World astrophysics has suffered a bereavement - one of the largest, and perhaps the most famous radio telescope in the world - Arecibo, has been shut down forever and will be dismantled. He acted in films and sent a signal to potential brothers in mind, he searched for aliens in the SETI @ home program and found the first planet outside the solar system, he mapped Venus and passing asteroids, but the metal fatigue took its toll 57 years after construction. The first rope broke in August 2020 of the second rope - in early November, and scientists have adopted yesterday the decision , that the repair is too dangerous for workers and easier to undermine the telescope support themselves, rather than wait for its collapse.

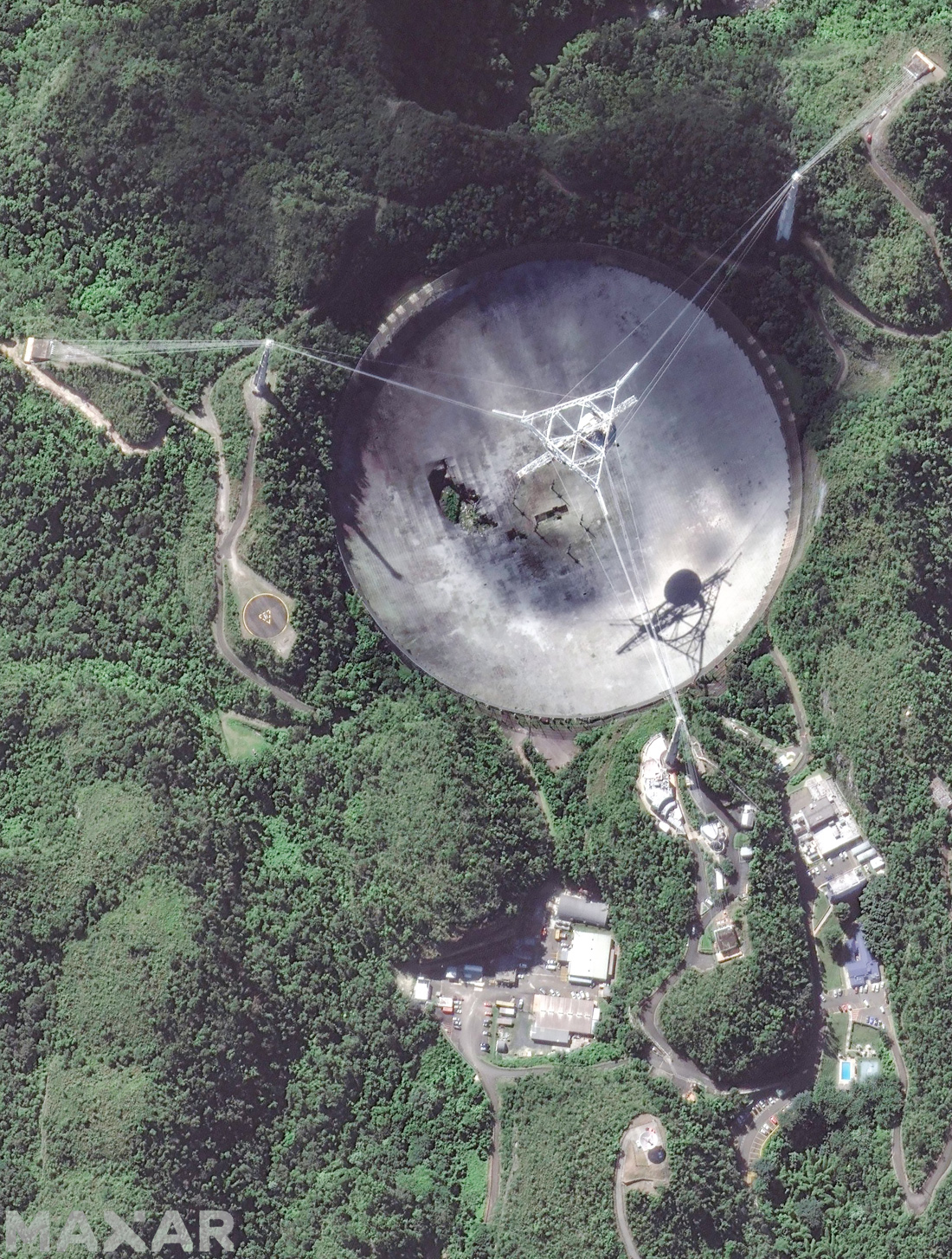
The radio telescope was built by the Americans in 1963 in Puerto Rico, a tropical island in the Caribbean. The place of construction was chosen for a number of reasons, including the geographical latitude, distance from civilization, and the terrain. Arecibo's design differs markedly from many other radio telescopes. Most of the "saucers", which astronomers call the "main mirror", have a pivoting design that allows you to direct the antenna to any point in the visible sky.

This expands their capabilities, but limits their size - the largest swivel antennas are 100 meters in diameter. Arecibo, on the other hand, has a diameter of 305 meters, but its main mirror is laid in the basin of an old karst funnel (sometimes it is mistakenly called an extinct volcano). The Arecibo collecting antenna is stationary relative to the ground, but the feed is moving - the receiving antenna in the focus of the "dish". For this, a platform is suspended above the main mirror at a height of 150 meters.
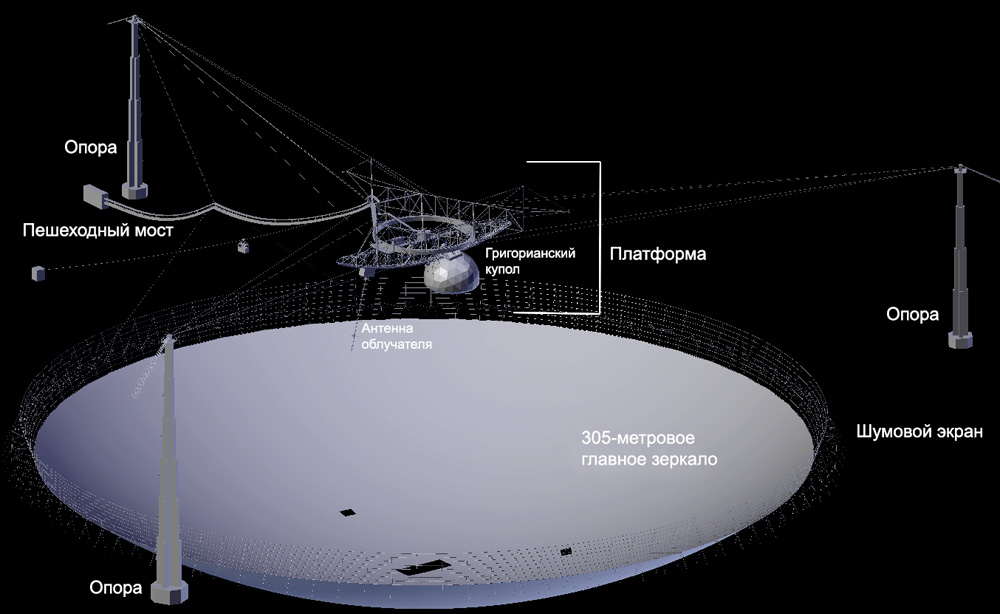
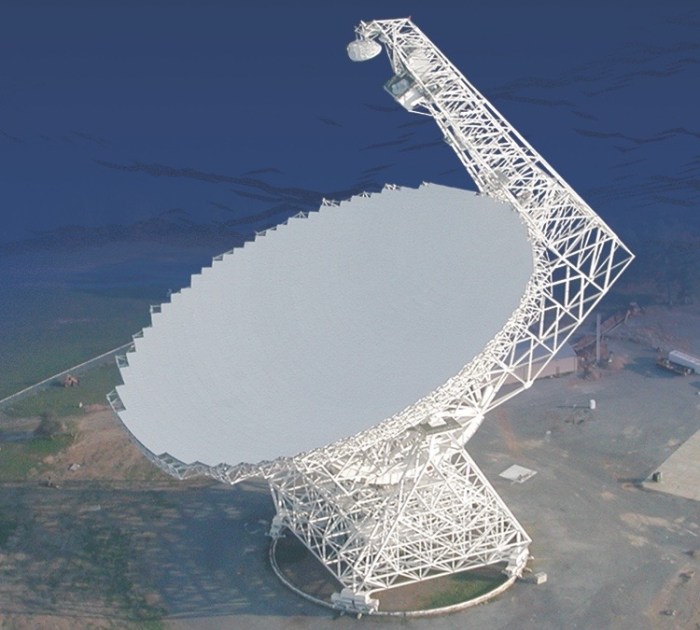
The mobility of the feed allows the radio telescope to cover a part of the sky within a radius of 20 ° around the zenith, but in order to realize this possibility, the main mirror was made spherical, not parabolic. Due to the tilt of the earth's axis, the observatory could observe a significant part of the sky of the northern hemisphere during the year. A similar technical solution was implemented in the Soviet-Russian radio telescope RATAN-600 , although the antenna designs there are noticeably different.
It is curious that now similar two-meter "micro-Arecibo" for schools and institutes are produced by the Russian private company " Lorette ". This arrangement is simple in design, easy to move and install, and convenient for placement on the roof.

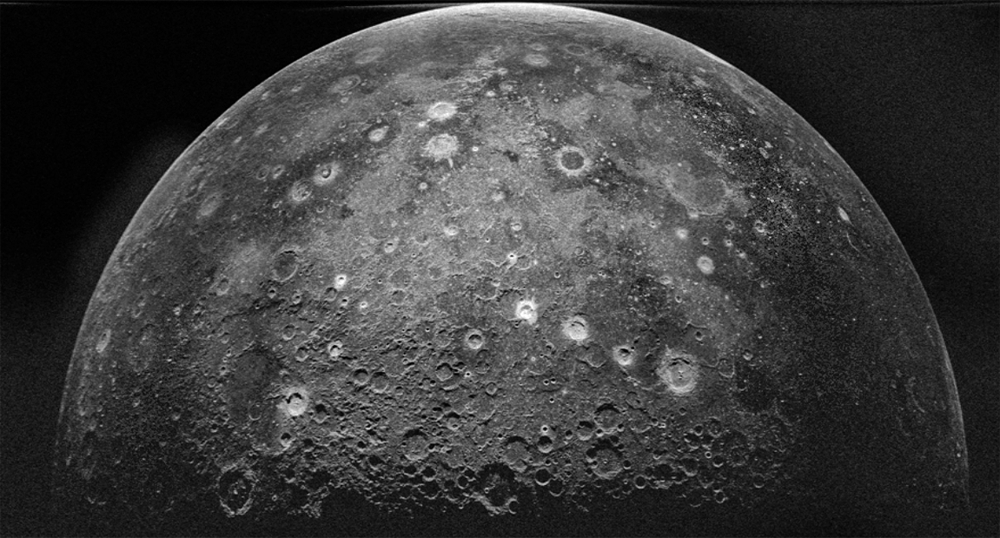
The Arecibo radio telescope, unlike many of its smaller counterparts, was not just an "ear", it could "speak", i.e. work like a radar. This opened up a unique opportunity for scientists - experimental astronomy. For the most part, astronomy is a passive science, scientists create scientific instruments and observe, collect signals and light that come to Earth in a natural way. Arecibo, on the other hand, shone in the radio range itself, and could receive reflected rays. So he managed to map Venus with a resolution of up to 1 km. More precisely, only the Soviet "Venus" and the American Magellan could create maps.
Arecibo was able to see strange deposits near the poles of Mercury, which the Messenger probe later identified as water ice.

Yes, there are water ice deposits on the closest planet to the Sun!
And he did not find anything like this on our moon. Although it is now believed that the subpolar soil of the Moon is relatively rich in water , and this has been confirmed by independent methods, it is probably not glaciers, but small ice crystals distributed in the soil.

In recent years, Arecibo radar has worked extensively in determining distance and even mapping passing near-Earth asteroids. In this case, he practically embodied the idea from which he grew - the prevention of a threat from space. Although sixty years ago, the Soviet Union was considered the source of such a threat, and not the Asteroid Belt.
In some cases, Arecibo did not observe the asteroid itself, but only "illuminated" it, and the reflected radio signals were received by other radio telescopes, for example the 100-meter Green Bank Telescope or the 70-meter Goldstone in the United States. Together they did a great job, and now we know a lot more about asteroids.
For example, that some "space stones" have satellites - smaller stones.

Some are double.
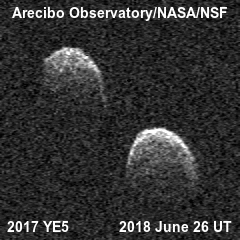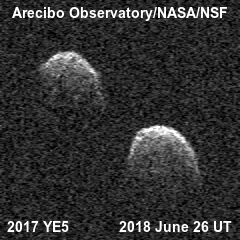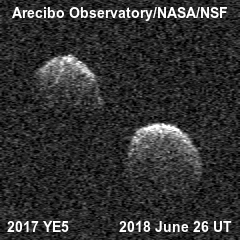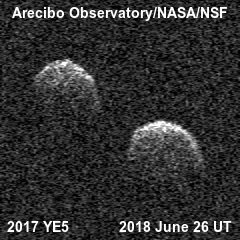
And some are double contact, which is more typical for comet nuclei .

The farthest "shot" Arecibo - the eponymous " message". The addressee of the message, the M13 star cluster, will wait for the signal for 25 thousand years, and then we will have to wait the same amount of time for a response. Therefore, it was more of a beautiful PR than real science, but it provided the observatory's popularity and sustainable funding for decades. Hollywood also helped in popularization, having fallen in love with the futuristic architecture of the telescope. Here, both James Bond defeated the villains, and Jodie Foster listened to alien signals in the science fiction film "Contact".
Arecibo has also proven itself in astrophysics and deep space observation. First, he confirmed a neutron star in the Crab Nebula, and then he was able to "hear" a planet near the pulsar. More precisely, he heard only a pulsar, but the nature of its radio pulses suggested to scientists that there was some kind of constant interference nearby. It turned out to be the first confirmed extrasolar planet. Now exoplanets have already been confirmed by several thousand, and even given the Nobel Prize, though not for the "pulsar", but the usual stellar, and they are looking for by other methods .
Arecibo also worked with our "RadioAstron" in the study of the most distant objects of the observable Universe - quasars. Together with other large telescopes, Arecibo contributed to one of the most important discoveries of RadioAstron - determinedextreme brightness of quasars, which is impossible according to the existing models of these phenomena.

Although the radio telescope remained the largest in its class for a long time, it was regularly modernized. Initially, he did not even have a "plate" - it was a fine mesh hanging from cables over the basin. Then more than 30 thousand aluminum perforated plates were hung on the grid. This expanded the "audibility" range of the radio telescope. To protect against growing interference, a mesh fence was placed around the perimeter of the "dish". In the 90s, a " Gregorian dome " was added to the irradiator, which looked like a large television antenna, - a secondary mirror, which increased the accuracy of received signals, and made it possible to place new equipment, both for receiving and transmitting.
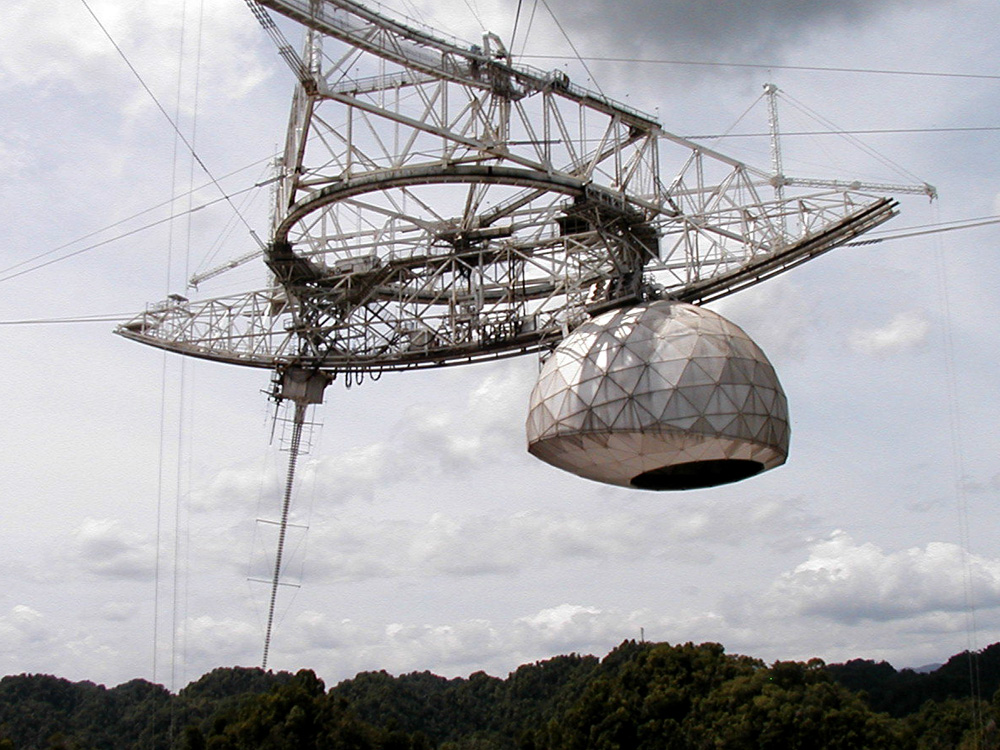

As a result, the capabilities of the observatory have increased, but the load on the cable system has also increased. On three supports not only the mesh base of the "plate" with aluminum sheets was held, but also the 900-ton platform of the irradiator and the "Gregorian dome". But the telescope held on. It was built in a seismically active region, in which tropical cyclones are frequent, so there was a margin of safety. Budgets were handed over first. Financial problems began back in the 2000s. Even then, scientists had to write appealsto politicians about the allocation of funds for the observatory. And here geography played against science - if he were in the continental United States, then its cultural and educational significance would help. And so, all his fame developed the tourism industry of Puerto Rico, and he had to pay for his work from the US budget. Therefore, American officials took advantage of any convenient excuse to cut the budget, while Puerto Rican officials did not have enough funds. NASA also made some contribution, and in total it was possible to recruit both for work and for maintenance of the telescope.
Then the equipment began to fail.
In 2008, the island was shaken by an earthquake of more than 6, and one of the auxiliary cables that held the platform began to unravel on Arecibo. He was quickly fixed with a steel " tire".
In 2017, Puerto Rico was hit by Hurricane Maria, which tore off two-thirds of the rod of the old "TV antenna" feed. She fell on the "plate" and knocked out several segments.
In 2018, the telescope lost its title of largest when China finished building the 500-meter FAST.
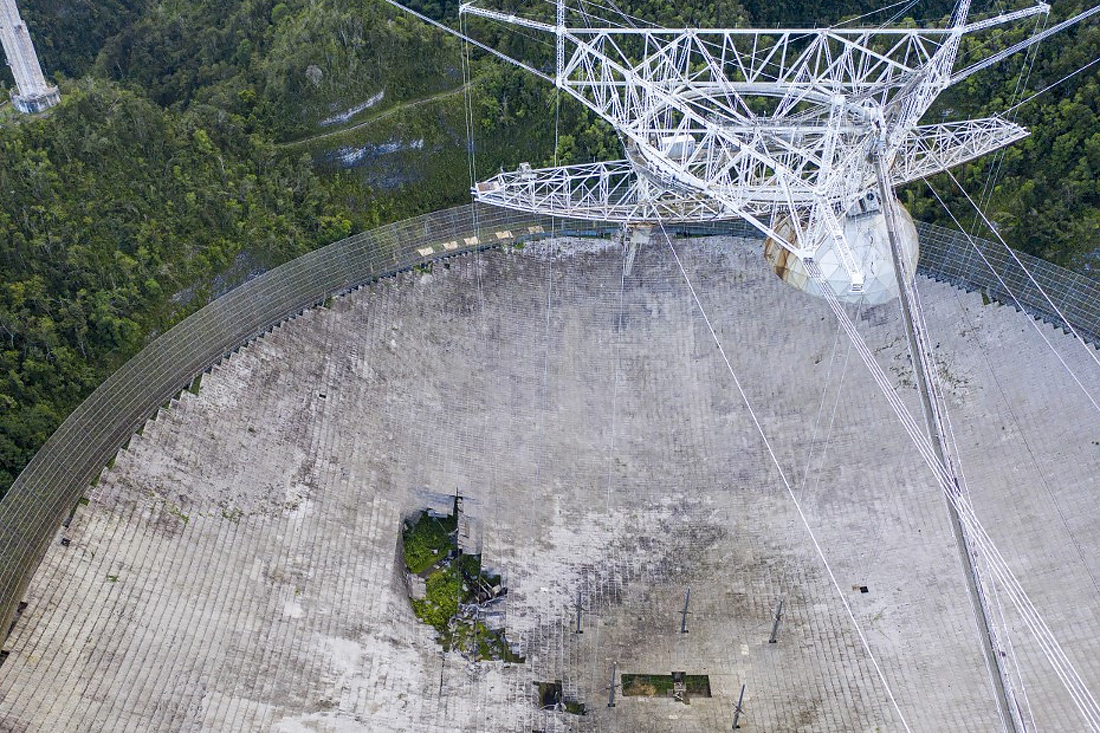
Finally, in August 2020, for no apparent reason, one of the auxiliary cables of the Arecibo platform jumped out of the mount, punched a 30-meter hole in the main mirror, and slightly damaged the Gregorian Dome.

As soon as the scientists were able to assess the damage, and with grief to knock out funds for repairs in half, the second cable broke. And this damage was much more serious than the first. The point is not the size of the hole in the main mirror, but the fact that it was one of six cables on which the whole "plate" hung over the hollow. The remaining ropes crackled and also began to lose fine threads. Moreover, it turned out that the main cable broke in calm weather, under the influence of 60% of the maximum permissible load. Those. if this is not a marriage of a specific cable, but a common property of all of them, then the rest can break in the same way - at any moment and at the flap of the hummingbird's wing.

In such conditions, emergency work is fraught with human casualties, which have so far been avoided. And it's not that Puerto Rico doesn't have enough suicidal adjusters willing to risk triple their salary. It's just that the current situation is a convenient excuse for officials to put a final end to the telescope. Now they are ready to give money only for a quick controlled dismantling. The observatory will remain there, but more as a cultural and educational facility. The value for fundamental science will be reduced to almost zero.
