
We will start our September selection with a case study. This time he is only one, but what a!
We never cease to admire the possibilities of GPT-3 and talk about the areas of its application, but many at the same time see in the algorithm a threat to their profession.
And VMO, which is engaged in A / B testing, decided to hold a competition - professional copywriters against GPT-3 .
They have integrated the algorithm into their visual editor so that users can choose between generated and authored texts. So far, the service only allows you to generate titles, product and service descriptions, and call-to-action buttons.
Why is this so interesting?The point is that in product management and marketing, a lot of resources are spent on testing hypotheses. Which headline will best increase engagement, or what color and shape the button should be for the client to take the targeted action. The answers to these questions enable products to become successful.
The outcome of this particular confrontation will not solve anything yet, but imagine if the algorithm could not only generate texts, but also track user behavior and modify the interface. Now remember that GPT-3 can typeset and create react components. That is why it is very interesting to follow this experiment. At the time of this writing, GPT-3 is in the lead by a small margin, let's see how it all ends.
And now to the rest of the finds of the last month:
Wav2Lip
The model generates lip movements for speech, thus synchronizing the audio and video streams. It can be used for online broadcasts, press conferences, and film dubbing. On the demo, you can see how Tony Stark's lips adjust to dubbing in different languages. Also, if communication deteriorates during skype calls, the model can generate frames that were lost due to a signal failure, and draw them based on the audio stream. The creators also suggest animating the lips of meme characters for more personalization of content. Like digital speakers, this model is able to adjust lip movement to speech generated from text.
It is noteworthy that in May the authors published the Lip2Wav model, which on the contrary “reads lips” and generates text and sound. A convolutional neural network extracts visual characteristics, after which a speech decoder generates a chalk-spectrogram based on them, and a voice is synthesized using a vocoder.

Flow-edge Guided Video Completion
New video augmentation algorithm that removes watermarks and entire moving objects, and also expands the video field of view, taking into account the movement of the frame. Like other similar algorithms, it first detects and restores the edges of moving objects. In this case, drawn borders do not look natural in the scene. The peculiarity of the method is that it tracks five types of non-locally adjacent pixels, that is, located on different frames, then determines which of them can be trusted, and uses this data to restore the missing areas. The result is a smoother video. You can already check out the source code , a collab will be added soon.

X-Fields
The neural network was trained on a series of images of one scene with marked coordinates of the viewing angle, time stamps and lighting parameters. So she learned to interpolate these parameters and display intermediate images. That is, having received several images with a gradually melting ice cube or an empty glass at the entrance, the model in real time can generate images taking into account all possible combinations of parameters. To make it easier to understand what it is about, we advise you to just watch the video demo . The source code is promised to be published soon.

Generative Image Inpainting
Another tool for removing objects from photos based on a generative neural network. This time it is a full fledged open source framework andpublic API . It works very simply - load the image and draw the mask of the object you want to remove, and - done, no additional post-processing. The project is deployed on a web server , so you can easily test it right in the browser. There are artifacts, of course, but it copes well with simple images.
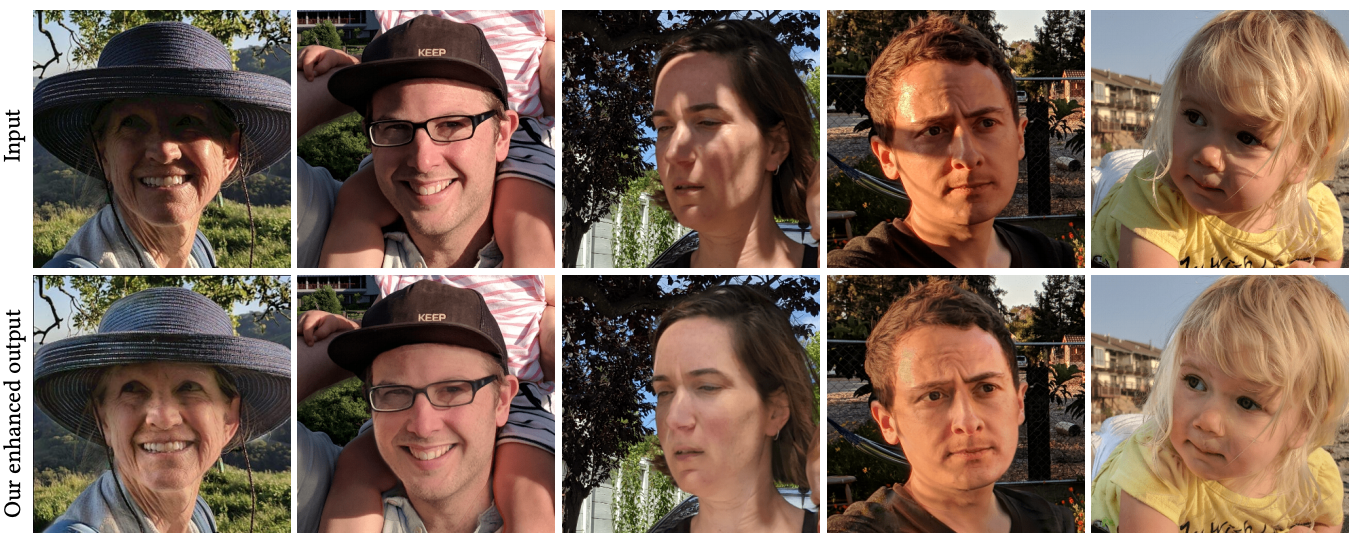

Portrait Shadow Manipulation
Portrait photos often suffer from improper lighting. The position and softness of the shadows and the distribution of light are environmental constraints that affect the aesthetic qualities of the image. Photo editor no longer required to remove unwanted shading - Berkeley researchers unveil open source algorithmwhich realistically removes shading from the photo and allows you to control lighting.
PSFR-GAN
An equally common task when working with photographs is their restoration and quality improvement. This open source tool does a pretty good job of upscaling portrait shots.
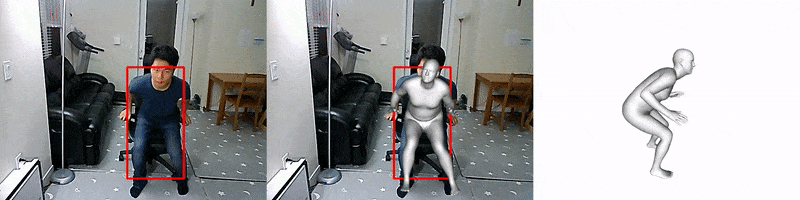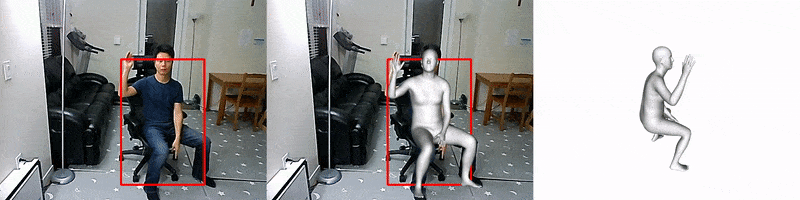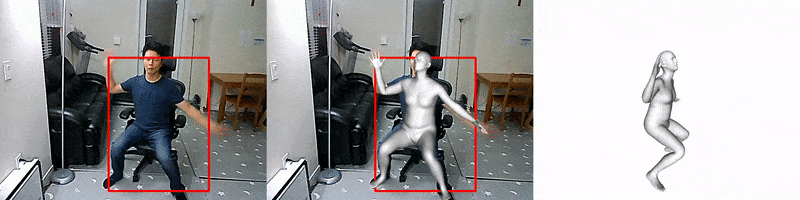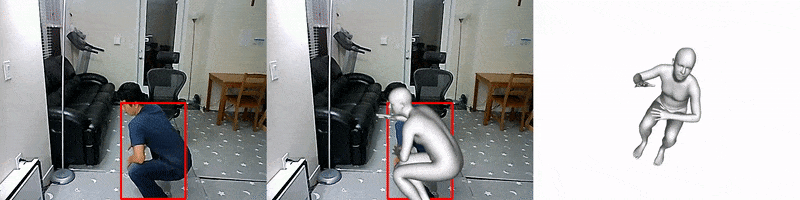
FrankMocap
Several interesting 3D modeling tools came out this month. Everyone who has worked with 3D knows that to create high-quality models, you need various expensive photographic equipment and the ability to use complex software. But machine learning algorithms are being actively used to make it easier for artists in this field.
Facebook AI introduced a system for creating 3D mockups of hands and bodies based on the analysis of monocular video. Motion capture works in near real time (9.5 frames per second) and creates 3D images of the body and hands in the form of a unified parametric model. Unlike other existing approaches, this one allows you to simultaneously capture both hand gestures and movements of the whole body. The source code is already available.
3DDFA
Another tool, which also appeared this month, is capable of marking up a human face from video to create a 3D mask.

PSOHA
Another technology from Facebook AI, which is also designed to simplify the process of 3D modeling - the neural network extracts many connections between the person in the image and other objects and generates three-dimensional mockups. Thus, on the basis of just one photograph, which depicts a person with some everyday object, a 3D model is created. The algorithm determines the shapes of people and objects, as well as their spatial location in natural conditions, in an uncontrolled environment. The creators promise to release the source code soon, so for now it remains to believe the examples from the demo, which, let's not be cunning, are impressive.

Monster mash
The new framework allows you to create and animate 3D objects using just one sketch. This greatly simplifies the process of animating objects, since you do not need to work with keyframes, multi-angle mesh, and skeletal animation. The model creates a three-dimensional model, which is immediately ready to create animations without long pre-setting of various parameters, which, for example, do not allow objects to pass through each other.
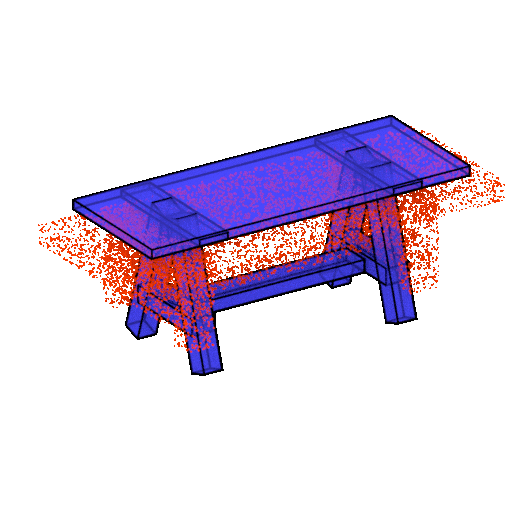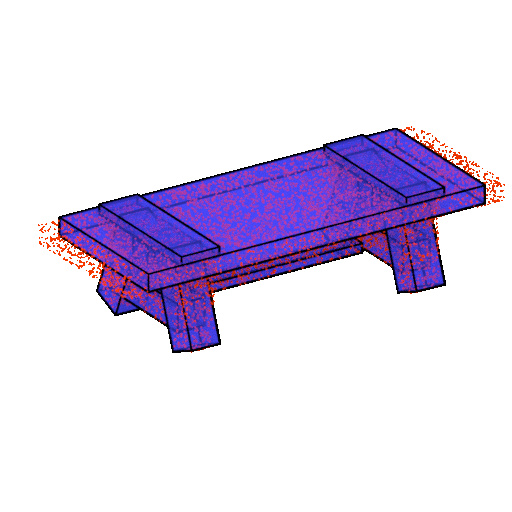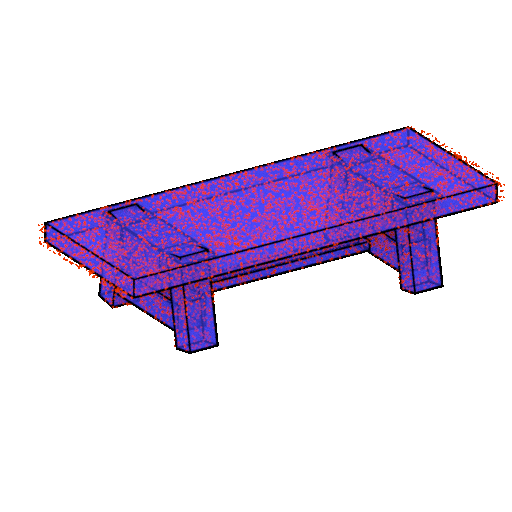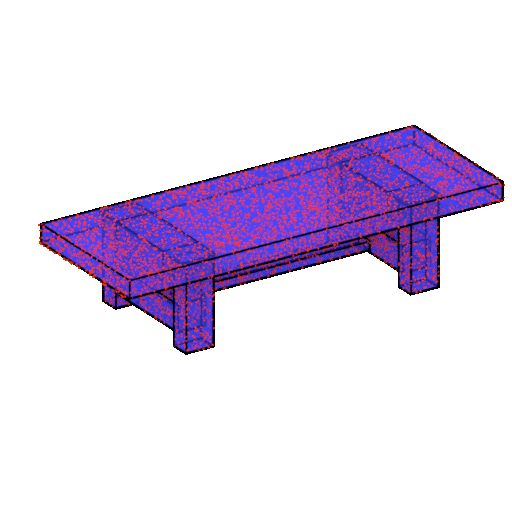
ShapeAssembly
The algorithm creates three-dimensional models of furniture from rectangular parallelepipeds. The ShapeAssembly approach takes advantage of the strengths of procedural and deep generative models: the former captures a subset of shape variability that can be interpreted and edited, and the latter captures the variability and correlations between shapes that are difficult to express procedurally. The network is already joking that the next step is to train the embedder based on IKEA instructions.
This concludes the topic with 3D modeling - for this area the month turned out to be especially intense. Thank you for attention!