Satellite Delay on SpaceX Network
Latency (English latency), or ping, is a huge advantage for satellite networks in low orbit over networks in geostationary orbit (GSO, 36 thousand km above the Earth). For GSO, the one-way delay is 600-800 milliseconds and is determined by the time the radio signal reaches the satellite and returns to Earth. Ping is equal to twice the delay time. Large latency not only introduces big problems for such critical Internet applications as VPN tunnels, remote desktop and even telephone conversations, not to mention computer games-shooters, but also corny dramatically reduces the speed of information transmission over the IP protocol in the channel, regardless on its formal physical bandwidth.

It is the low latency (ping) that is a key element for LEO networks and their main advantage over satellites operating in geostationary orbit. It is critical for SpaceX to have a ping of less than 100 milliseconds, which is a criterion for the FCC when considering applications for grants from the budget for connecting subscribers in rural areas (the RDOF program). With a longer delay, it is almost impossible to obtain this grant. If we talk about the amount of delay, then for the subscriber it is formed from the delay in the satellite network (between the gateway and the subscriber terminal) and the delay in the terrestrial network - from the gateway to the NCC of the Starlink network - the traffic exchange point and the site the subscriber needs.
The delay in a satellite segment consists of three components:
- Delay in outer space (there is a delay of 3-4 milliseconds),
- Hardware delay when modulating and demodulating IP traffic into a radio signal (this is 5-20 milliseconds),
- Delay in NCC assignment of a place in a frame (superframe) for traffic transmission from a gateway / terminal. For a number of modes of operation, for example, in the case of using frequencies in the mode of a dedicated channel, this delay can be equal to zero. For time division multiple access (TDM) modes, this delay can be tens of milliseconds.
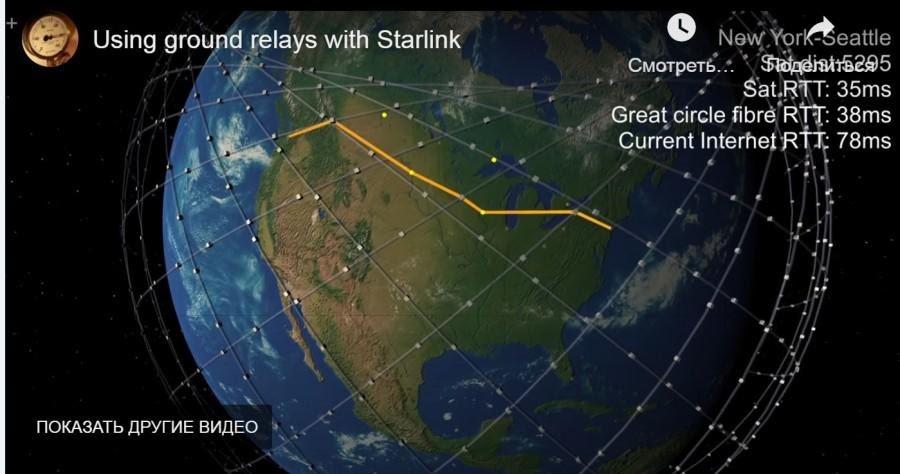
In connection with the above, the assumptions of some authors that the transfer of information for trading on the stock exchange in the Starlink network can be faster than in terrestrial optical networks, due to the use of several hops via satellite, are unequivocally erroneous - due to the accumulation of hardware error upon landing on the gateway and a new ascent to the satellite.
On September 29, 2020, SpaceX sent a letter to the FCC, in which it cited the data obtained during the closed beta testing of subscriber terminals in August-September 2020. The letter contains the following schedule for a weekly testing of a group of 30 terminals, with file transfers within 15 seconds. More than 1 million delay time measurements have been made.

As you can see from the graph, in 95% of cases the delay was less than 42 milliseconds, and in 50% less than 30 ms, which perfectly suits the requirements of the RDOF program, but can hardly be used for organizing high-frequency exchange trading ...
RF spectrum access techniques
Among the methods of access of the subscriber terminal to the radio frequency spectrum on the satellite, the following are distinguished:
- With permanent assignment of the frequency band to the terminal.
- Demand Assigned Multiple Access.
The first method is much simpler in hardware implementation, while a certain part of the frequency spectrum on the satellite is assigned to each terminal.

Figure: Spectrogram of the use of the frequency resource in the mode of a dedicated channel of the SCPC - Single Channel per Carrier type.
The advantage of this method is the speed of establishing a connection - as soon as the terminal antenna is pointing at the satellite, information transmission to the gateway can begin. The disadvantage of this method is that the satellite segment is used irrationally, since most of the time the subscriber terminal does not transmit information, the efficiency (or utilization rate) of such a channel rarely exceeds 5%. So, for example, if the Starlink network service plan promises a subscriber a speed of 100/40 Mbit / s, then the maximum number of subscribers when using the dedicated channel mode will be 6 Gb / 100 Mbit = 60 subscribers, which makes the network deeply unprofitable.
The second principle is the access of several subscribers to one frequency channel with time or frequency division.
Methods with group access (TDMA - Time Division Multiple Access, FDMA - Frequency Division Multiple Access, etc.), despite the complexity of their implementation and the requirements of synchronization in sending packets from subscriber terminals, allow several tens of times more efficient use of the frequency range of the network and transmit tens of times more information (subscriber traffic).

Figure: Scheme of access to a satellite frequency resource using TDM / TDMA group access.
Another advantage of such systems is that it is possible to vary the data transfer rate to a separate terminal in a wide range - the system allows you to redirect almost the entire bandwidth of the gateway station to one subscriber terminal. However, this significantly increases the delay in transmission, because the Network Control Center (NCC) is responsible for assigning the time and place in the frame for sending the packet by the subscriber terminal, and first the information that the subscriber terminal X wants to go online and start transmission should go to The NCC, to be processed there, must determine the presence of free slots in the frame on the nearest satellite (and if it is fully loaded, on another one), and information about free frequencies will be transmitted to the gateway, and from it to the subscriber terminal.Only after that they can start transmitting, and on this frequency the subscriber terminal will transmit only during the time it is in a mini-spot with a given polarization and frequencies, that is, no more than 6-7 seconds, after which the terminal will fall into the zone of another mini-beam, with different frequencies and / or polarizations. It is optimal if information about the volume of traffic required by the subscriber is reported in advance to the NCC, and the latter will be able to book slots in the frame for this terminal in all mini-spots that the subscriber terminal will fall into when the satellite moves over the subscriber's house. If there is such a roadmap in the memory of the subscriber terminal, it will be possible to provide seamless communication and continuous video viewing on the Internet.while it is in a mini-spot with a given polarization and frequencies, that is, no more than 6-7 seconds, after which the terminal will fall into the zone of another mini-beam, with different frequencies and / or polarization. It is optimal if information about the volume of traffic required by the subscriber is reported in advance to the NCC, and the latter will be able to book slots in the frame for this terminal in all mini-spots that the subscriber terminal will fall into when the satellite moves over the subscriber's house. If there is such a roadmap in the memory of the subscriber terminal, it will be possible to provide seamless communication and continuous video viewing on the Internet.while it is in a mini-spot with a given polarization and frequencies, that is, no more than 6-7 seconds, after which the terminal will fall into the zone of another mini-beam, with different frequencies and / or polarization. It is optimal if the information about the volume of traffic required by the subscriber is reported in advance to the NCC, and the latter will be able to book slots in the frame for this terminal in all mini-spots that the subscriber terminal will fall into when the satellite moves over the subscriber's house. If there is such a roadmap in the memory of the subscriber terminal, it will be possible to provide seamless communication and continuous video viewing on the Internet.will be notified in advance to the NCC, and the latter will be able to book slots in the frame for this terminal in all mini-spots that the subscriber terminal will fall into when the satellite moves over the subscriber's house. If there is such a roadmap in the memory of the subscriber terminal, it will be possible to provide seamless communication and continuous video viewing on the Internet.will be notified in advance to the NCC, and the latter will be able to book slots in the frame for this terminal in all mini-spots that the subscriber terminal will fall into when the satellite moves over the subscriber's house. If there is such a roadmap in the memory of the subscriber terminal, it will be possible to provide seamless communication and continuous video viewing on the Internet.
Naturally, this increases the complexity of the equipment of gateways, subscriber terminals and the entire network, requiring continuous control from the Control Center, maintaining synchronous operation of all gateways and subscriber terminals.
For general reasons, the first dedicated channel method is more suitable for organizing communications for military / government tasks, and the second is for providing services to ordinary commercial customers. There is currently no information on what method of access to the space segment and its details will be used in the Starlink system. However, given that the original Starlink project was carried out by natives of Broadcom, which specializes in terrestrial broadband and 5G, the access protocols can be taken from them.
On September 29, SpaceX sent a letter to the FCC, countering comments from ViaSat about its application to change the StarLink network, this letter for the first time provides data on the format of the satellite channel on the line to the subscriber terminal:
Until recently, the network had been grouping user terminals in groups of 8 per radio-frame, instead of the 20 terminals per radio-frame the system supports. This operating choice is to support on-going optimization and testing of the network but has the consequence of introducing 2.5 times longer delay between radio-frames for a given user in a fully loaded cell, corresponding to the smaller group sizes. Importantly, this software feature has just been enabled and is specifically designed to optimize speeds in highly populated cells, increasing throughput by approximately 2.5 times.
Based on this paragraph, we can conclude that the channel uses the TDM access method.
Information about additions to previously published materials
...
1. 14/12/20 , 14 2020 . — SpaceX , 50-
8. " 14/11/20 Starlink RIDGELINE MOUNT
8. " 14/11/20 Starlink RIDGELINE MOUNT
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 1. Birth of the project
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 2. Starlink Network
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 3. Ground complex
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 4. Subscriber terminal
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 5. Starlink constellation status and closed beta
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 6. Beta testing and service for subscribers
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 7. Starlink Network Bandwidth and RDOF Program
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 8. Installation and activation of the subscriber terminal
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 9. Service in non-US markets
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 10. Starlink and the Pentagon
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 11. Starlink and Astronomers
- Everything about the Starlink Satellite Internet project. Part 12. Starlink and space debris problems