
We continue to collect materials for you from the ML area. As always, we give preference to projects that contain links to non-empty repositories, or provide high-level APIs.

Iris
The company MediaPipe, which specializes in open ML solutions for recognizing objects in space - like FaceMesh and Handpose, on the basis of which we assembled a demo - presented a new tool Iris . As the name suggests, this machine learning model recognizes the iris, pupil, and eye contour using a simple RGB camera in real time. With an error of less than 10%, it also determines the distance between the subject and the camera without depth sensors. Unfortunately, so far the algorithm cannot determine in which direction a person is looking, just as it is not capable of identifying a person, but in combination with Pose Animator, it allows you to create more “live” animated characters, so we are waiting for a trend for cartoon masks.
FMKit
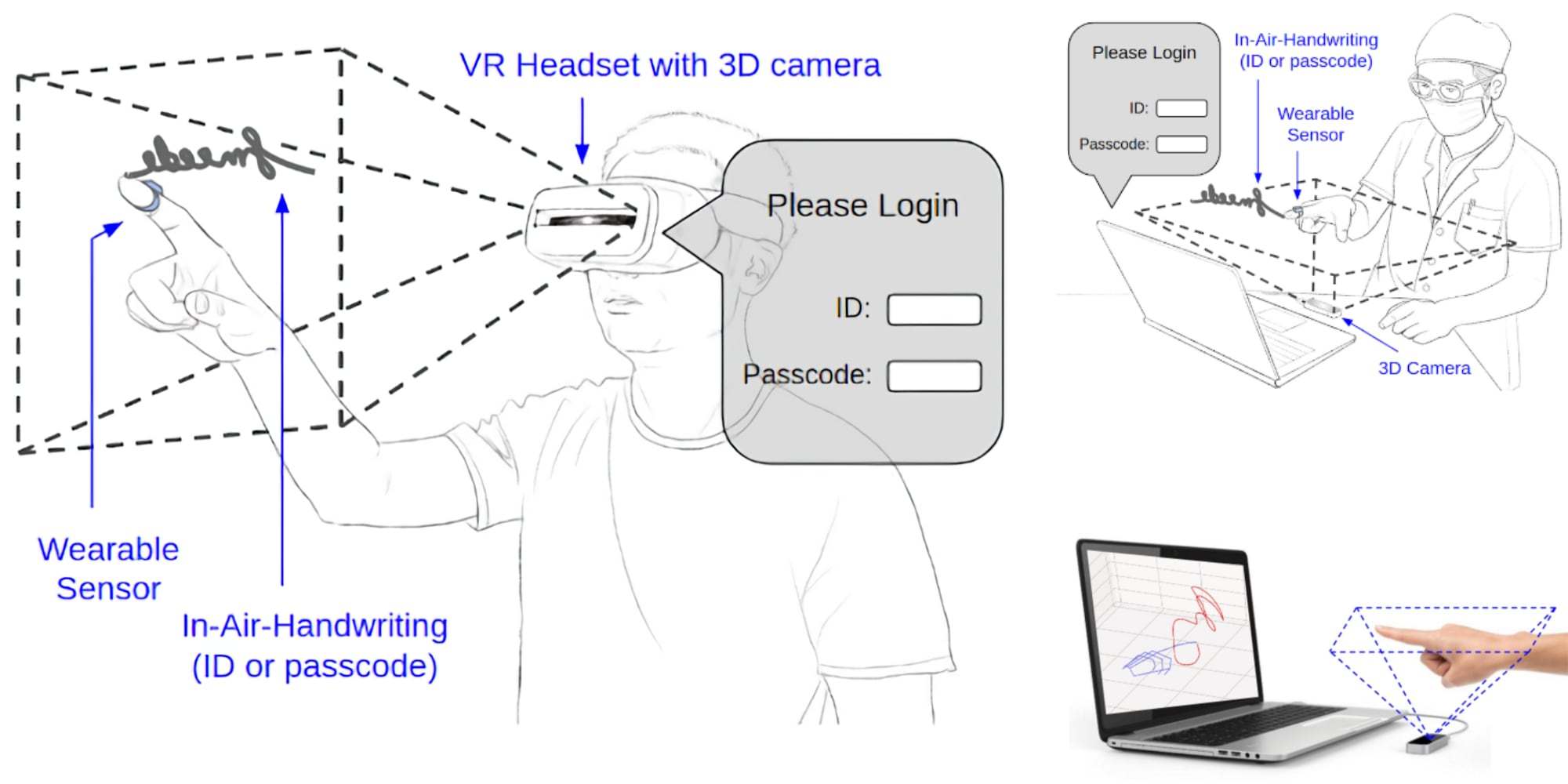
Not only Mediapipe is trying to solve the problem of expensive peripheral equipment using machine learning algorithms - researchers from the University of Arizona have developed a way to interact with VR or AR environments without special controllers.
Their algorithm recognizes words written in the air with your finger. It was impossible to do without input devices at all, the developers use the Leap Motion motion capture sensor. GitHub with FMKit source code and datasets.

Style and Semantics
Researchers at the Swiss Higher Technical School of Zurich have developed an open neural networkwhich allows you to manipulate the generated image with high-level attributes and text descriptions. At the input of the model, you can give a mask of objects with their classes. The neural network will create an image that is similar in structure. You can edit the content of the image using text queries. The model works in two stages. On the first, the background of the image is created, on the second - the generator synthesizes the foreground of the image taking into account the created background. This solves the problem of artifacts that appear in the background when removing or moving images from the foreground.
Semantic Reactor
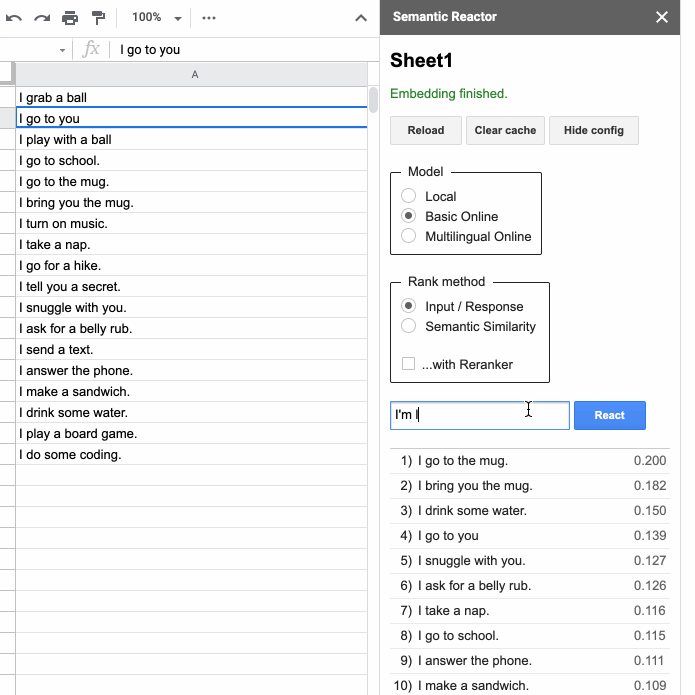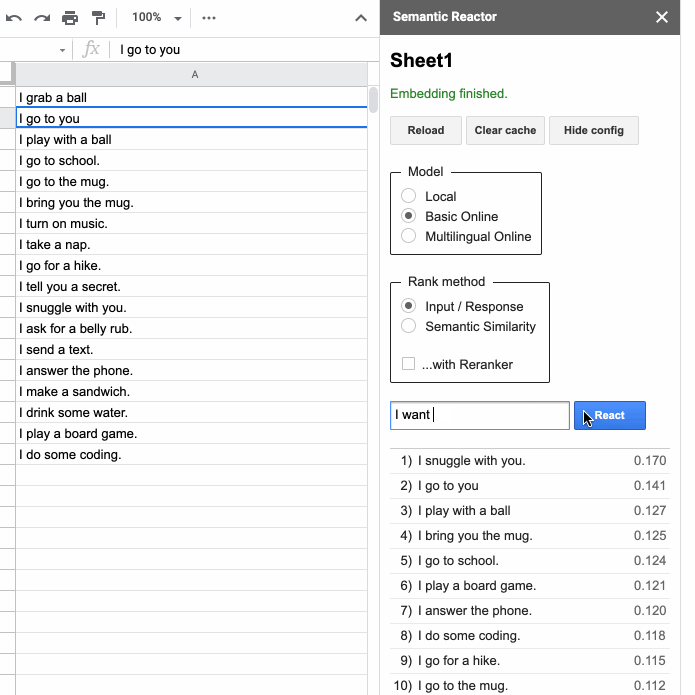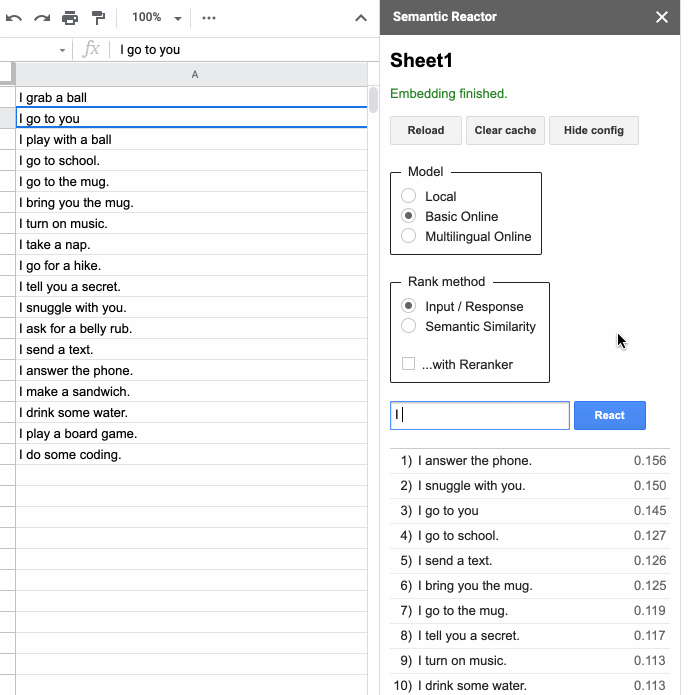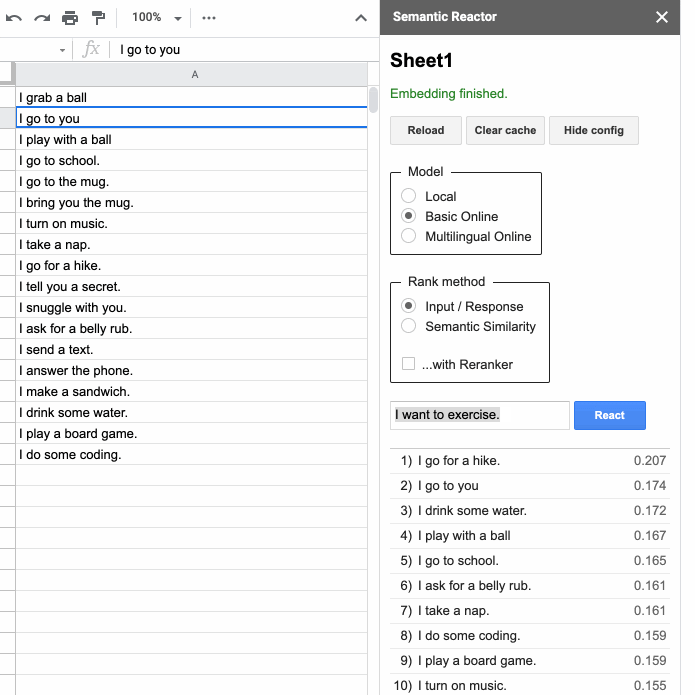
If you are building a language-based application, such as a customer service chatbot or a quest game, then you might be interested in this tool. Semantic Reactor is a Google Sheets plugin that lets you run natural language understanding models on your own data. This browser game shows what the tool is capable of. Fortunately, it also supports a multilingual model trained on 16 pairs, including Russian.
Fawkes
Machine learning raises many ethical controversies that can be resolved ... the same machine learning. Researchers at the University of Chicago have developed an algorithm that makes pixel-level changes invisible to the human eye in photographs so that they become unusable for other models. They call this process image masking. The instrument was named after Guy Fawkes, who is known to everyone thanks to the anonymous mask. The creators claim that disguised photos can be posted on social networks, and if they are used to train face recognition models, then masking will prevent the model from recognizing you in the picture due to distortion. As they say, wedge wedge.

See & Spray
A case study of machine learning in the agricultural industry. John Deere, the world's largest agricultural equipment manufacturer, has turned to machine learning and computer vision to better control weeds. The neural network identifies weeds from the images, and then instantly sprays them with herbicides. This saves resources without damaging the crop. The PyTorch framework was used to train all models. The first difficulty faced by the creators was the preparation and labeling of datasets, due to the external similarity of weeds with other crops. Deploying models on devices was also difficult, as the robot must quickly make decisions and move around the field.
AI Economist
The development of economic policy and the assessment of its effectiveness does not keep pace with the changes in the surrounding world, as, for example, is evident against the backdrop of a global pandemic. In addition, economic models require many assumptions, which limits their ability to fully describe current economic conditions: for example, they can study income taxes in isolation, but exclude consumption taxes.
Salesforce is proposing ML algorithms to solve these problems and has published a framework that uses reinforcement learning and economic modeling to quickly design and evaluate new economic policies based on data.
ScaNN
It is not difficult to search even a large database of articles using queries that require an exact match of the title or author, since such parameters are easily indexed. In the case of more abstract queries, you can no longer rely on similarity metrics, such as the number of common words between two phrases. For example, the query “science fiction” is more about “future” than “science,” even though the second query has one word that matches the query.
Machine learning models have excelled at understanding the language and can transform inputs into embeddings, vector representations of words trained to combine similar inputs into clusters. Google introduced an open source similarity search tool for such vectors.

Re-rendering people from one image
Re-rendering a person based on a single image is a tricky task. Modern algorithms often create artifacts like unrealistic distortion of body parts and clothing.
This study demonstrates a new algorithm that allows people to change into new clothes through texture re-rendering. It presents posture and body shape in a parametric grid that can be reconstructed from a single image and easily modified. Instead of color UV maps, the creators suggest using attribute maps to encode the appearance. While the quality is weak and there are no sources, you can already imagine how this technology will soon be applied in Ecommerce.
Bonus: in May we toldabout the algorithm that determines the depth of frames in the video, but then it was possible to evaluate only the video demonstration, now the source code of the project has become available .
That's all, thanks for your attention!