
In the classic version of MultiSIM Reservation, when providing IPVPN services over two mobile networks, there are the following problems:
- For each client, you need to create your own private APN, configure BGP or static routing in it, immediately calculate the required number of hosts for the correct IP addressing plan.
- , , .
- ().
- IPVPN LTE , , — IPVPN LTE «».
On the other hand, we have IPSec, in which all routing and client settings are abstracted from transport, whether it is a wired Internet channel or LTE of different operators, and traffic labels can also be stored inside the tunnel, albeit without ensuring SLA, since the Internet and especially LTE / 3G is a rather unpredictable medium for data transmission.
Therefore, we had an idea - "Why not use IPsec over LTE as well?" Put standard SIM-cards with pre-created APNs in routers and build IPSEC through them to our VPN HUB and release the client to its VRF. And if there is a wired channel, then use a wired connection as the main transport, and in case of an accident on it, switch traffic to LTE.
Thus, the network diagram began to look like this:
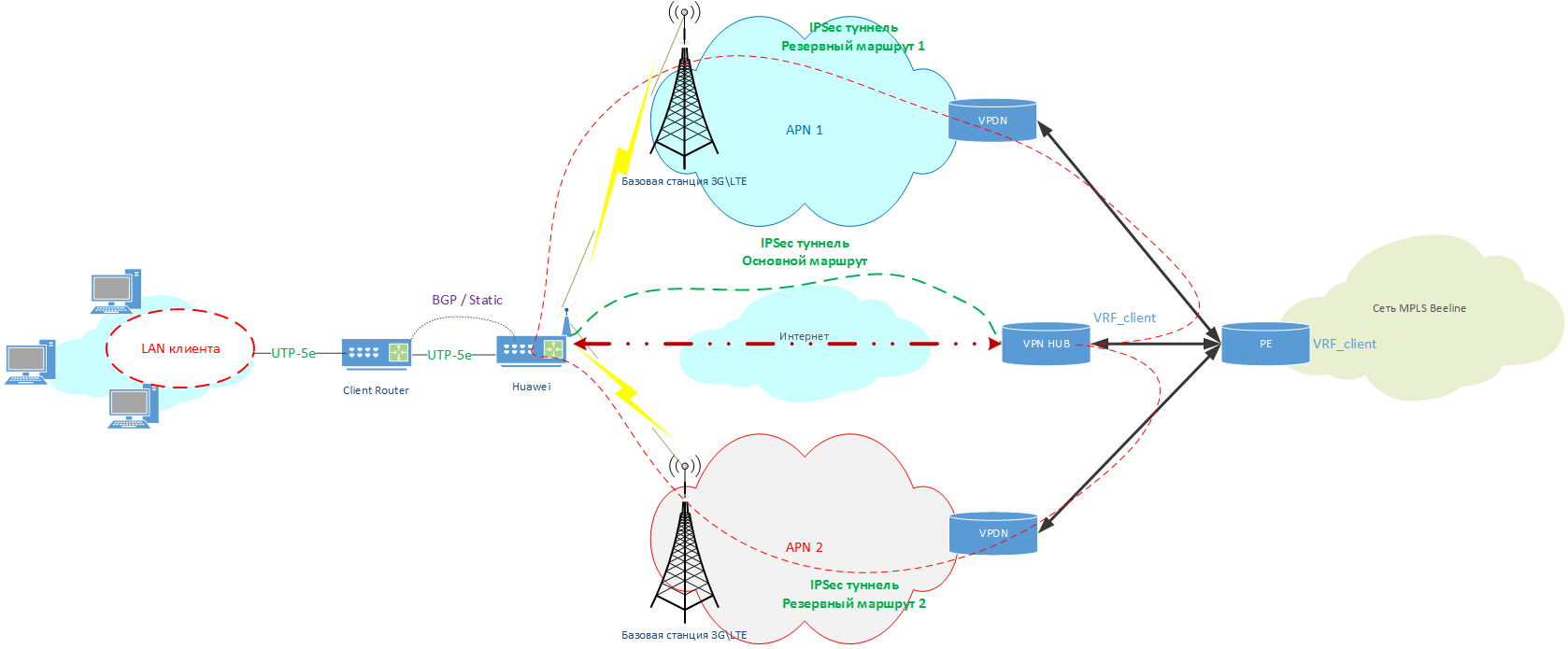
Clickable
The client gets up to three WAN channels at once, which will play the role of "underlay" for IPSec traffic:
- Wired Internet access channel.
- The first (main) LTE network.
- Second (Backup) LTE network (if needed).
Now it remains to select and configure a router for this service delivery option.
Configuring a router
When choosing a router, we were interested in two models from Huawei - AR161 and AR129. They have IPSec support, an LTE modem with support for two SIM cards, 4 Ethernet LAN ports + 1 Ethernet WAN, and the AR129 also has WiFi, that is, everything that is needed for our circuit to work, and even a little more.
But with the settings, everything turned out to be much more complicated.
While configuring routers for Multisim Redundancy, we faced the problem of priorities between wired WAN and two LTE networks to choose the best traffic route.
The Huawei AR161 / 129 has two tools for this:
- Network Quality Analysis functionality (aka NQA-test).
Conducts basic testing with icmp requests to the specified host to determine its availability. - Open Programmability System (OPS) + Python functionality.
A very powerful tool, it allows you to save information in logs and carry out "intelligent" switching based on icmp statistics, but also difficult to learn.
To solve our problem, we chose the OPS + Python functionality to enable only two LTE SIMs, and mixed mode for the Internet + two LTE SIMs.
An approximate configuration on routers is as follows:
In case of only 2x Sim LTE connection
# IP WAN ( DHCP)
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/4
ip address dhcp-alloc
# APN , Cellular0/0/0
apn profile [APN #1]
apn [APN 1 NAME]
apn profile [APN #2]
apn [APN 2 NAME]
sim-id 2
# Cellular0/0/0
interface Cellular0/0/0
dialer enable-circular
apn-profile [APN #1] priority 120
apn-profile [APN #2]
dialer timer autodial 60
profile create lte-default [APN #1] sim-id 1
profile create lte-default [APN #2] sim-id 2
ip address negotiate
modem reboot
# IPSec
ipsec authentication sha2 compatible enable
ike local-name [IPSEC_LOGIN]
# IPSec
ipsec proposal ipsec
esp authentication-algorithm sha2-256
esp encryption-algorithm aes-256
ike proposal 1
encryption-algorithm aes-256
dh group2
authentication-algorithm sha2-256
authentication-method pre-share
integrity-algorithm hmac-sha2-256
prf hmac-sha2-256
# IPSec
ike peer ipsec_1
pre-shared-key simple [IPSEC_PASSWORD]
ike-proposal 1
local-id-type fqdn
remote-id-type ip
dpd type periodic
dpd idle-time 10
dpd retransmit-interval 2
remote-address 100.64.0.100
route accept
config-exchange request
config-exchange set accept
config-exchange set send
ipsec profile ipsecprof_1
ike-peer ipsec_1
proposal ipsec
# IPSec -
interface Tunnel0/0/0
tunnel-protocol ipsec
ip address [ IP - Huawei] 255.255.255.252
source Cellular0/0/0
ipsec profile ipsecprof_1
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Tunnel0/0/0
ip route-static [VPN HUB INTERNAL ADDRESS] 255.255.0.0 Cellular0/0/0 In case of Internet + 2x Sim LTE-inclusion
# IP WAN ( DHCP)
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/4
ip address dhcp-alloc
# APN , Cellular0/0/0
apn profile [APN #1]
apn [APN 1 NAME]
apn profile [APN #2]
apn [APN 2 NAME]
sim-id 2
# Cellular0/0/0
interface Cellular0/0/0
dialer enable-circular
apn-profile [APN #1] priority 120
apn-profile [APN #2]
dialer timer autodial 60
profile create lte-default [APN #1] sim-id 1
profile create lte-default [APN #2] sim-id 2
ip address negotiate
modem reboot
# IPSec
ipsec authentication sha2 compatible enable
ike local-name [IPSEC_LOGIN]
# IPSec
ipsec proposal ipsec
esp authentication-algorithm sha2-256
esp encryption-algorithm aes-256
ike proposal 1
encryption-algorithm aes-256
dh group2
authentication-algorithm sha2-256
authentication-method pre-share
integrity-algorithm hmac-sha2-256
prf hmac-sha2-256
# IPSec
ike peer ipsec_1
pre-shared-key simple [IPSEC_PASSWORD]
ike-proposal 1
local-id-type fqdn
remote-id-type ip
dpd type periodic
dpd idle-time 10
dpd retransmit-interval 2
remote-address 81.211.80.50
route accept
config-exchange request
config-exchange set accept
config-exchange set send
ipsec profile ipsecprof_1
ike-peer ipsec_1
proposal ipsec
ike peer ipsec_2
pre-shared-key simple [IPSEC_PASSWORD]
ike-proposal 1
local-id-type fqdn
remote-id-type ip
dpd type periodic
dpd idle-time 10
dpd retransmit-interval 2
remote-address [VPN HUB INTERNAL ADDRESS]
route accept
config-exchange request
config-exchange set accept
config-exchange set send
ipsec profile ipsecprof_2
ike-peer ipsec_2
proposal ipsec
# IPSec-
interface LoopBack32
ip address [ IP - Huawei] 255.255.255.252
interface Tunnel0/0/0
ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack32
tunnel-protocol ipsec
source GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ipsec profile ipsecprof_1
interface Tunnel0/0/1
ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack32
tunnel-protocol ipsec
source Cellular0/0/0
ipsec profile ipsecprof_2
# ( )
nqa test-instance [username] inet
test-type icmp
destination-address ipv4 81.211.80.50
source-interface GigabitEthernet0/0/4
frequency 16
probe-count 2
start now
#
ip route-static 81.211.80.50 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet 0/0/4 dhcp track nqa [username] inet
ip route-static [VPN HUB INTERNAL ADDRESS] 255.255.255.255 NULL0 track nqa [username] inet
ip route-static [VPN HUB INTERNAL ADDRESS] 255.255.0.0 Cellular0/0/0 preference 70
ip route-static 80.240.216.155 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet 0/0/4 dhcp
ip route-static 194.67.0.206 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet 0/0/4 dhcpEverything, the configured router can be installed to the client.
Plans
From plans to develop this solution:
- Do the same, but on Cisco / Mikrotik routers.
- Translate all switching logic to OPS + Python only
In the following articles, we will tell you how we made friends with Multisim Reservation services with our Cloud PBX , made L2-over-L3 mode on the same Huawei using x-connect, lay out scripts for switching SIM-cards in Python and tell about USB-Deployment on routers.
Thanks to my colleagues from RnD, especially Denis Zinchenko (Dzinch) and Andrey Voronov in preparing these technical solutions and helping to write the article!
PS: The first part of the post is here .