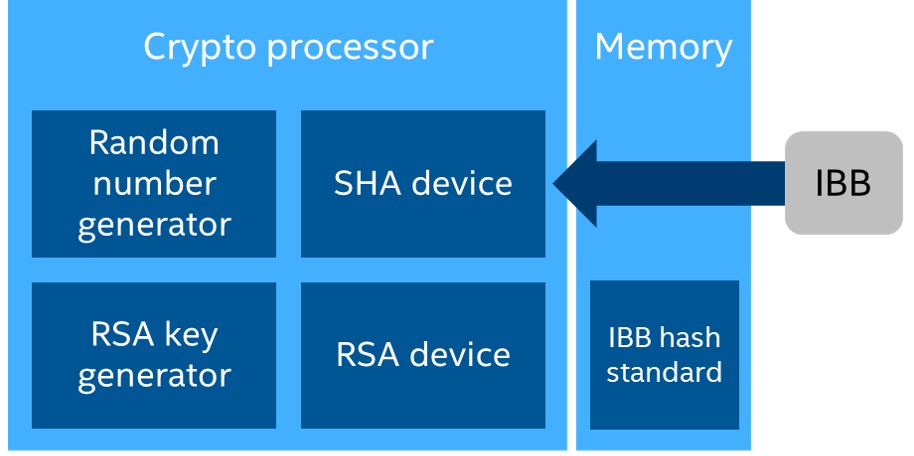
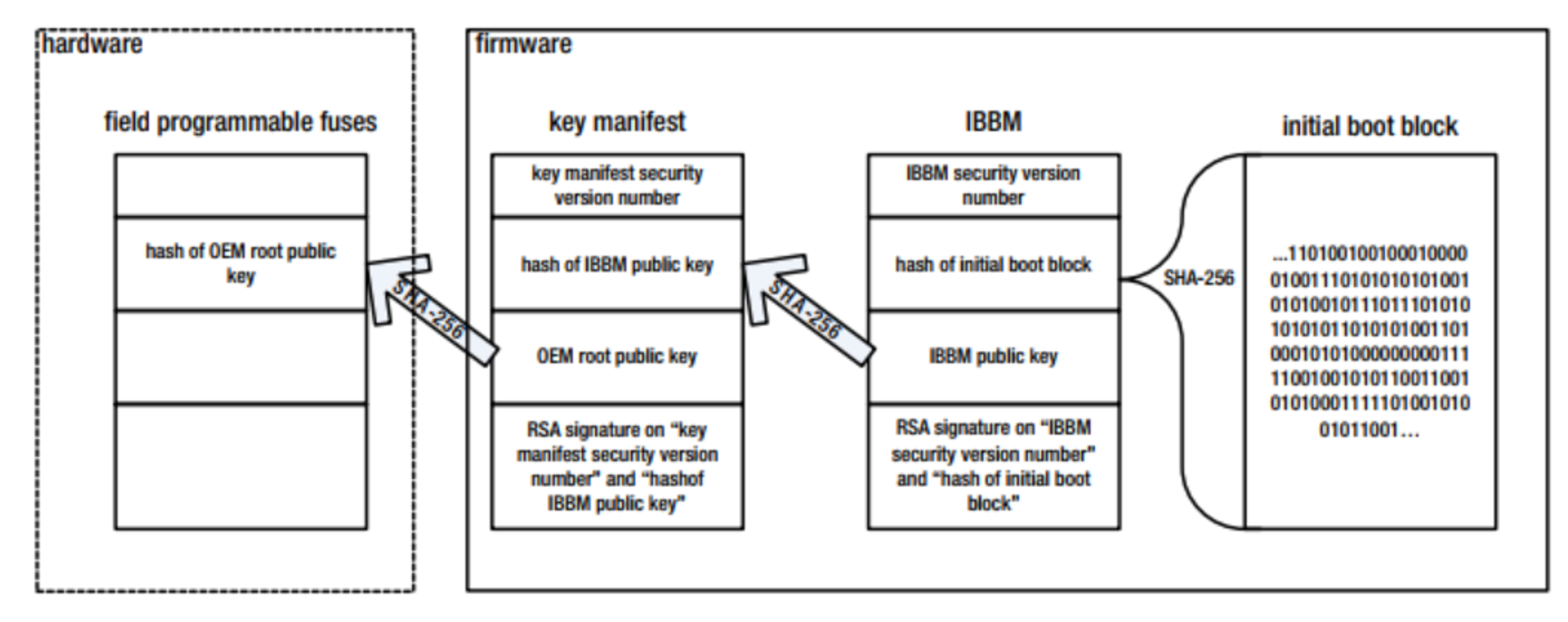
Boot Guard , (IBB) : IBB (IBBM) . IBB , IBB, RSA, RSA IBB. , RSA IBB, RSA , RSA RSA IBB. RSA . (ACM). Boot Guard :
ACM RSA .
. , . , .
RSA . .
RSA . .
RSA IBB . .
RSA IBB. .
IBB IBBM. .
.
.
In conclusion, I would like to add that despite all the charm and reliability of Boot Guard, it is important to understand that the configuration of this technology is entrusted to the hardware manufacturer. In 2017, six motherboard models were discovered in which Boot Guard was incorrectly configured and allowed to bypass the BIOS integrity check. Take care of your computers and choose a reliable hardware manufacturer!
When writing the article, the following literature was used:
Ruan X. Platform Embedded Security Technology Revealed - Apress, Berkeley, CA, 2014 .-- P. 263 - ISBN 978-1-4302-6572-6