
This week, chipmaker Qualcomm unveiled a new flagship SoC dubbed the Snapdragon 888. It is made on 5nm technology and is based on the ARM Cortex-X1 architecture. The chip already includes 6E and 5G Wi-Fi modules.
Whatever one may say, the new processor is very productive. Compared to Snapdragon 865, it is promised an increase in CPU speed by 25%, GPU and ISP - by 35%. There are no test results yet, so you have to rely on the words of the developers. By the way, romantics seem to be working at Qualcomm. In any case, this chip was called Qualcomm 888, and not 875, as it should have been, since 8 is a lucky number for the Chinese. So, for example, the Olympic Games in Beijing started on 08.08.2008 at 8:08 pm. The company clearly wants the Chinese to like the flagship smartphones based on the new chip, the name of which is full of "eights".
So what is this chip?
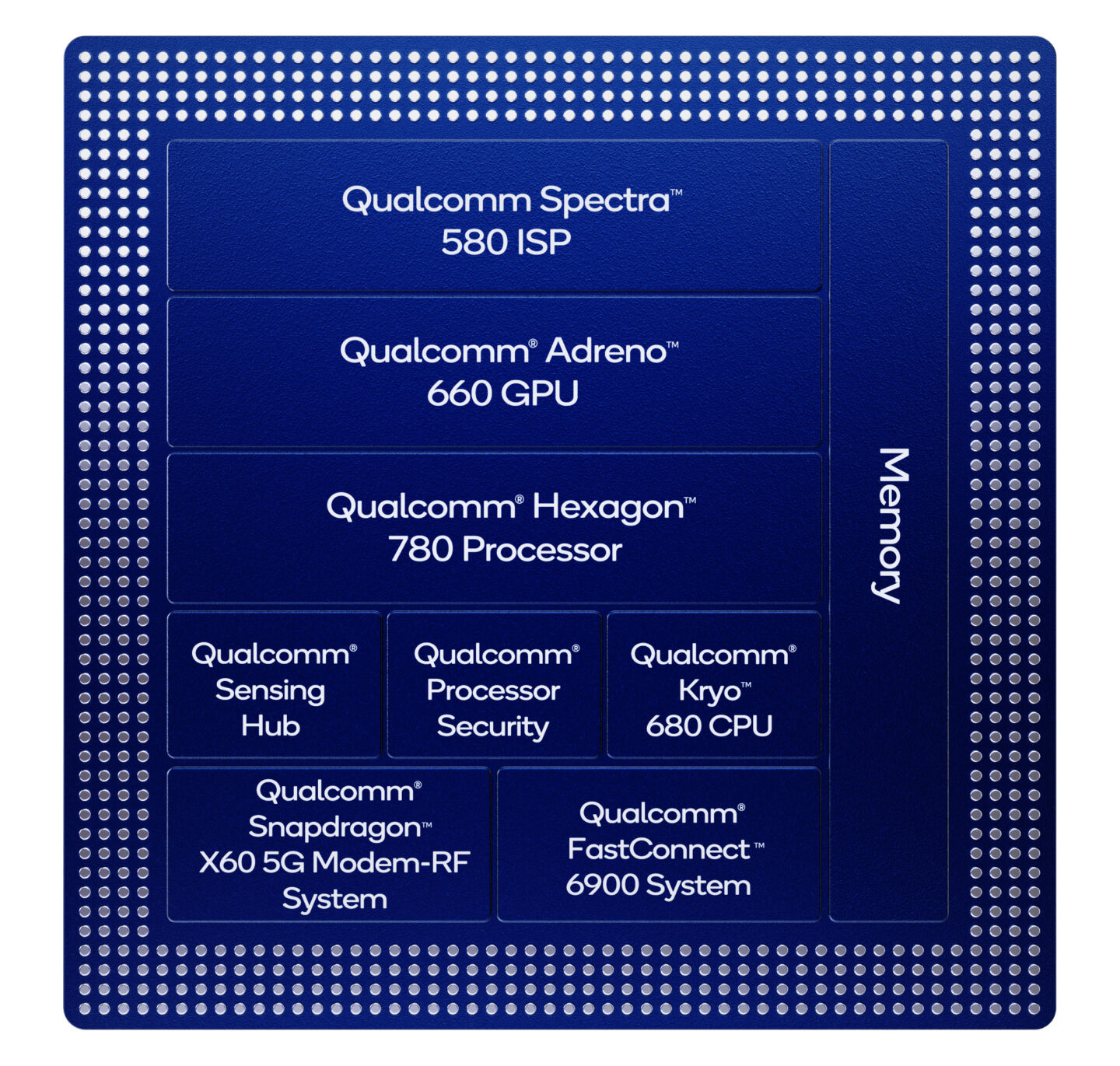
As usual, the processor has 8 cores (again "eight"). The main core for high-performance tasks, three cores for performing background resource-intensive tasks, and four more for performing background non-priority tasks. The main core in the chip, Cortex-X1, runs at 2.84 GHz. Three additional cores are Cortex A78, four others are A55.
The Cortex A78 is the successor to the Cortex A76, the technology that was used in the previous generation chip, the Snapdragon 865. ARM claims the new architecture offers 20% better "stable performance" In general, the processor is manufactured to provide a balance between size, power consumption, and processor performance. The Cortex-X1, on the other hand, was designed with no regard for power consumption in order to maximize performance. As a result, the A78 delivers "consistent performance" and the X1 comes into play when additional resources need to be deployed. For example, while loading resource-intensive applications and web pages.

When it comes to GPUs, Qualcomm doesn't really talk about graphics. It is known that this year support for Variable Rate Shading (VRS) technology has been added. This will allow game developers to control rendering and detail for every frame of any part of the image. So, for example, if the scene is dark or the object is moving very quickly, then it makes no sense to render it with high detail, so you can spend less resources rendering a lower quality picture. If the object is shown in close-up and is moving slowly, you must use all the capabilities of the video for rendering.
The processor interacts with wireless modules thanks to FastConnect 6900 System - a technology that makes it possible to increase the data transfer rate. Thus, phones with the new chip will support Bluetooth 5.2 and Wi-Fi 6E. Unless, of course, phone developers add new elements that allow working with these standards. Wi-Fi 6E is ideal for users who live in areas with high noise levels on the wireless spectrum. The 6E also adds the ability to operate in the 6 GHz spectrum.
True, this whole wireless story requires coordination with regulators in different countries. But in the USA, for example, devices with the new module will have access to three WiFi frequencies at once - 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz. All this helps to improve the performance of wireless networks in homes, multi-storey office buildings, public places. By the way, 6E was also supported by the Snapdragon 865 Plus chip, but so far there are no phones with this technology - they just have to enter the market. Perhaps the first such smartphone will be the Galaxy S21 Ultra. Well, access points are also still under development, so we expect new systems to enter the market.
A little more about wireless technologies, including 5G
One of the major improvements to the Snapdragon 888 is the fix for the Snapdragon 865 issue, which was split by the company into two elements. This is the main SoC and modem. This solution increases the chip size, operating temperature, power consumption, and costs. Accordingly, devices with such chips need larger packages, larger batteries, etc. All of this ultimately leads to an increase in the cost of devices - all for the sake of fifth generation networks.
The new chip, as far as we can tell, solves this problem. It is not known how it will affect the cost of devices, but there will be clearly fewer problems with it than with the Snapdragon 865. As for the built-in modem, it is Qualcomm X60, which was presented back in February this year. It does not increase the bandwidth, but it does improve work with new wireless technologies. These are DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing), VoNR and other joys.
The developers of the new type have added a few more improvements. For example, they completely changed the structure of the Hexagon 780 coprocessor, making it less power hungry, but more efficient. The coprocessor is used in applications with AI elements - smart cameras, voice assistants, etc.
Another image from all three cameras is received simultaneously. You can also capture images from the front and rear cameras at the same time. The company has not yet provided technical details for the implementation of this function.
Well, and the last thing that can be said is the Type-1 hypervisor, which, according to the developers, isolates application data and the operating system itself on the device. So, hacking such devices becomes difficult for attackers.
As for devices based on the "three eights", then, as mentioned above, the first will be the Samsung Galaxy S21 - it will be released in the first quarter of 2021.
