
Data centers consume 3-5% of all electricity on the planet, and in some countries, such as China, this figure reaches 7%. Data centers need electricity 24/7 to keep equipment running smoothly. As a result, the work of a data center provokes greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere, and in terms of the level of negative impact on nature, they can be compared to air travel.
At Selectel, we have collected the results of the latest research to find out how data centers affect the environment, whether it can be changed, and whether there are similar initiatives in Russia.
According to a recent study by Supermicro, green data centers could reduce their environmental impact by 80%. And the stored electricity is to keep all Las Vegas casinos lit for 37 years. But at the moment only 12% of the world's data centers can be called "green".
Supermicro reportbased on a survey of 5,000 IT industry representatives. It turned out that 86% of respondents generally do not think about the impact of data centers on the environment. And social responsibility and the assessment of the energy efficiency of the enterprise is of concern to only 15% of data center managers. Most of the industry is focusing on resiliency goals rather than energy efficiency. While focusing on the latest data centers is profitable: the average enterprise can save up to $ 38 million in energy costs.
PUE
PUE (Power Utilization Efficiency) is a measure of the energy efficiency of a data center. The measure was approved by members of The Green Grid consortium in 2007. PUE reflects the ratio of the electrical energy consumed by the data center to the energy that is consumed directly by the data center equipment. So, if the data center receives 10 MW of power from the network, and all equipment "holds" at 5 MW, the PUE indicator will be 2. If the "gap" in the readings decreases, and most of the electricity reaches the equipment, the coefficient will tend to the ideal indicator is one.
Uptime Institute's Global Data Center Survey for August (900 data center operators surveyed) estimated the global average PUEat the level of 1.59. In general, the indicator has varied at this level since 2013. For comparison, in 2013 the PUE was 1.65, in 2018 - 1.58, and in 2019 - 1.67.
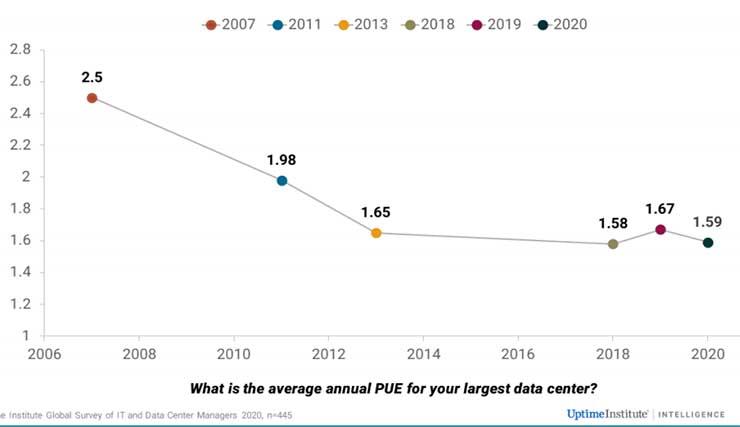
Although PUE is not fair enough to compare different data centers and geographic regions, the Uptime Institute compiles such comparison tables.

The comparison is unfair because some data centers are in the worst climates. So, to cool a conditional data center in Africa, much more electricity is needed than a data center located in northern Europe.
It is logical that the most energy-inefficient are data centers in Latin America, Africa, the Middle East and parts of the Asia-Pacific region. The most "exemplary" in PUE-indicator were Europe and the region uniting the USA and Canada. By the way, there are more respondents in these countries - 95 and 92 data center providers, respectively.
The study also evaluated data centers in Russia and the CIS countries. True, only 9 respondents took part in the survey. PUE of domestic and "neighboring" data centers was 1.6.
How to lower PUE
Free cooling
According to research , about 40% of all energy consumed by data centers goes to artificial cooling systems. The implementation of free cooling (freecooling) helps to significantly reduce costs. With such a system, outside air is filtered, heated or cooled, and then supplied to the server rooms. "Exhaust" hot air is thrown out or partially mixed, if necessary, to the incoming stream.
In the case of freecooling, the climate is of great importance. The more the outdoor temperature is suitable for the data center hall, the less energy is needed to bring it up to the required "condition".
In addition, the data center can be located near the reservoir - in this case, the water from it can be used to cool the data center. By the way, according to Stratistics MRC forecasts, by 2023 the market value of liquid cooling technologies will reach $ 4.55 billion. Among its types are immersion cooling (immersion of equipment in immersion oil), adiabatic cooling (based on evaporation technology, used in Facebook data centers) , heat exchange (the coolant of the required temperature goes directly to the rack with the equipment, removing excess heat).
More about freecooling and how it works at Selectel →
Monitoring and timely replacement of equipment
Correct use of the capacity available in the data center will also help improve energy efficiency. The servers already purchased must either work for the clients' tasks or not consume energy during downtime. One way to control the situation is to use infrastructure management software. For example, Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM). Such software automatically redistributes the load on the servers, turns off idle devices and gives recommendations on the speed of the cooling units fans (again, to save energy on unnecessary cooling).
An important part of improving data center energy efficiency is timely equipment upgrades. An outdated server is often inferior in performance and resource intensity to the new generation. Therefore, in order to lower PUE, it is recommended to update the equipment as often as possible - some companies do this every year. From Supermicro research: Optimized hardware upgrade cycles can reduce e-waste by more than 80% and improve data center performance by 15%.

There are also ways to optimize the data center ecosystem at no significant cost. For example, you can close the slots in server cabinets to prevent cold air leaks, isolate hot or cold aisles, move a heavily loaded server to a colder part of the data center, and so on.
Fewer physical servers - more virtual machines
VMware has calculated that switching to virtual servers can reduce power consumption by 80% in some cases. This is because placing more virtual servers on fewer physical machines logically reduces hardware maintenance, cooling and power costs.
An experiment by NRDC and Anthesis showed that replacing 3,000 servers with 150 virtual machines saves $ 2 million in electricity bills.
Among other things, virtualization makes it possible to reallocate and increase virtual resources (processors, memory, storage) in the process. Therefore, electricity is spent only to ensure work, excluding the costs of idle equipment.
Of course, alternative energy sources can also be selected to improve energy efficiency. For this, some data centers use solar panels and wind generators. These are, however, rather expensive projects that only large companies can afford.
Greens in practice
The number of data centers in the world has grown from 500,000 in 2012 to over 8 million. The figures for their electricity consumption are doubling every four years. The generation of electricity required by data centers is directly related to the amount of carbon emissions generated by the combustion of fossil fuels.
Scientists at the UK's Open University estimate that data centers generate 2% of the world's CO2 emissions. This is about the same as the largest airlines in the world throw away. Power plants emitted 99 million tonnes of CO₂ in 2018 to power 44 data centers in China, according to a 2019 GreenPeace study.

Major world leaders such as Apple, Google, Facebook, Akamai, Microsoft take responsibility for the negative impact on nature and try to reduce it by using green technologies. For example, Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella spoke about the company's intention to achieve negative carbon emissions by 2030, and by 2050 to completely eliminate the consequences of emissions for all the time since the company was founded in 1975.
These business giants, however, have sufficient resources to carry out their plans. We will mention in the text a few lesser-known "greening" data centers.
Kolos
The data center, located in the commune of Ballengen (Norway), positions itself as a data center operating on 100% renewable energy. So, to ensure the operation of the equipment, water is used to cool the servers, water and wind power generators. By 2027, the data center plans to go beyond 1,000 MW of electrical capacity. Kolos now saves 60% of electricity.
Next-Generation Data

British data center serves companies such as the telecommunications holding BT Group, IBM, Logica and others. In 2014, NGD announced that it had achieved an ideal PUE of one. Solar panels located on the roof of the data center have brought closer to the maximum energy efficiency of the data center. However, then the experts questioned the somewhat utopian result.
Swiss Fort Knox

This data center is a kind of loft project. The data center "grew" on the site of an old Cold War bunker built by the Swiss military in case of a nuclear conflict. In addition to the fact that the data center, in fact, does not take up space on the surface of the planet, it also uses glacial water from an underground lake in cooling systems. This keeps the temperature of the cooling system at 8 degrees Celsius.
Equinix AM3
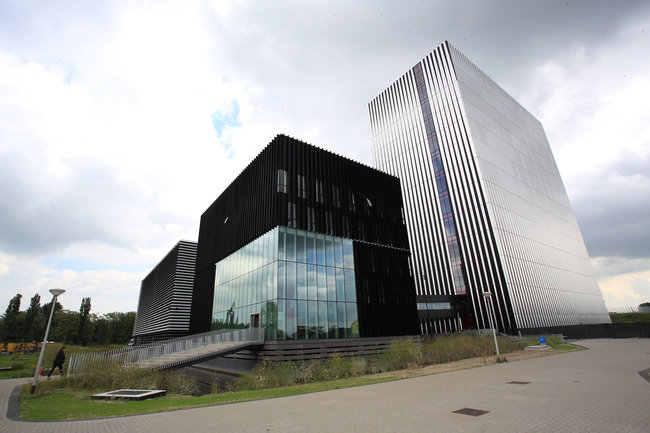

Data Center, located in Amsterdam, uses Aquifer Thermal Energy Storage cooling towers in its infrastructure. Their cool air lowers the temperature of the hot corridors. In addition, the data center uses liquid cooling systems, and the heated waste water is used to heat the University of Amsterdam.
What is in Russia
Research "Data processing centers 2020" by CNews revealed an increase in the number of racks at the largest Russian data center service providers. In 2019, the growth was 10% (up to 36.5 thousand), and in 2020 the number of racks may increase by another 20%. Data center providers promise to set the record and provide 6,961 more racks to customers this year.
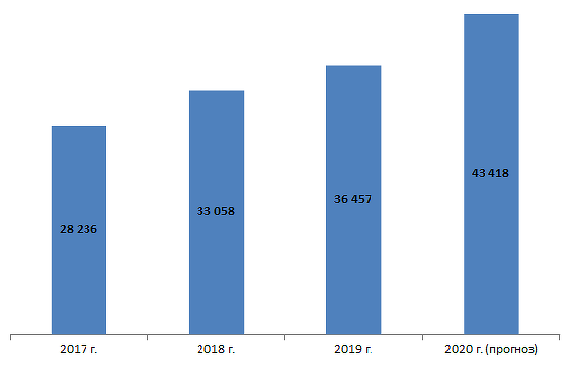
According to the assessment of CNews, the energy efficiency of applied solutions and equipment to ensure the efficiency of the data center at a very low level - at 1 W of useful power up to 50% non-operating expenses.
Nevertheless, Russian data centers have a motivation to reduce PUE. However, the engine of progress for many providers is not concern for nature and social responsibility, but economic benefits. An irrational approach to electricity consumption costs money.
At the state level, there are no environmental standards for the operation of data centers, as well as any economic incentives for those who implement "green" initiatives. Therefore, in Russia it is still the personal responsibility of data centers.
The most common ways of manifesting the eco-consciousness of domestic data centers:
- ( );
- -;
- - .
, Selectel
PUE - Selectel 1,25 ( «» ) 1,15—1,20 ( «-2» ). , . , 10 . , -, — .
, Selectel , . , : , . — , -.
Seletel went further and launched the Green Selectel program. The company will now plant one tree annually for each server operating in the company's data centers. The first mass planting of forests was carried out by the company on September 19 - in the Moscow and Leningrad regions. A total of 20,000 trees were planted, which in the future will be able to produce up to 200,000,000 liters of oxygen per year. The actions will not end there, the plans are to implement "green" initiatives throughout the year. You can learn about new promotions on the Green Selectel website and in the company's Telegram channel .
