Győző Kmethy - CEO and President of the DLMS Association - and Milan Kozole - Chair of the DLMS Association Technical Committee - in their article "Efficiency of DLMS / COSEM for large systems with constrained resources" talk about ways and means of effectively using the DLMS / COSEM stack, allowing Reduce the amount of transmitted data 10 times and reduce the number of information exchanges between the client and the server.
Introduction
DLMS / COSEM is the world's leading standard (IEC / EN 62056, EN 13757) governing the exchange of data with smart devices. Currently it is used mainly in intelligent metering systems. As a rule, such systems consist of a head subsystem that collects data from millions of devices, and also controls these devices using various data transmission media for this purpose.
DLMS / COSEM includes three main components: (1) COSEM object model, which describes the functionality of the end device; (2) DLMS application layer, which defines services for accessing COSEM objects; and (3) communication profiles, which define how these services can be transferred over various media. In addition, DLMS / COSEM is based on a client-server architecture, where the head subsystem acts as a client sending requests to the end device, and the end device acts as a server sending responses to client requests.
Some communication networks and devices implementing DLMS / COSEM have sufficient resources, but DLMS / COSEM is increasingly being used where these resources are limited. The resources of the device may be limited by its ability to process and store data or power from built-in batteries during its entire service life. Communication networks can be limited in the number and length of transmitted data packets, and the limitation of the system can be due to the requirement to meet the specified service levels.
DLMS / COSEM has been designed with an emphasis on efficiency, which allows it to be successfully applied in the resource constrained environments discussed above. As DLMS / COSEM expanded into new applications, ways to improve its effectiveness also evolved.
Ways to Improve DLMS / COSEM Efficiency
DLMS/COSEM , COSEM, DLMS. . 1.
1 – DLMS/COSEM
| COSEM | DLMS |
|---|---|
| NULL-data | |
| compact-array | |
| «Compact data» |
. . BlueBook, COSEM, GreenBook, DLMS.
COSEM , :
-
logical_name, ; -
value, , ; - , , , , , , ..
COSEM, , , , ..
, , , . , , , .
.
( ) . DLMS, . c:
- «Profile Generic»,
buffer, .buffer, /. , : , , ; - «Data Protection», ;
- «Register table», , . , , , , ;
- «Compact data», , ; . .
, , , , . , , , , , . «Profile generic», «Data protection» «Compact data».
NULL-data
NULL-data , , buffer «Profile Generic», . , null-data, . (, , ), (, , ).
, delta-array . .
, long-64-unsigned, 9 ( ), delta-unsigned, 2 , .
.
compact-array
compact-array , . , , , . , .
«Compact data»
«Compact data», , compact_buffer. , . , buffer «Profile generic» «Compact data».
, template_description. template_id. compact_buffer , template_id. compact_buffer .
, .
DLMS – COSEM. , – . .
, / / . , .
WITH-LIST . GET, SET, ACTION, READ, WRITE UnconfirmedWrite. WITH-LIST / , WITH-LIST – , .
ACCESS GET-SET-ACTION, , , /.
DLMS/COSEM . , , , . , , . 1.

1 —
xDLMS APDU, DLMS. APDU , COSEM, .
V.44.
, , , . APDU General Block Transfer . General Block Transfer , .
DLMS/COSEM , . ( ) , / , .
. . . 2.
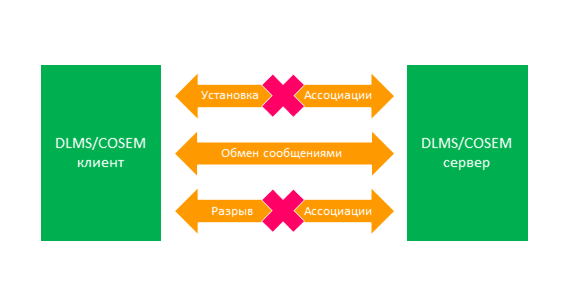
2 —
. , , DLMS, .
, . , .
, , , , . , , .
, .
DLMS/COSEM , . 3:
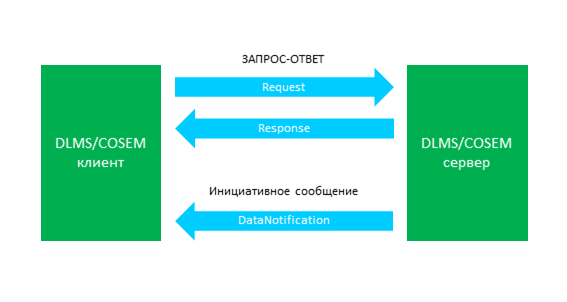
3 — -
- -, (, ) (, ), . :
GET,SET,ACTION,ACCESSRead/Write; - – , . , . , . , , .
DataNotification , « ».
, . , . , , , ..
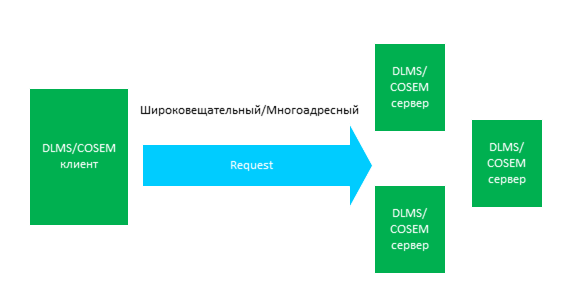
, «», «» . «».
, object_list «Association LN», , «» , 10 , .
