With the idea sorted out, now you can dive inside. What processes allow you to form a metal product? What happens to energy and material? What factors influence the final result? What is the difference between different approaches to solving the same problems?
Terminology
, , . – , . , , . , ISO ASTM, . 182 « » «». .
57558-2017 . . 1. . ISO/ASTM 52900:2015, Additive manufacturing. General principles. Terminology, IDT.
(, , additive manufacturing) - , , , , () ( ) (, ).
, :
(directed energy deposition) - , .
«». , :
– . , . , , , . . , - , .
, , . « . . .»:
() – . . « » 57558.
Spoiler
«», . « ?» , .
, , :
– , , . .
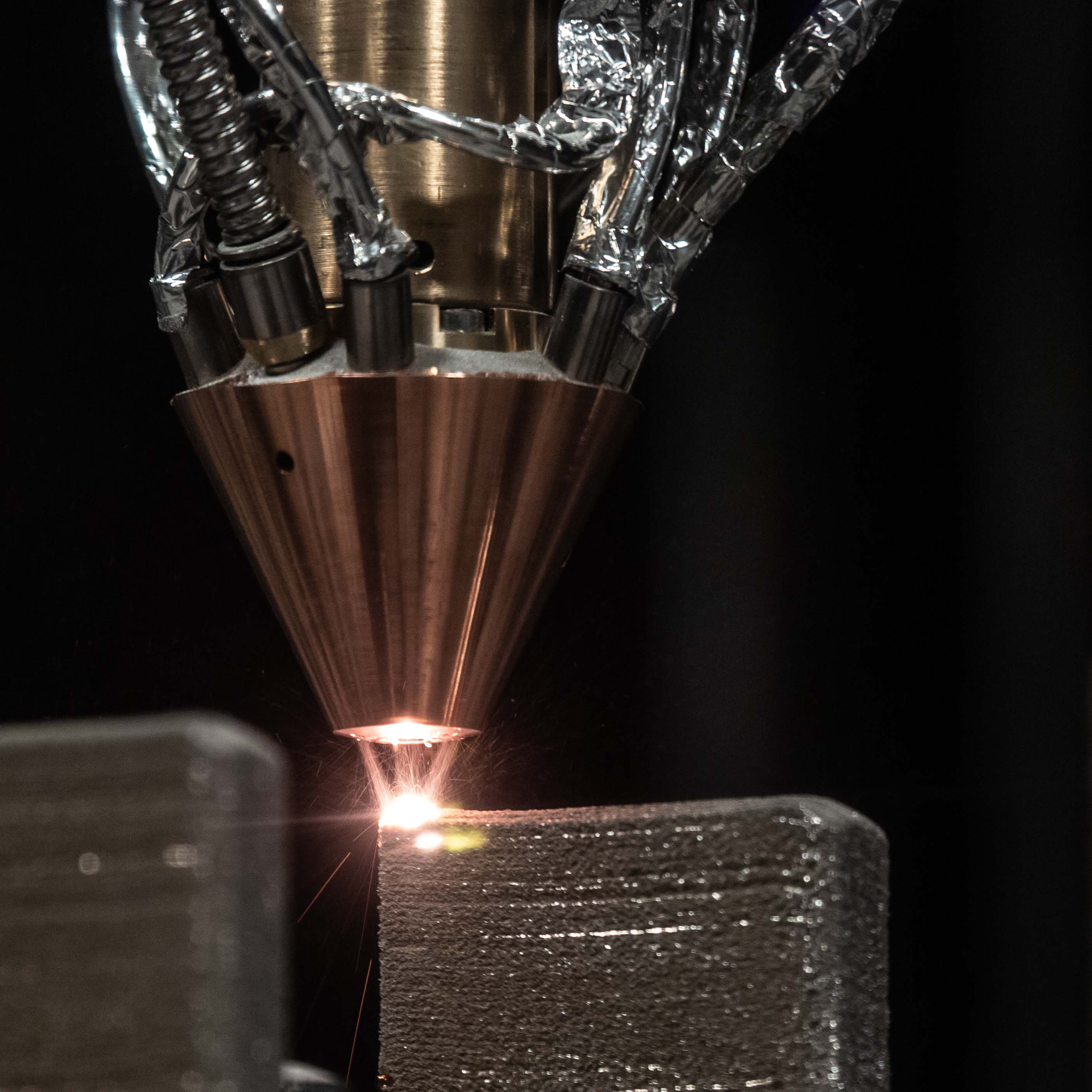
– , , – , . .
– ().
– , , .
– , .
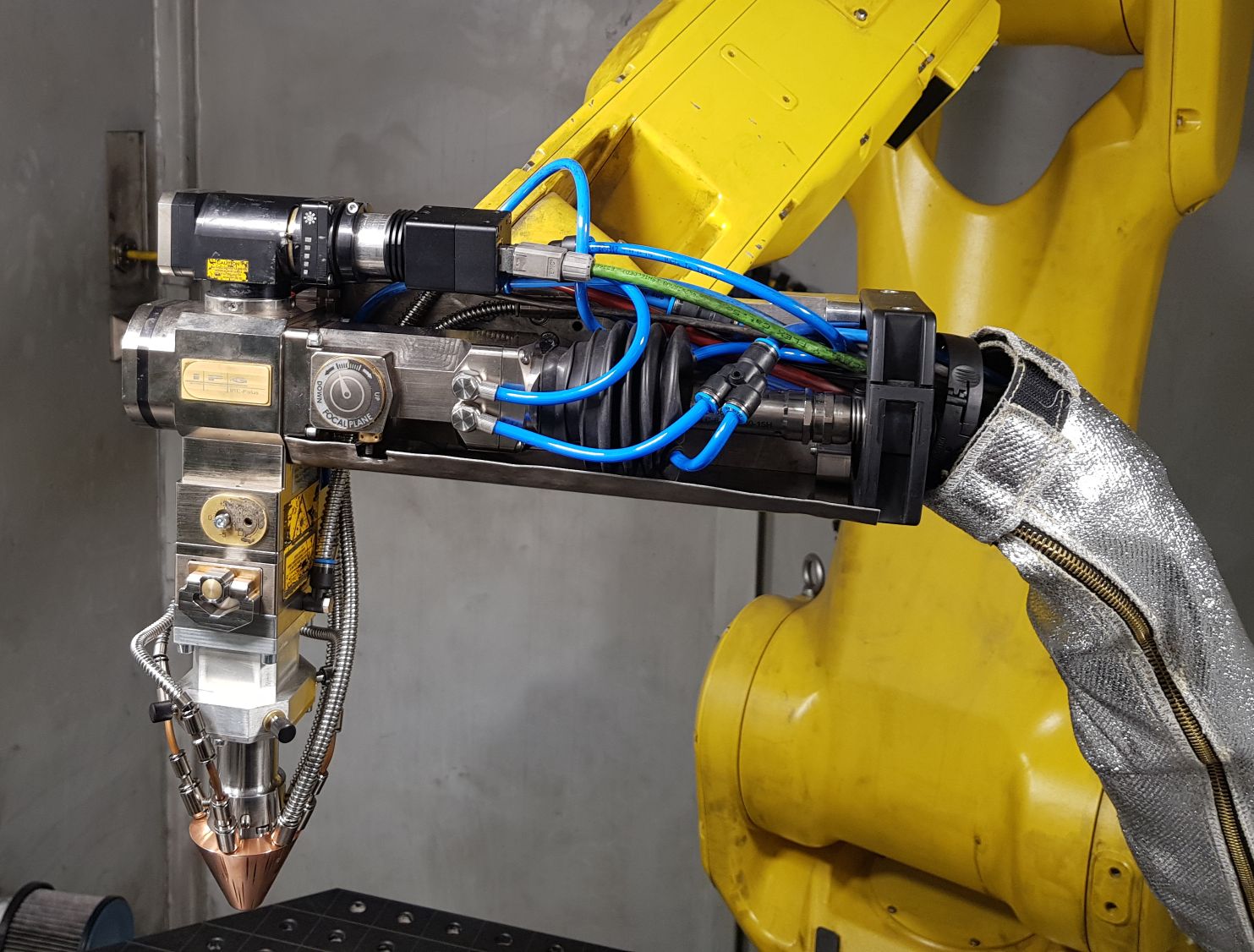
30 . , , , . – , , . , . – 25 25 . 2-, , . . , -, IPG Photonics, (80% ). , IPG – .
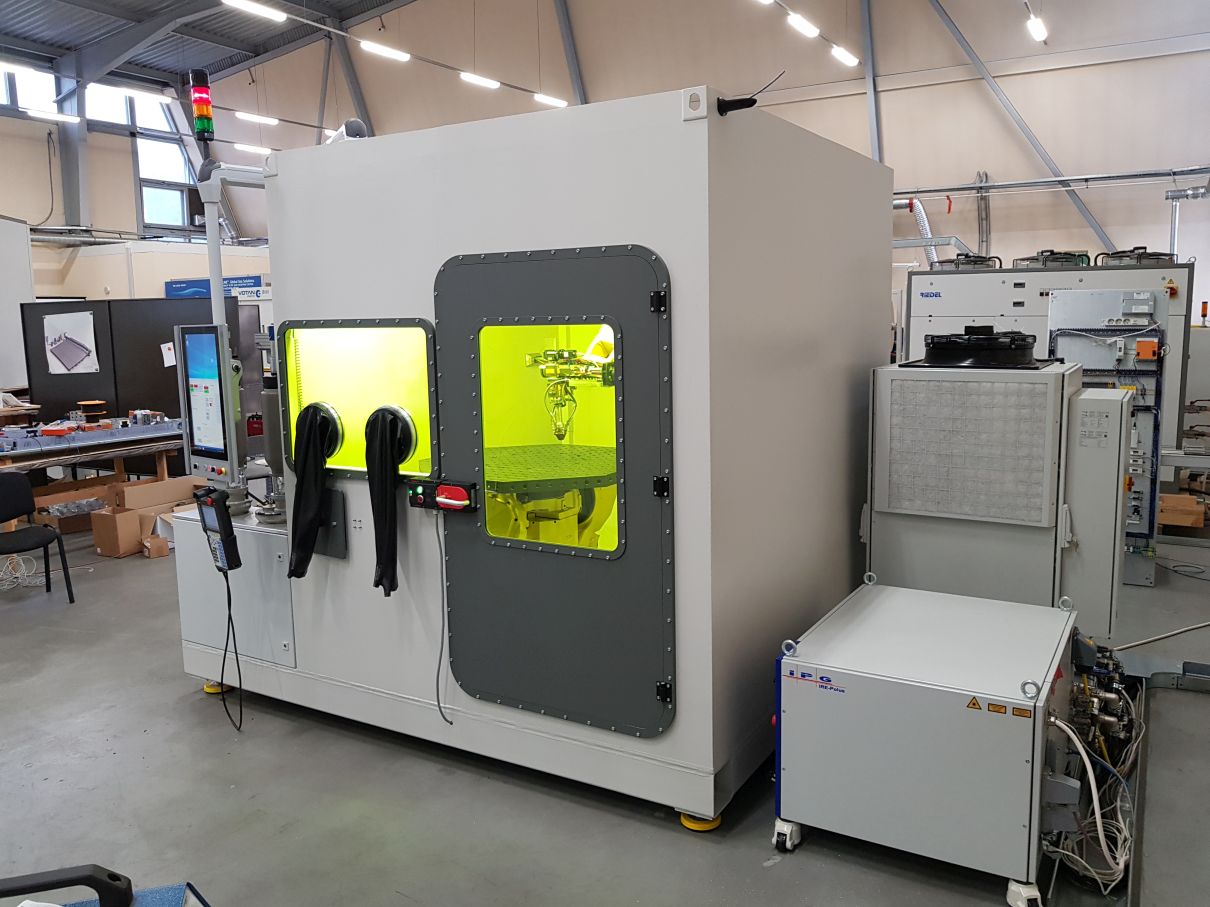

– , . 1070 ( ) . 10-100% 8 . , . , , , .
. ( 100 ) ( – 2). , 200 . , 1-5 . , , . – , .
, 2 . , 2 .
, .
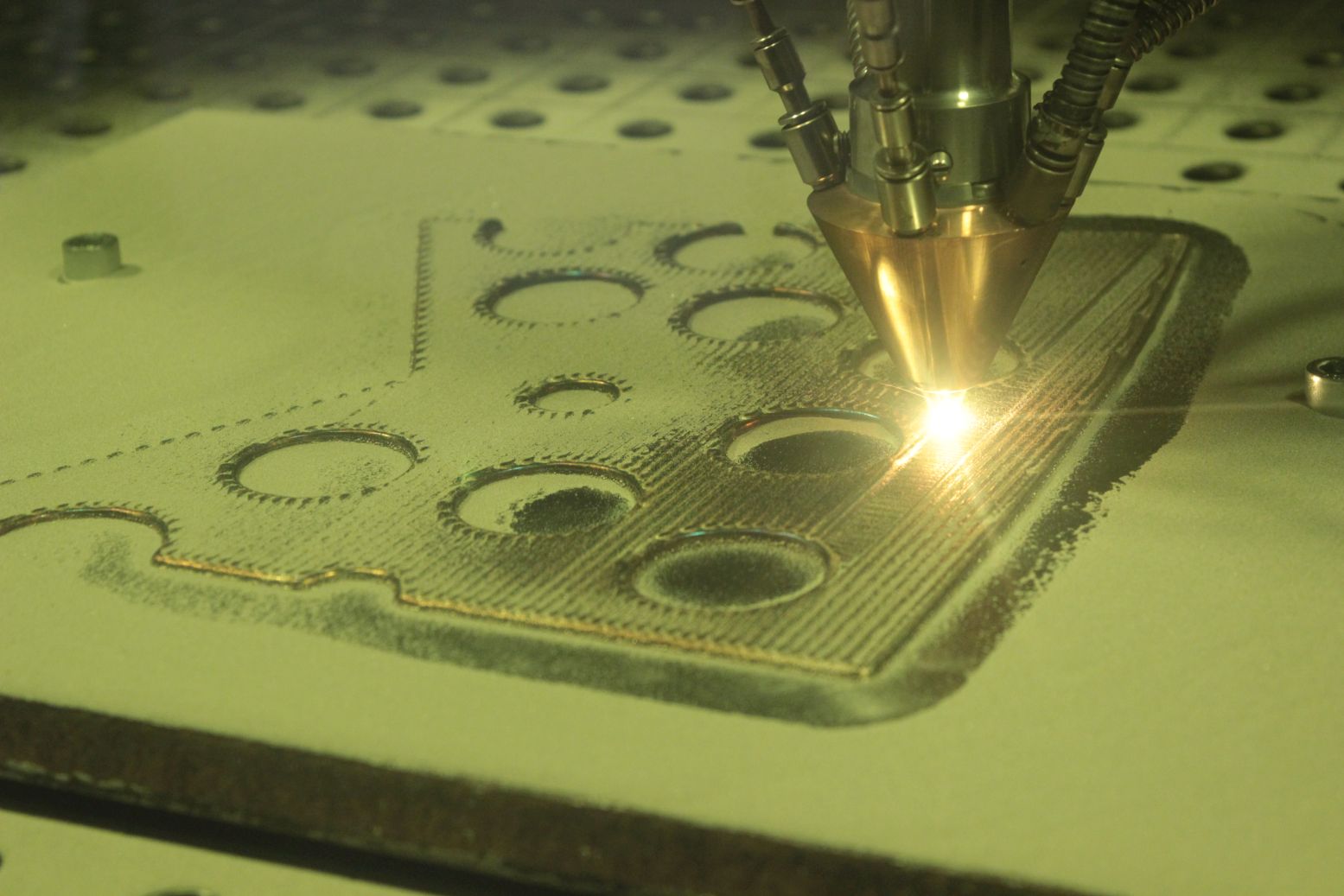
. (30-50%), , . , . , , , 1070 . , , – - . , , . , 515 450 , 10 . 500-1000 . , 10 , , .
, , . , , , . . – . , «» . , , .
, (, , ) (, , ). . , , , . , , . , . , -. - , .
50-150 . , . , . SLM, . , . SLM, . , , , . - 200 , . , . – . – . – .
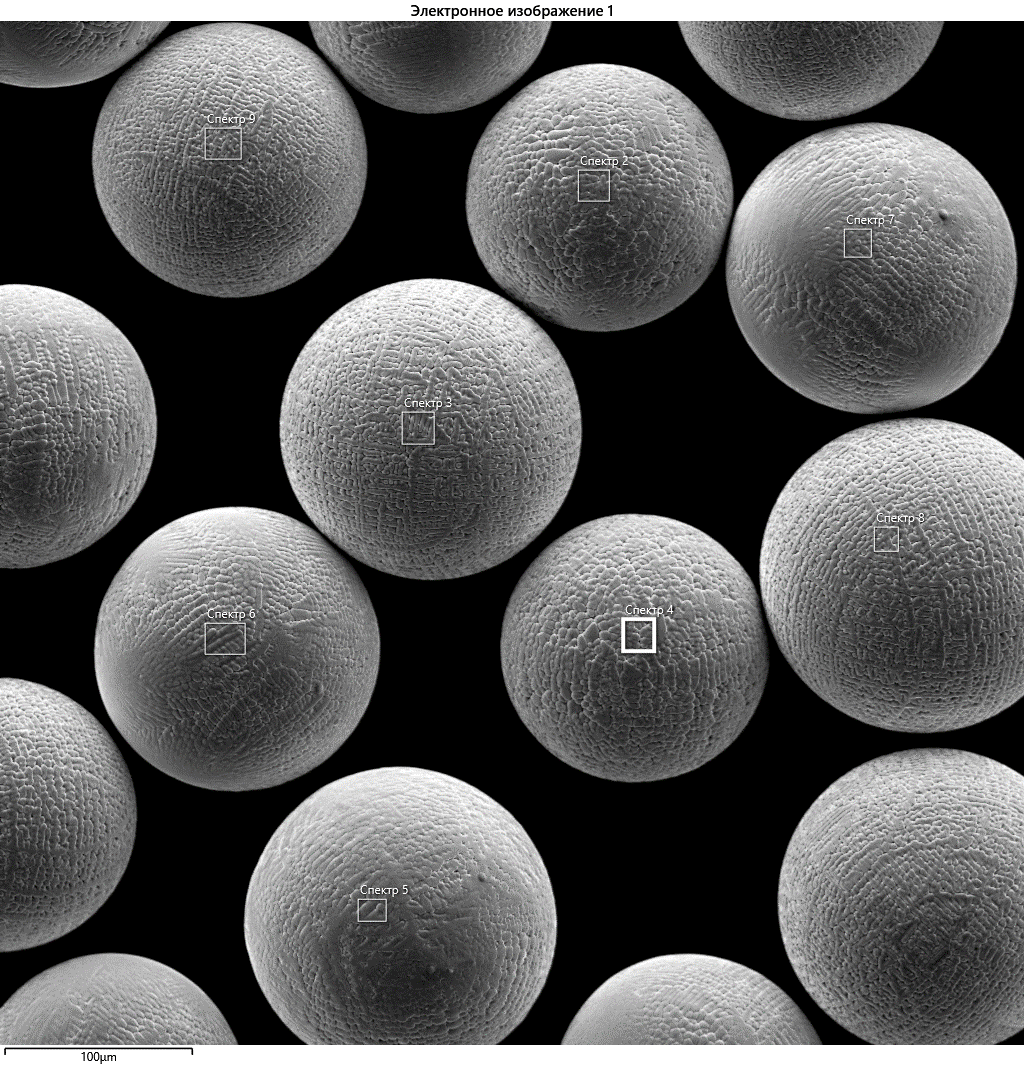

, . , . – , , , . , . . , . – .
. . , , , . – , . : . , . . , , , 30 . , , . . – , , . . , ( , =)).
. , . . , . , , , .
– , . – , . , , . – .
– Insstek, , . . , , .
, :
, – . , , , . insstek , .
. 15 000 , . , , .
Insstek , . .
– :
:
, . .
. , , .
The utilization rate of the material was 93%. We save the customer's money.
Performance. The preparation time for the control program was 8 hours. Growing time - 6.5 more. If you need to change the geometry, in two days the new product will be on the table. No traditional technology can do this.
Conclusion
We briefly figured out what is happening in the core. Ahead is a conversation about materials, equipment, our competitors, an automatic control system, preparation of control programs, target details, economics and a couple of dozen other, no less voluminous things.