
Cyber threat landscape
When making forecasts for 2020, we could not have foreseen how the new reality that brought down the global economy would affect our lives. However, now we can take stock of the first half of the year and show how the cyber threat landscape has changed during this time.
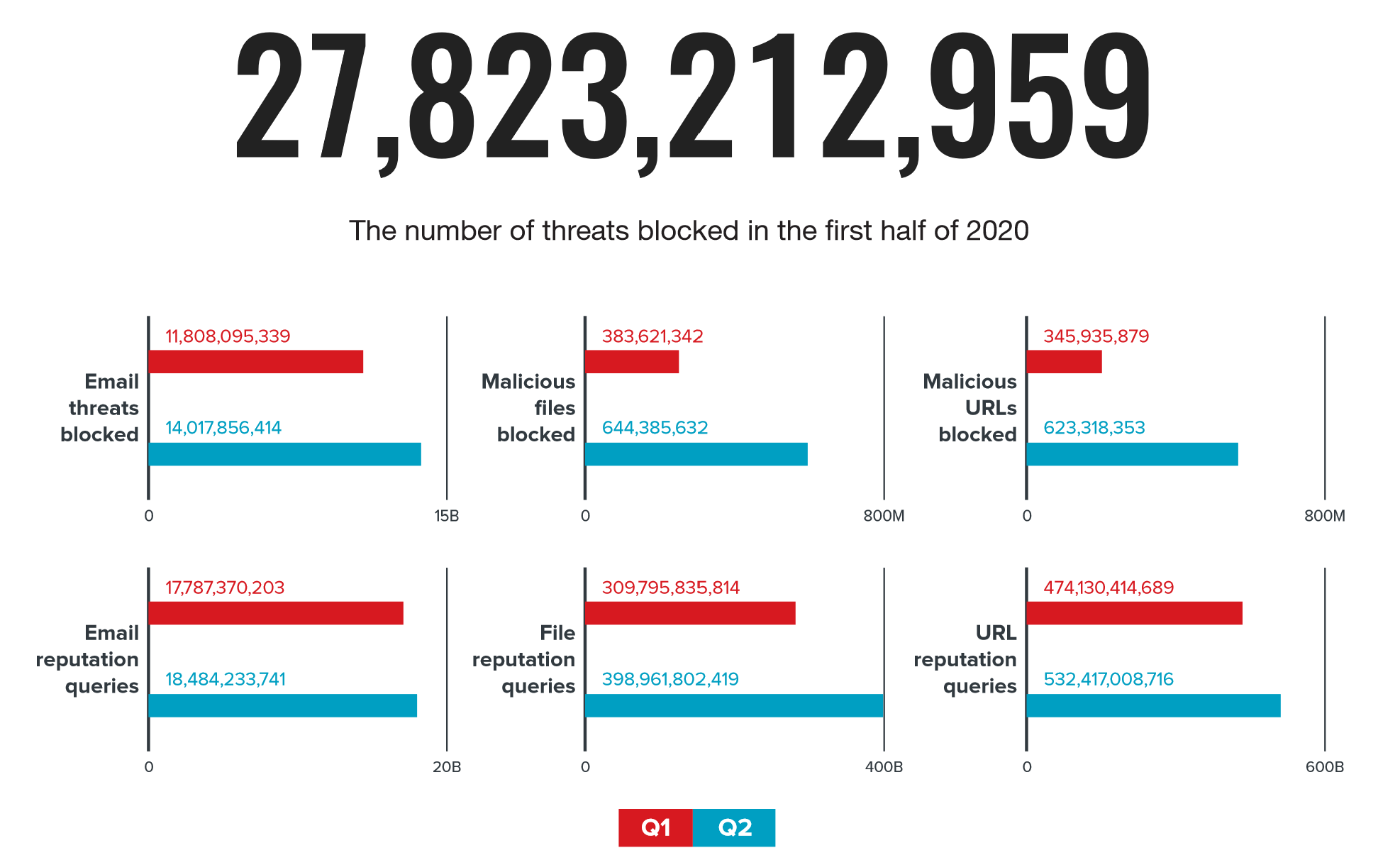
The number of threats blocked by Trend Micro Smart Protection Network in the first half of 2020. Source here and below: Trend Micro
In the first half of 2020, Trend Micro's security solutions blocked more than 27 billion fraudulent emails containing malicious attachments and phishing links. The second quarter saw a significant increase in the number of malicious messages compared to the beginning of the year.
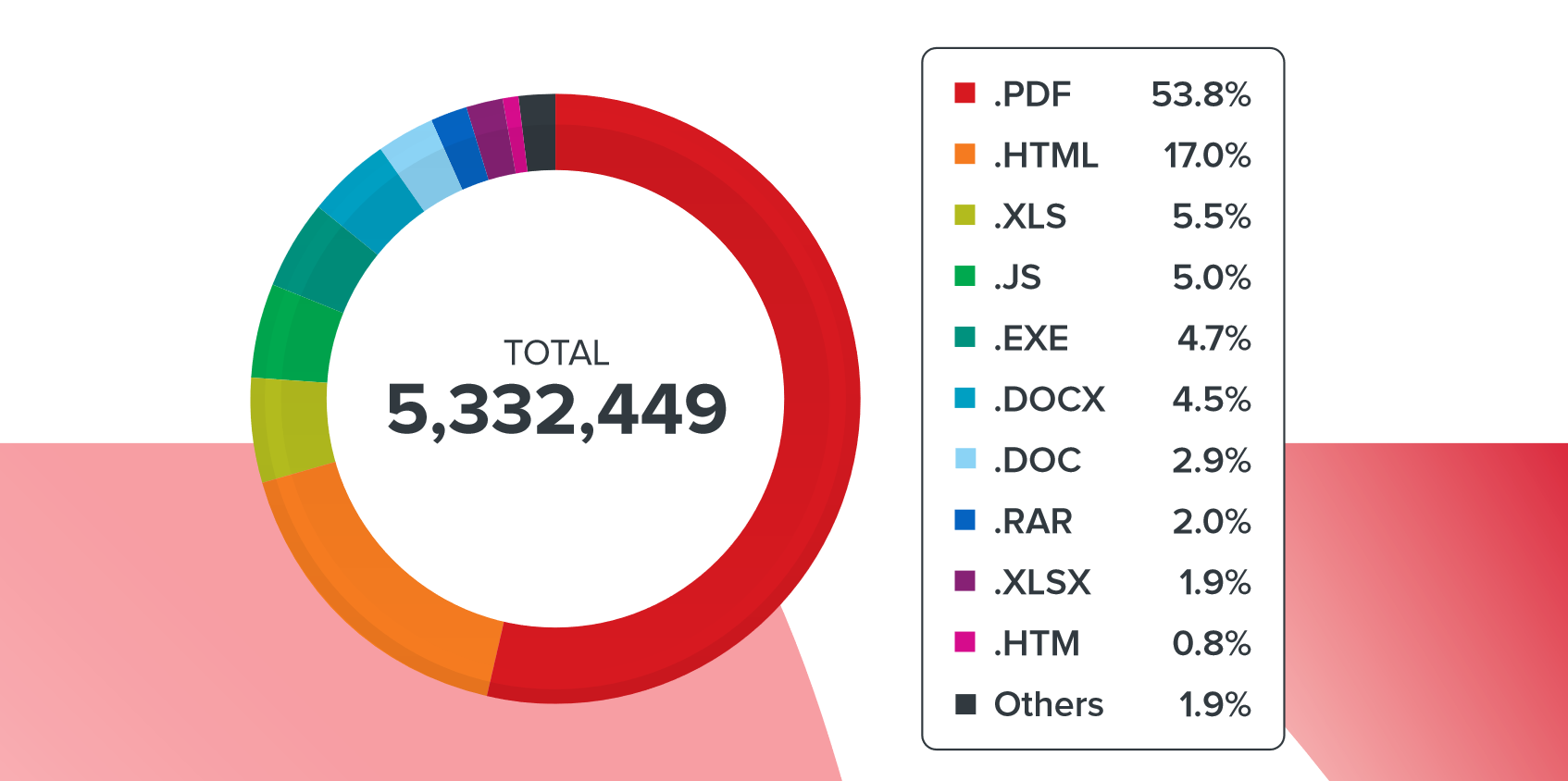
Types of malicious attachments in spam campaigns in the first half of 2020
PDF files became the most popular type of malicious attachments in the first half of 2020, accounting for over 50% of mailings. The second most popular attachment type was HTML files. About six percent of emails contained XLS attachments, slightly less popular were JavaScript files, executables, and MS Word documents.
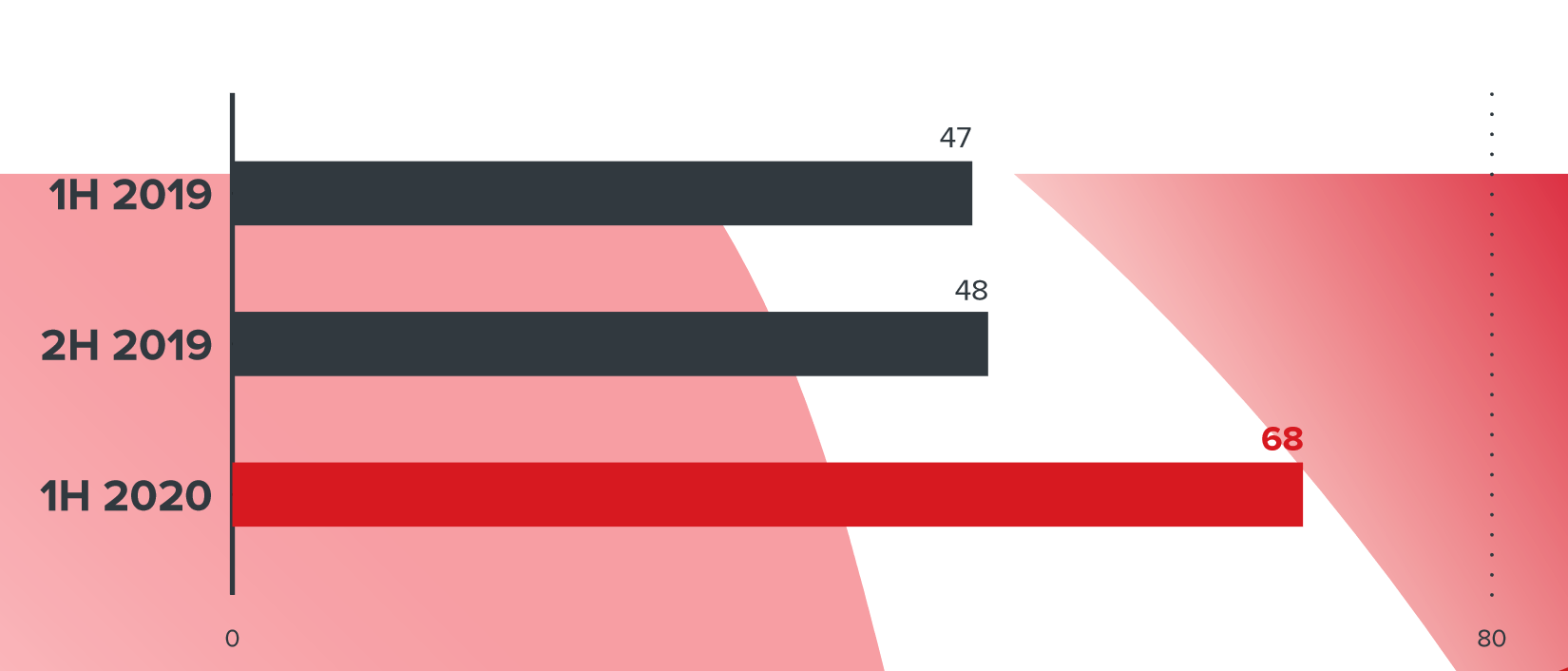
The number of ransomware ransomware in the 2019 and 2020 campaigns
A characteristic feature of 2020 was the growing popularity of ransomware ransomware. Compared to 2019, their number increased by 45% - from January to June of this year, 68 new families of this type of malware were discovered.

Number of mobile malware samples detected over six months
The number of mobile threats also continues to grow, with campaigns becoming more sophisticated. For example, at the end of March, we discovered a fraudulent cyberattack dubbed Operation Poisoned News. It was a watering hole attack against iOS users in Hong Kong. Users of iOS devices received links to news on various forums in social networks and messengers. These links did lead to relevant news sites, but contained hidden iframes with malicious code that exploited vulnerabilities in iOS 12.1 and 12.2. The attacks infected devices with LightSpy, which allowed attackers to execute commands and manipulate files on devices.
Advertising fraud remains the most popular type of attacks on mobile users. Malicious applications on Google Play disguise themselves as useful utilities, and after installation, they display ads to the user and perform other unwanted actions, including stealing bank card data and personal data of the user.

Change in the number of BEC attacks in 2019-2020 on the graph
Another characteristic feature of 2020 is the increase in the number of attacks aimed at compromising business correspondence (Business Email Compromise, BEC). Compared to the second half of 2019, the number of BEC campaigns increased by 19%.
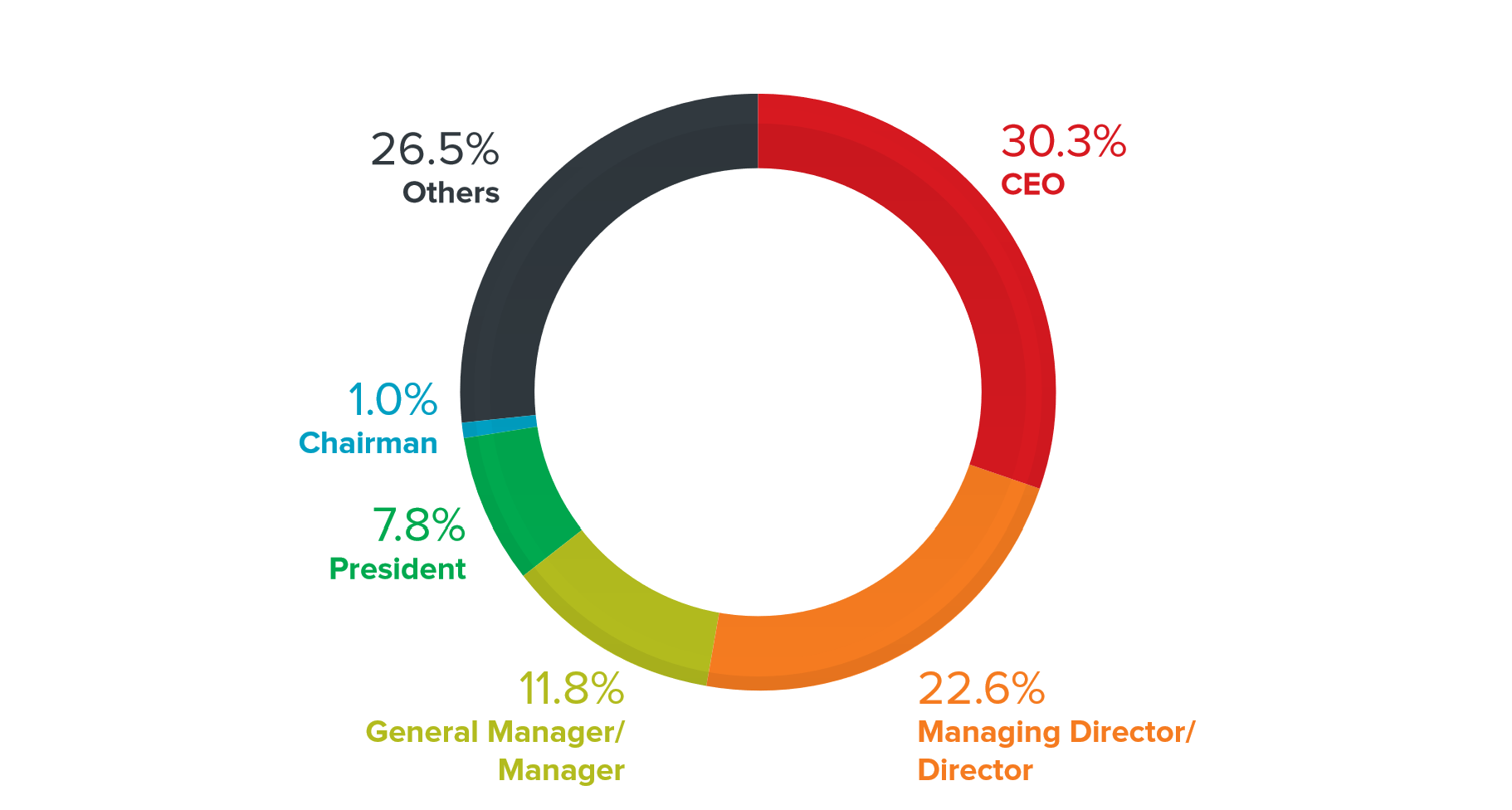
The most popular target for BEC attacks was the CEO of the company. This category of employees accounts for 30% of all incidents
It is curious that the number of letters “from the CEO” has decreased: in 2019, the share of such letters was 41%. Scammers may be experimenting with other jobs to gauge their effectiveness.
Naturally, the most in-demand people are people related to finance, for example, financial managers and CFOs.
Growth in COVID-19-branded attacks
Between January and June 2020, the Trend Micro Smart Protection Network (SPN) identified nearly 9 million COVID-19 threats. These threats consisted of e-mail messages containing links and malicious files, directly or indirectly exploiting the topic of the pandemic. This could be, for example, informer applications or notifications about delays in the provision of services due to a virus.

The number of COVID-branded attacks and their distribution by country
The leader in the number of such threats - 38% of cases - was the United States. The three "leaders" also included Germany with 14.6% and France with 9.2%. Most of the cases detected were in April, which corresponds to the peak incidence in many countries.
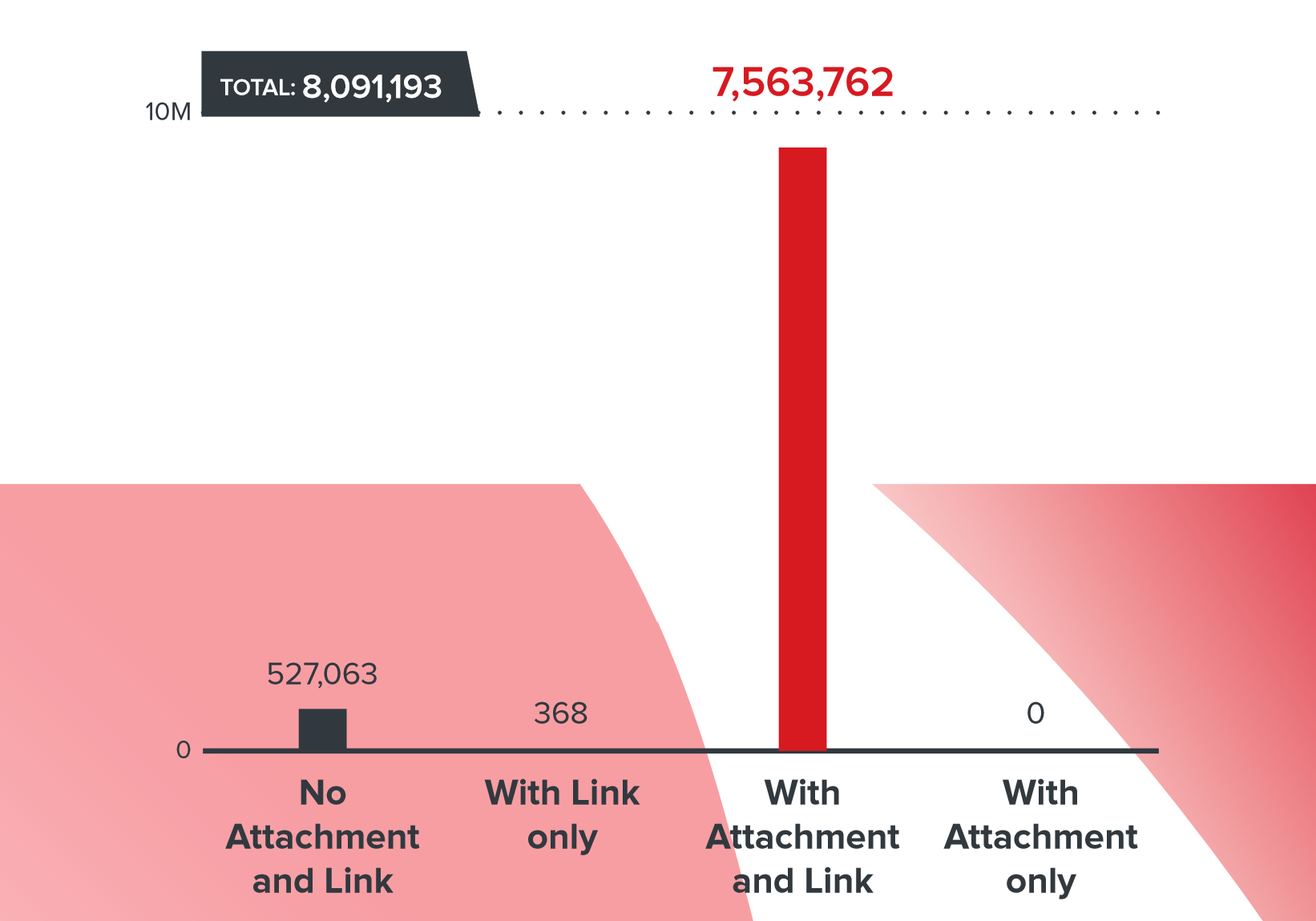
Distribution of types of malicious content in fraudulent emails in COVID-19 campaigns
The vast majority of email threats - 93.5% - contained both a malicious attachment and a malicious link. There were significantly fewer letters containing a link or a file.
The COVID-19 theme was also widely used in BEC attacks. The effectiveness of these shenanigans was reinforced by the fact that the shift to remote work made it difficult to track communications between employees and organizations.
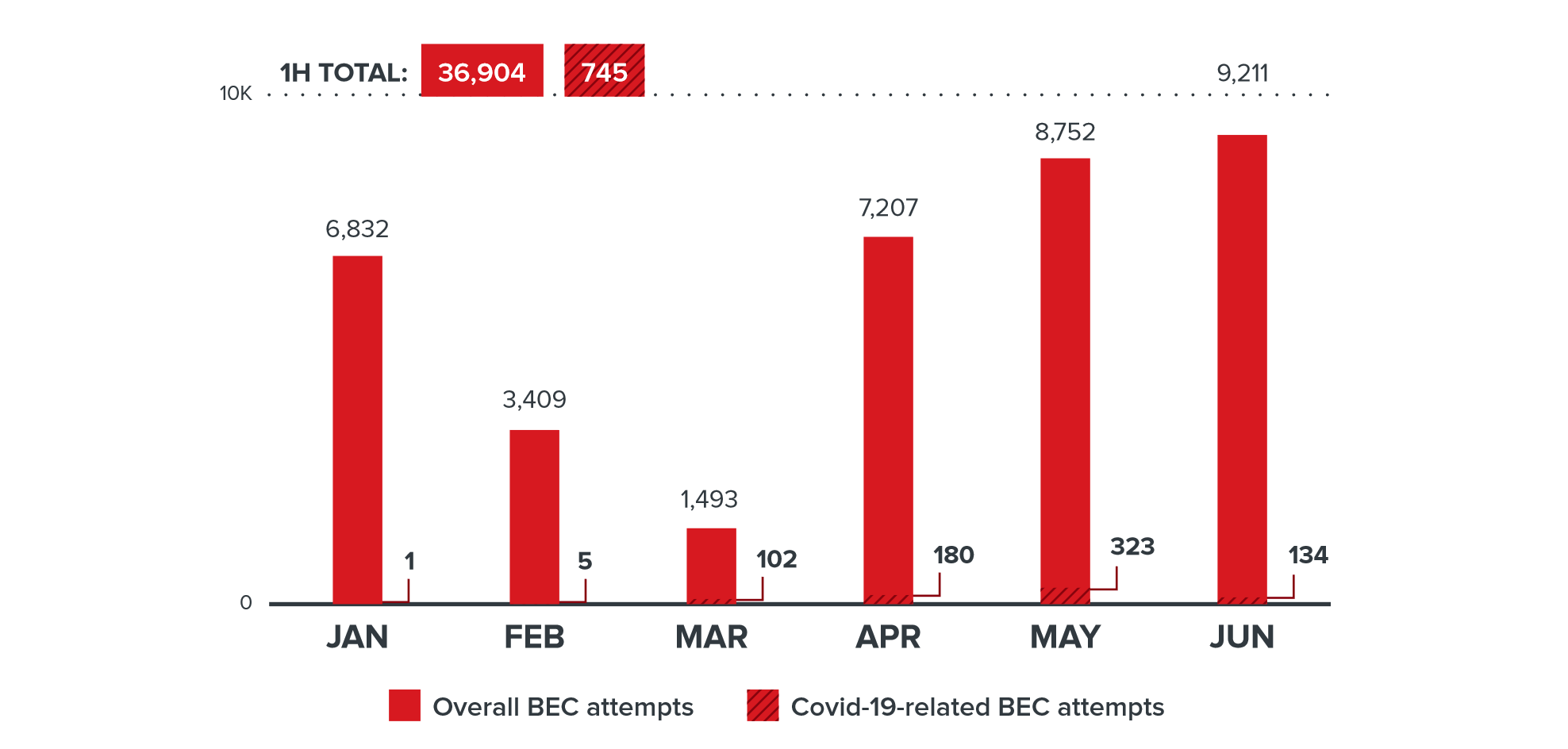
The number of BEC campaigns related to COVID-19
For example, during one of the BEC attacks, the criminals sent a notification to the employees of a potential victim about the change of bank in connection with the pandemic, indicating the recipient's account "mule" in Hong Kong.
Attempts to navigate to malicious sites related to COVID-19 grew throughout the year, peaking in April. Most of these sites have been used for some kind of pandemic scam, for example:
- applications that allegedly protected their users from coronavirus infection, but instead added the victim's device to the botnet;
- sale of non-existent WHO-approved vaccine kits for only $ 4.95;
- issuing fake compensation for various types of damage from the pandemic;
- theft of credentials and bank card details to obtain "tax benefits" in the United States.
Adapting to a new reality
Faced with quarantine restrictions, companies were forced to transfer a significant portion of their employees to remote work. To ensure the safety of such a regime, several problems had to be solved at once:
- - ;
- ;
- , ;
- -;
- .
Cybercriminals also took advantage of the new reality and began to attack routers and devices of home users more actively The
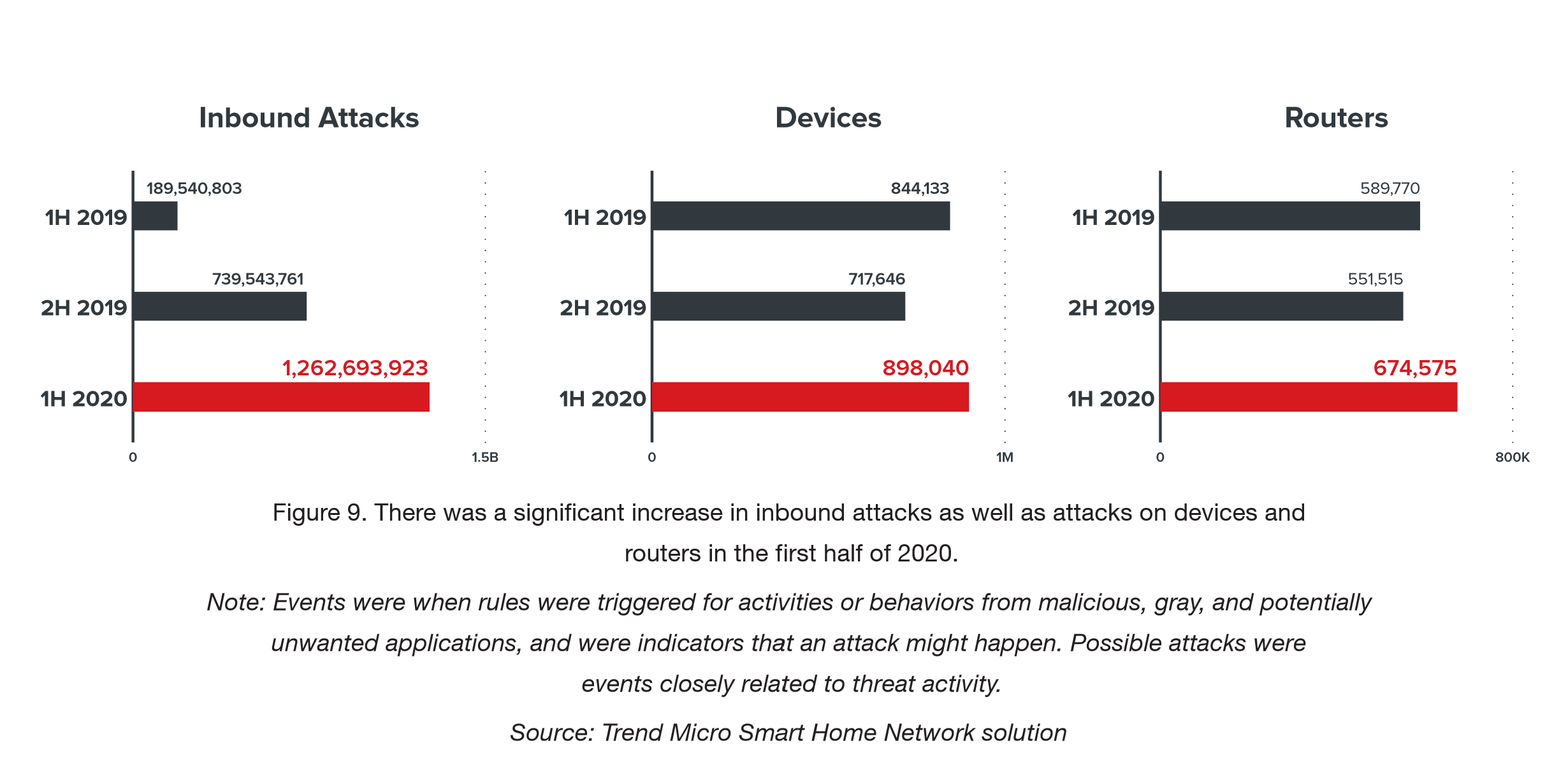
number of attacks on devices of home users in 2019-2020
Most of all attacks are bruteforce attacks on various services for remote access: RDP, SSH, FTP. The share of such attacks was almost 90%.
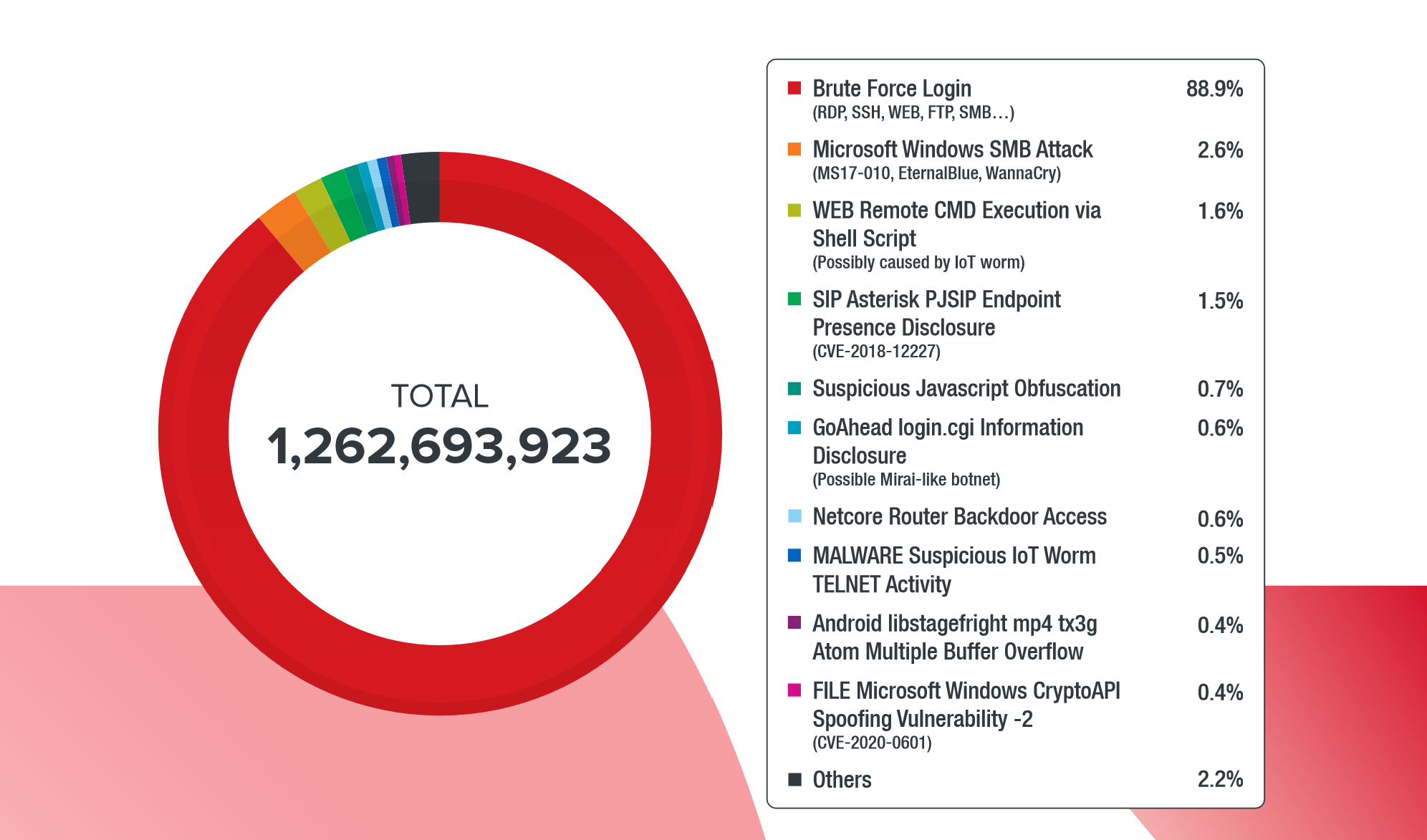
Distribution of Attack Types on Home Users' Devices
Compromising routers and other devices working remotely at home users enables attackers to use them to attack corporate networks.
Zumbombing and other attacks on video conferencing services
The need for constant communication has fueled an explosive growth in the use of Zoom, Cisco Webex, Google Meet, Microsoft Skype, and other video meeting platforms. One of the sensational phenomena that even caused the appearance of a new term was troll attacks on conferences held using the Zoom service. During these attacks, outsiders would tap into private calls and meetings and then stage a show of varying degrees of indecency, such as playing porn videos or insulting other participants.
The popularity of video services was also exploited in another way: scammers registered phishing domains whose name was somehow connected with Zoom or another similar service, after which they offered to download the Zoom or Skype distribution kit loaded with a malicious additive.
Ransomware campaigns
The number of ransomware incidents this year has dropped significantly compared to last year, but their quality has changed.

Number of components detected, associated with ransomware attacks in 2019-2020 Ransomware
operators no longer waste their time on trifles, sending thousands of spam emails to everyone and demanding a small ransom amount. Modern attackers prefer to target large companies, healthcare organizations or government agencies and demand large ransoms. This approach increases the likelihood that the ransom will be obtained, which means that the attack will pay off many times over.
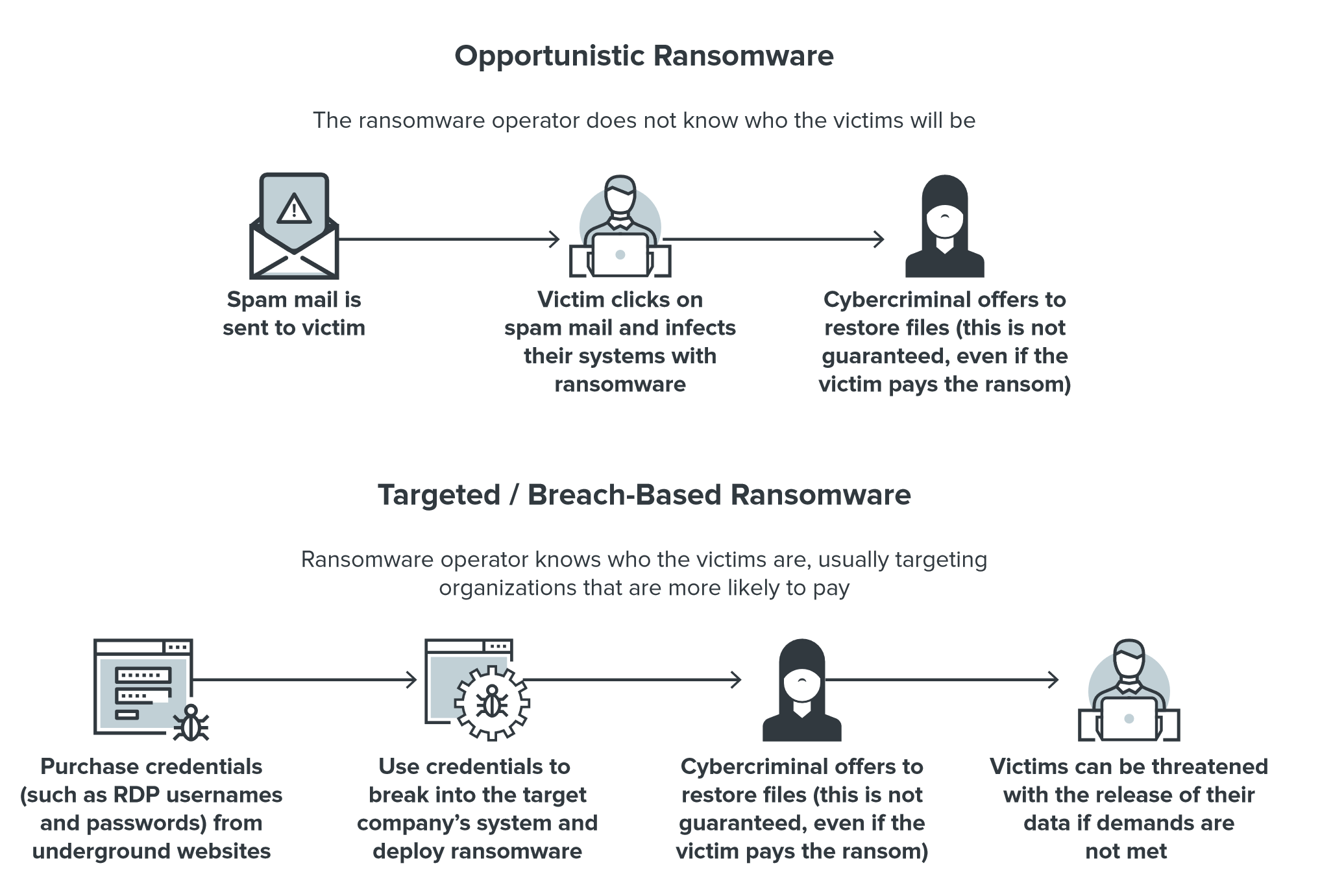
The "old" and new variant of the ransomware attack
The sensational WannaCry has collected much less in the form of a ransom over the entire period of its operationwhat, say, Ryuk ransomware can earn in one attack.
Ryuk attacks companies in critical industries. The importance of the data stored and processed by these organizations allows malware operators to demand huge ransoms: according to a report by Coveware, in the first quarter of 2020, the average ransom for Ryuk rose to $ 1.3 million .
Another characteristic change in modern ransomware is the predominant distribution through targeted campaigns that exploit vulnerabilities or stolen credentials for hacking.
Conclusions and recommendations
The pandemic has changed not only our lives, but also the thinking style of software companies. Recognizing the new realities, they adopted a new approach to security.
- Microsoft , Windows 7, Windows 10: 2020 99, ( — 129 Patch Tuesday);
- Zoom ;
- .
Tough times call for reliable security technologies. Separate tools and one-level protection of individual components of a company's information system are no longer enough. Only layered solutions can provide combined protection against multi-component and multi-platform threats to email, user devices, servers, network and cloud infrastructure.
Ideally, such solutions should provide a wide range of metrics and analytics that allow IT staff to see the big picture without having to devote a significant portion of their time and resources to sifting through mountains of alerts and other data.
The methods that attackers use to profit from the pandemic remain the same. Social engineering has become even more effective due to the fear and uncertainty caused by the virus. In the current environment, organizations simply need to pay particular attention to educating remote users about safe behavior through cybersecurity awareness programs.
For their part, users must exercise vigilance and common sense when interacting remotely with company information resources.
Another issue that requires a mandatory solution is the prompt delivery of updates to users' personal devices. With the growing number of attacks targeting remote users, keeping their devices up to date will increase the security of the corporate network.