
In October, traditionally, GPT-3 is again in the spotlight. There are several news related to the model from OpenAI - good and not so good.
OpenAI and Microsoft deal
We'll have to start with a less pleasant one - Microsoft took over exclusive rights to GPT-3. The deal predictably sparked outrage - Elon Musk, founder of OpenAI and now a former member of the company's board of directors, said that Microsoft had essentially taken over OpenAI.
The fact is that OpenAI was originally created as a non-profit organization with a high mission - not to allow artificial intelligence to be in the hands of a separate state or corporation. The founders of the organization called for the openness of research in this area, so that technology works for the benefit of all mankind.
Microsoft, in their defense, says they are not going to restrict access to the model API. Thus, in fact, nothing has changed - before that OpenAI also did not publish the code, but if earlier even partner companies were allowed to work with GPT-3 only through the API, now Microsoft has exclusive rights to use.
ruGPT3 from Sberbank
Now to more pleasant news - researchers from Sberbank have published a model in open access that repeats the GPT-3 architecture and is based on the GPT-2 code and, most importantly, is trained in the Russian-language corpus.
A collection of Russian literature, Wikipedia data, snapshots of news and question-and-answer sites, materials from the portals Pikabu, 22century.ru banki.ru, Omnia Russica were used as a dataset for training. The developers have also included data from GitHub and StackOverflow to teach how to generate and program code. The total amount of cleaned data is over 600 GB.
The news is definitely good, but there are a couple of caveats. This model is similar to GPT-3, but not. The authors themselves admitthat it is 230 times smaller than the largest version of GPT-3, which has 175 billion weights, which means that it cannot exactly repeat the benchmark results. That is, do not expect this model to write texts indistinguishable from journalistic texts.
It is also worth considering that the described GPT-3 architecture may differ from the real implementation. You can say for sure only after reading the training parameters, and if before the weights were published with a delay, then in the light of recent events they can not be expected.
The fact is that the project budget depends on the number of training parameters, and according to experts, GPT-3 training cost at least $ 10 million. Thus, only large companies with strong ML specialists and powerful computing resources can reproduce the work of OpenAI.
State of AI 2020 Report
All of the above confirms the conclusions of the third annual report on the current state of affairs in the field of machine learning. Nathan Benaich and Ian Hogarth, investors who specialize in AI startups, have published a detailed presentation that covers technology, human resources, industrial applications and legal intricacies.
Curiously, as many as 85% of research is published without source code. If commercial organizations can be justified by the fact that code is often woven into the infrastructure of projects, then what about research institutions and non-profit companies like DeepMind and OpenAI?
It is also said that an increase in datasets and models leads to an increase in budgets, and given that the field of machine learning is stagnating, each new breakthrough requires disproportionately large budgets (compare the size of GPT-2 and GPT-3), which means that they can afford it only large corporations.
We advise you to familiarize yourself with this document, as it is written concisely and clearly, well illustrated. Also, four forecasts for 2020 from the last report have already come true.
We will not exaggerate further, there are still good stories, otherwise this collection would not exist.
Open multilingual models from Google and Facebook
mT5
Google has published the source code and dataset of the T5 family of multilingual models. Due to the hype associated with OpenAI, this news went almost unnoticed, despite the impressive scale - the largest model has 13 billion parameters.
For training, a dataset of 101 languages was used, among which Russian is in second place. This can be explained by the fact that our great and mighty is the second most popular place on the web.
M2M-100
Facebook is also not far behind and has laid out a multilingual model , which, according to their statements, allows directly translating 100x100 language pairs without an intermediate language.
In the field of machine translation, it is customary to create and train models for each individual language and task. But in the case of Facebook, this approach is not able to scale effectively, as users of the social network publish content in more than 160 languages.
Typically, multilingual systems that handle multiple languages at once rely on English. The translation is mediated and imprecise. Bridging the gap between source and target languages is difficult due to lack of data, as it can be very difficult to find a translation from Chinese to French and vice versa. To do this, the creators had to generate synthetic data by reverse translation.
The article provides benchmarks, the model copes with translation better than analogs that rely on English, as well as a link to the dataset .

Advances in video conferencing
In October, some interesting news from Nvidia appeared at once.
StyleGAN2
First, we posted updates for StyleGAN2 . The low-resource architecture of the model now provides improved performance on datasets with less than 30 thousand images. The new version introduces support for mixed precision: training accelerated ~ 1.6x times, inference ~ 1.3x times, GPU consumption decreased ~ 1.5x times. We also added an automatic selection of model hyperparameters: ready-made solutions for datasets of different resolutions and a different number of available graphics processors.
NeMo
Neural Modules is an open source toolkit that helps you quickly create, train, and tune conversational models. NeMo consists of a core that provides a single "look and feel" for all models and collections, consisting of modules grouped by scope.
Maxine
Another announced product is likely to use both of the above technologies internally. The Maxine video calling platform combines a whole zoo of ML algorithms. This includes the already familiar resolution improvement, noise elimination, background removal, but also gaze and shadow correction, image restoration based on key facial features (i.e. deepfakes), subtitle generation and translation of speech into other languages in real time. That is, almost everything that previously met separately, Nvidia combined into one digital product. You can now apply for Early Access.
New developments of Google
Due to the quarantine, this year there is a real race for leadership in the field of video conferencing. Google Meet shared a case study of creating their algorithm for high-quality background removal based on the framework from Mediapipe (which can track the movement of the eyes, head and hands).
Google has also launched a new feature for the YouTube Stories service on iOS that improves speech quality. This is an interesting case , because many times more enhancers are available for video than for audio. This algorithm tracks and records correlations between speech and visual markers, such as facial expressions, lip movements, which it then uses to separate speech from background sounds, including voices from other speakers.
The company also presented a new attemptin the field of sign language recognition.
Talking about video conferencing software, it is also worth mentioning the new deepfake algorithms.
MakeItTalk
Recently, the code of the algorithm that animates the photo, relying solely on the audio stream, was published in the open access . This is noteworthy, since usually deepfake algorithms take video as input.
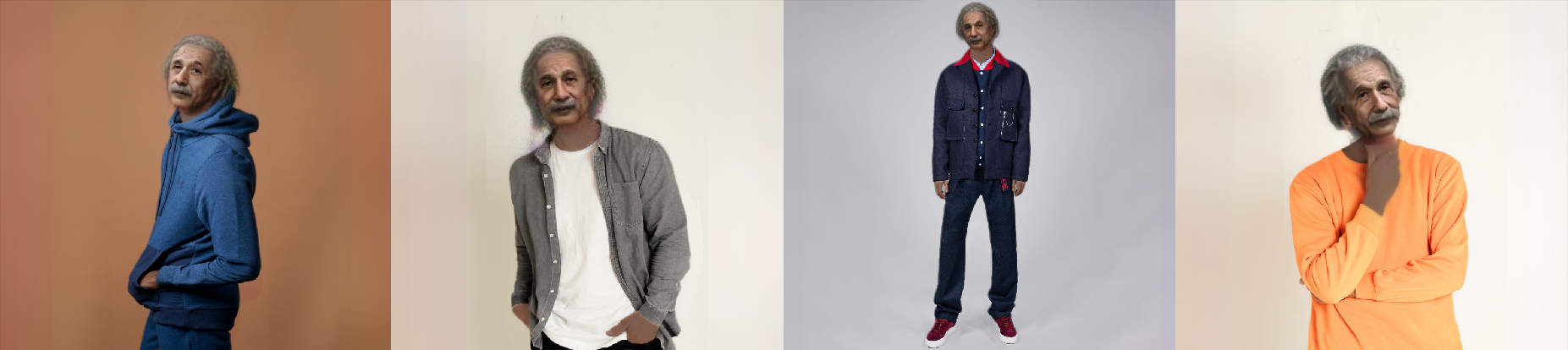

BeyondBelief
The new generation of deepfake algorithms sets itself the task of replacing not only the face, but the whole body, including hair color, skin tone and figure. This technology is primarily going to be applied in the field of online shopping, so that you can use photos of goods provided by the brand itself, without having to hire individual models. More applications can be seen in the video demo . So far, it looks unconvincing, but soon everything may change.
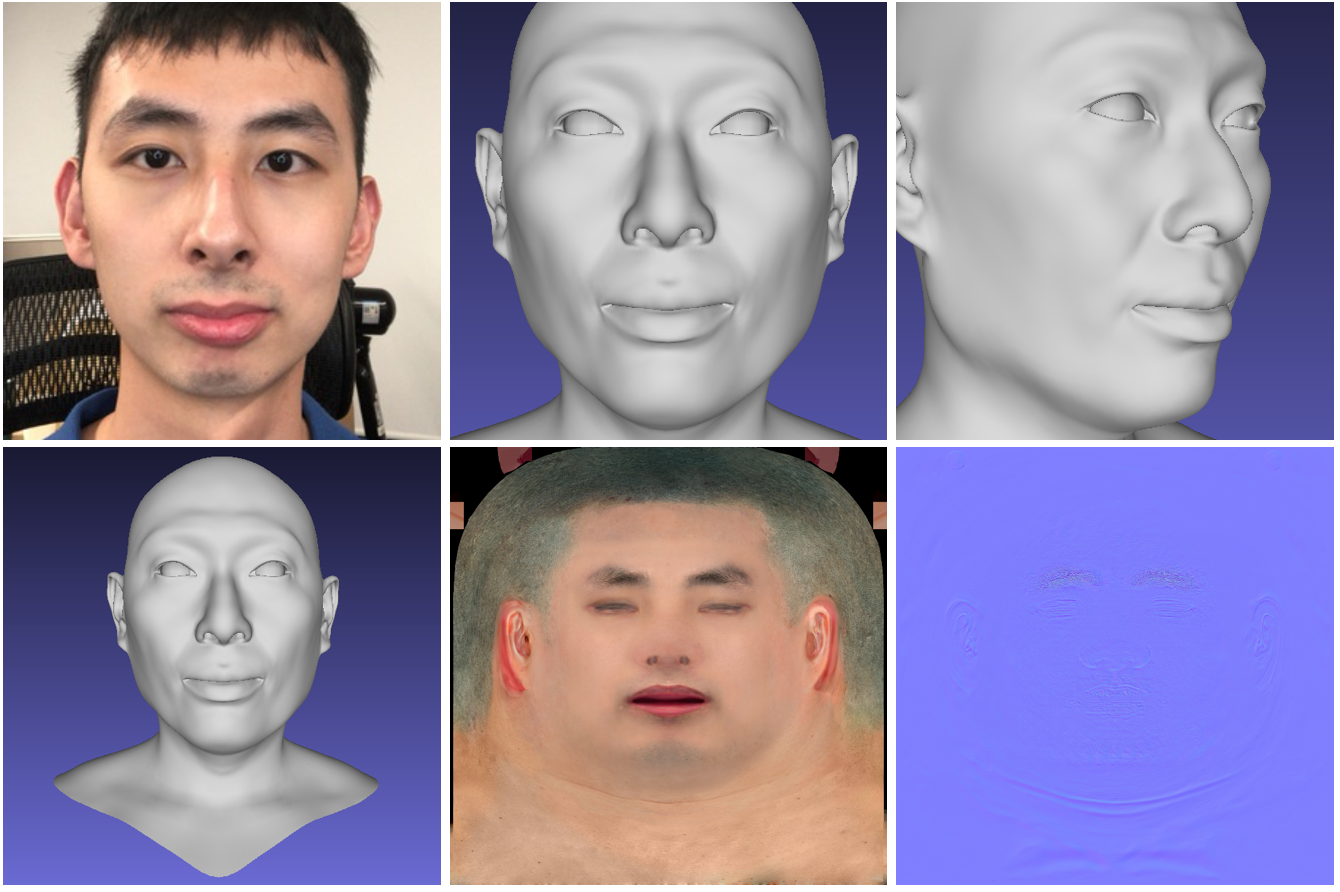
Hi-Fi 3D Face
The neural network generates a high-quality 3D model of a person's face from photographs. The model receives a short video from a regular RGB-D camera as input, and at the output it gives a generated 3D model of the face. The project code and 3DMM model are publicly available .

SkyAR
The authors presented an open source technology to replace the sky with video in real time, which also allows you to control the styles. Weather effects such as lightning can be generated on the target video.
The pipeline model solves a number of tasks in stages: the grid mattes the sky, tracks moving objects, wraps and recolours the image to match the color scheme of the skybox.
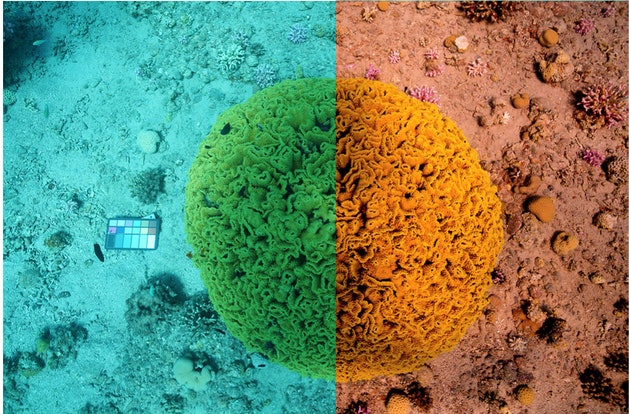

Sea-thru
The tool solves the extraordinary task of restoring true colors in underwater images. That is, the algorithm takes into account the depth and distance to objects in order to restore lighting and remove water from images. So far, only datasets are available.
MIT model for diagnosing Covid-19
In conclusion, we will share an interesting case on a relevant topic - MIT researchers have developed a model that distinguishes asymptomatic patients with coronavirus infection from healthy people using forced cough recordings.
The model has been trained on tens of thousands of audio tapes of cough samples. According to MIT , the algorithm identifies people who have been confirmed to have Covid-19 with an accuracy of 98.5%.
Government authorities have already approved the creation of the application. The user will be able to download an audio recording of his cough and, based on the result, determine whether it is necessary to take a full analysis in the laboratory.
That's all, thanks for your attention!