
Course table of contents
1. Role of product manager and framework
2. Market segmentation and competitive analysis
3. User personas
4. Hypothesis testing
5. Product positioning
6. Product roadmap
7. Writing requirements for development
8. Business model and Business plan
9. Financial plan and pricing <- You are here
10. Launching an IT product and conducting a marketing campaign
- To be continued
As we said in the previous post, any product needs a business plan. And the financial plan is an integral part of it - even if the business plan is made in a minimal version. But do not treat your financial plan as something static. To understand this aspect of planning, three quotes from the book "The Art of War", which we already saw in the post on market segmentation and competitive analysis, are very well suited .
- “Preparing for any battle must begin with planning” - We need to try to predict how it will go, to think over our actions in case of different situations.
- "The battle will never go according to plan" - Because there are an infinite number of factors that cannot be taken into account.
- “Lack of plan always leads to failure” - Even though things will not go according to plan anyway, a complete lack of planning is likely to result in failure. If there is a plan, it can be adapted to the real situation.
Thus, a financial plan is needed for any product. But it must be constantly corrected. And for this, you need to create a financial model that will allow you to re-perform calculations at least every day, checking the profitability of the product in new conditions.
Lack of planning leads to popular misconceptions in the IT world:
- In an IT company, the most important thing is to create a product, and then it will sell itself.
- We'll work on the weekends and then everything will be fine.
- It's all about development - up to 90% of the costs can be spent on it.
- Marketing is not necessary for a good product; consumers will appreciate it.
These and similar misconceptions lead to the failure of products that could be successful with reasonable planning.
Basic concepts of financial planning
If you have not yet come across the basic financial concepts, we will briefly go through them (otherwise, scroll below).
So,
Profit = Income - Cost
- Revenues ( Revenue ) - this is the direct earnings from the company, such as sales, commissions, subscription or pay license fees.
- Costs ( Expenses ) - all kinds of expenses.
- Profit ( Net Income \ Profit ) - the difference between all total income, and the cost of production, operation, marketing, and so on.

Costs are usually divided into capital ( CAPEX ) and operating ( OPEX ).
CAPEX is an investment in fixed assets. For example, buying servers, you contribute to CAPEX, and renting capacity in the cloud - to OPEX.
In general, if we are talking about financial planning, then CAPEX is inconvenient for pricing, because capital expenditures are a large investment for a long period of time. To account for them financially, CAPEX costs need to be "smeared".
Example:
The server costs 300,000 rubles, the warranty period is 3 years, which means that in fact the server will cost 300,000 / 36 = 8,333 rubles per month. Further, to this amount you need to add the cost of electricity, which will be consumed by the system in three years. Of course, the purchase has its advantages, because the server will remain your property, it will continue to work after the end of the warranty period (if it does not break). But very often it turns out to be more profitable to consider renting a server, including leasing equipment or obtaining computing resources by subscription from the cloud.
In addition, you need to take into account the nature of the costs - after all, they can be fixed ( Fixed ) and variable ( Variable ).
For example, for a manufacturer of on-line games, Fixed costs are salaries for software development and payment systems, equipment operation, and Variable costs are server resources per player, as well as outsourcing personnel.
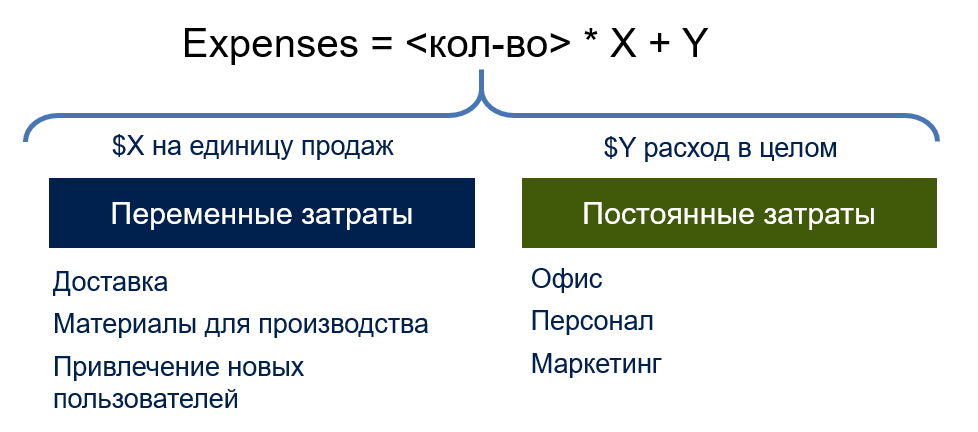
Profit margin is the difference (in% or ₽ / $) between the price and variable costs. The most important thing to know about profit margin is that it should cover fixed costs. In other words, your product should not lose profitability as the number of customers or users grows.
The marginality can be very high. For example, the iPhone 11 Pro was priced roughly $ 1,000 in the spring of 2020, although the estimated cost of parts and manufacturing is $ 500. Low marginality is typical, for example, for ticket booking and sale services, where the commission can be as low as a few percent.
The portfolio of one company can contain both products and services with both high and low margins. The main thing is to draw up such a financial plan so that the entire ecosystem is profitable.
Time is money
Very often when we start working on a product, we do it with great enthusiasm. Startups are ready to sleep 4 hours a day, sit all weekend, just to get their product ready for release. But we must not forget that the time spent is a valuable resource that must also be taken into account in costs. Otherwise, you will not be able to correctly calculate the cost of goods or services, taking into account future salaries.
How do you know how much your time is worth?
- Conduct an honest, adequate and realistic assessment - admit how much you need per month.
- Calculate the cost of an hour of your work based on 8 working hours per day, 21 working days per month.
- Adjust the indicator for the average workload, for example, 50%
- In total, it turns out that with an income of 100,000 rubles a month , an hour of your work will cost about 600 rubles. And after adjustment - 1200 rubles / hour.
Pricing
A financial plan cannot be created unless you have already decided how much a product should cost and how it will sell. Once you have chosen a business model , you can use the following different approaches to determine the price of a product:
- Study the proposals of competitors.
- Calculate Unit Economy (you can read about it here and here ).
- , , . : , , , . .
- .
- 1 . , , . , . .
The only thing you shouldn't do is ask people how much they would like to pay for your product or service. There are several reasons for this:
- More often than not, people would like to pay much less than they pay in reality. So this amount will be lower than the product is actually worth.
- What people say and what they actually do are completely different things.
- Consumers rarely understand how much a thing costs to produce and what the fair price is. It is easier to estimate the cost of a product by comparison.
Check out this interesting selection of subscriptions:

It has the last two options (print and print + subscription) cost the same - $ 125. As a result, 16% choose subscription and 84% choose print + subscription. Naturally, nobody chooses the middle option.
But when the company removed this item for the sake of experiment, the number of customers for different versions of the subscription changed: 68% began to choose a subscription, and 32% - print + subscription. Accordingly, the company's losses were significant. So “bad” options are not meaningless - they help people make the right choice for you!
A similar example is shown in the following screenshot. You visually highlight the price plan that you want the user to buy more often. As an "option" you add a more expensive option, in comparison with which the consumer will more willingly choose the average tariff, considering that this is a bargain:

Price for product with magic numbers 9, 99, 999

Perhaps the sight of such prices causes sensible indignation and comments among some: “sellers are trying to manipulate me by visually showing the price lower than it really is, but the difference is insignificant”. Yes, today all people are very smart and understand that there is practically no difference between 999 and 1000. But the reality is not that simple: From 1987 to 2004, 6 independent studies were conducted, and they all showed that prices with a "nine" increase sales. On average, the difference is 24% compared to the nearest round price.
Maybe that's why Steve Jobs managed to convince people to pay $ 0.99 per track for music instead of free download?
Here are a few more rules to follow when setting prices:
- , , .
- ( edition) , . .
- , .
- , , . , -.
- , , , .
Once you've decided on the price, don't forget to draw up a sales plan. This is a very important document, which according to research is prepared by only 15-20% of small business representatives.
For the sales plan, you need to determine the break-even point . To do this, it is necessary to calculate the volume of sales of a product or service, at which expenses will be offset by income. After passing the break-even point, each next sale already brings you profit.

The break-even point can be determined in pieces or in monetary terms.
Payback point ( pay-back point) Is a characteristic of time. It reflects the period after which the income from the project will exceed the funds spent on it. In fact, we are talking about the same break-even point, only we are not talking about pieces, subscriptions and boxes, but about days, months and, sometimes, years.
It is impossible to determine a payback point without a sales plan . And although there is an opinion that “the sales plan is the biggest lie in the world”, when launching a new product, it is imperative to draw up one.

Why is a sales plan a very important element in your startup? Here again, thoughts from the book "The Art of War" are extremely useful. Based on the potential sales of competitors, market capacity, demand and other forecasts, it is important to have at least some kind of sales plan. Starting from the first days of doing business, it can and should be adjusted. Working with ROI parameters will help you understand how the right strategy you have chosen and will give early signals that something needs to be changed in the business plan even before the mismatch of expectations in real life hits the product.
In addition, the sales plan will influence your strategy, determine how many leads you need to generate with a given conversion (more on this in the following posts) in order to fulfill this sales plan. Accordingly, you will know the volumemarketing activities that you must complete in order to be paid back.
Conclusion
In this post, of course, we have not covered all aspects of calculating marginality and other nuances of determining financial indicators. However, these materials are in great abundance on the Internet, and they make sense only after you have understood the basic positions of the financial plan and decided on the prices of products and services.
If you are interested in any specific calculation of the financial plan for your product, which can be done according to my Excel template, write in a personal , we will analyze your case together.
In <a href = " habr.com/ru/company/acronis/blog/522124> In the next post, we will talk about product launch and marketing - the next steps to bring a product to market, which just need to be done after drawing up all the elements of a business plan and determining the right prices.
→ Video recording of all lectures of the course is available on YouTube.Lecture
on business plan, financial plan and pricing: