Introduction
We continue a series of articles on the topic of legal artificial intelligence, aspects of its development and prospects for practical application in the domestic market. In previous publications, we have repeatedly said that, in our opinion, the development of Legal AI can be ensured by creating and applying a new semantic block, which includes:
- tools for linguistic analysis of natural language texts;
- a structured model of legal knowledge (knowledge graphs and ontologies);
- pretrained neural networks.
In the first article, we examined in detail the existing tools for processing Russian-language text. In the second article, we examined approaches to creating products based on artificial intelligence, as well as issues of interaction between specialists in the field of IT and law. In this article, we propose to dive into the topic of ontologies and answer the following questions:
- What is the role of ontologies in the process of creating artificial intelligence?
- Why are the existing ontologies in the field of law inapplicable for Legal AI, despite the many years of attempts by foreign experts to structure legal knowledge?
- What properties should legal AI ontologies have in order to solve practical problems?
1.
1.1.
, , Legal AI, — (, , ), . , «» 99,99%.
— (reasoning). .
, - « », . , : « , ?». , - : « , ».
, , . , . , -, , , . , (-) , . . - , , , , . , .
, , , , , , .
, , , , . , .
data science, Judea Pearl 3 : Association, Causation Counterfactuals ( ).

Association . , . , , .
— Causation. - , . , , , , . ausation , - . : Causation , . Causation , , - .
, , — Counterfactuals. - , . , , , , .
, Association. / , .
, -, « » - . , , Counterfactuals, , . - , .
1.2.
Legal AI. , , , «first principles» .
(reasoning). : . , . , , () - -, — , , .
, : «S P». . , .
(«») , :
- , ;
- , (/, , .) ;
- , (/, , .) .
, / : «: «», . , . , . 1, 1». , . , NER :
- « «»» «» « »;
- «. , . , . 1, 1» «».
, : « «» «» «. , . , . 1, 1». , . reasoning'.
, , , . , «» « » «». : « ?». - .
1.3. -
( , ) — , , , . , , , — , , , .
1980- . . 2000- , . OWL , — . , , , . , , , , ( ). , , , . , OWL. OWL XML, , OWL XML.
, . . — ̆ ( , , ̆ .), . ̆ , ̆ ̆, . , .
, , - , . , , , .
, , , , , .
, . , ( , - ), (, ), . , - , , .
, , . , , / ( ). , , , .
, . , , (, ), /. . , , , , . , - , , 20-30 % . , .
— . 1986 (The British Nationality Act) Prolog. ( ), . , (, , .) , . , - , . , . . , , , . , - .
. OWL , , .

, , , . , : « , , 01.09.2015 . 01.09.2019 .» OWL, (object properties) .
OWL , :
- ;
- (instances) .
- , . , W3C 2017 . Shapes Constraint Language (SHACL), RDFS/OWL . , ( ), .
2.
2.1.
, . , , , , (Relationships) , .
, ( — «subclass of»), . , , . .
XX . 1990- , ̆, (OMEGA, SUMO, DOLCE ). 2000- . , 2004 . W3C OWL 1.0, 1.1 2.0. , OWL (KIF, Ontolingua, XOL .). , ( ).
. (, , , , - .). . 1990- (Functional Ontology of Law by Valente et al. (1994), Frame-based ontology by van Kralingen (1997) .). : LKIF, UFO, FIBO, FBO Legal Rule ML. ( 2.1.1-2.1.6).
, . .
, , - . , , .
, , , , , , , .
5 () :
- ( );
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- .
2.1.1. FIBO
Financial Industry Business Ontology (FIBO) . OMG, ̆ - 1989 . FIBO ( .).
. , FIBO ( /, .), . , , FIBO , . , , , , , .

, FIBO . -, FIBO Legal AI, , -, , . , FIBO -, , .
FIBO 3099 . FIBO : ̆ ̆ OWL, ̆ ̆ . ̆ OWL ̆ Protege. , FIBO ̆ , -. , - . - , FIBO, ̆ , ̆ () . , FIBO .
FIBO , , «». ̆ (, , /, / ..). ̆ FIBO Foundations, ̆ ̆ ̆. FIBO Foundations , FIBO Business entities (-) FIBO Indices and Indicators ( ). , ̆, .
FIBO Foundations ̆, ̆ ̆ . , ̆ , ̆, , ( , .). FIBO Foundations - («Proxy» concept) , . , ̆, (address) (country). : , ̆ , ̆ , - , .

̆ , FIBO Foundations , ̆. ̆-̆ , ̆ ̆ ̆ , (, , , ..). FIBO Foundations, FIBO.

FIBO Business entities FIBO Foundations . ̆ -̆, ̆ , ̆. , ̆ (business entities), -- , . FIBO Business entities , -. FIBO Business entities ̆, , , , , , ̆ .

FIBO, . FIBO 3099 , , . , , ( ) ( ). - , . . , FIBO, , Legal AI , .
2.1.2. LKIF
LKIF (Legal Knowledge Interchange Format), Estrella. LKIF . : , , . LKIF , ̆, . () ̆. , LKIF - LRI-core ontology. LRI-core , , , , , , , .

LKIF , 15 , , , . :
- – , « » (Mental entity), « » (Abstract entity), «» (Occurrence), « » (Physical entity);
- — . , : « » (is component), « » (is part of), « » (member of) ;
- — , ;
- – . «» ( ) «» ( , ). : « » (before), «» (finish), «» (between) ;
- — . : , , ;
- – , . : , ;
- – . ;
- — , .
- – , ;
- – , - ;
- – : (Contract), (Directive), (Code) .
(Legal Concepts). Legal Concepts LKIF : Legal role, Legal action Legal norm.

Legal role Role, , , . , , , , .

Legal action Action , , Legal role.

Legal norm , . : , , ., .

, LKIF, , - . , , , . , LKIF (.. .. ), . « - 2020 2025 ». . , . OWL-, ̆ , . - , , :
- «» (Medium) , : ̆ ̆ , , , , .;
- , , ̆ , ;
- ̆ «» (Proposition) / ̆ (Qualification);
- ̆ ̆ .


.. .. , LKIF . , LKIF , , .
LKIF , , . :
- M. Ceci, A. Gangemi («An OWL ontology library representing judicial interpretations», Semantic Web, 2016);
- Cevenini C., Contissa, G., Laukyte, M., Riveret, R., Rubino, R. («Development of the ALIS IP ontology: Merging legal and technical perspectives», Computeraided innovation (CAI), Boston, 2008);
- Distinto, I., d’Aquin, M., & Motta, E. («LOTED2: An ontology of European public procurement notices», Semantic Web, 2016);
- Ghosh, M. E., Naja, H., Abdulrab, H., & Khalil, M. («Towards a legal rule-based system grounded on the integration of criminal domain ontology and rules», In Procedia Computer Science: 112, 2017);
- Rodrigues, C. M. O., Azevedo, R. R., Freitas, F. L. G., da Silva, E. P., & da Silva Barros, P. V. (An ontological approach for simulating legal action in the brazilian penal code. In Proceedings of the 30th annual ACM symposium on applied computing», New York, 2015) .
, LKIF - . , .
2008 Estrella, LKIF, .
2.1.3. Legal Rule ML
, , Legal Rule ML. OASIS, (, , , , , IoT .) 1993 . , , , . . , Legal Rule ML , Estrella LKIF Core ontology. Estrella 2008 . LKIF Core, Legal Rule ML LKIF, , .
, Legal Rule ML . (, , , .) , . , , , . , , . , OASIS, (XML) . , , . Legal Rule ML.

, Legal Rule ML , XML, Rule ML , . Legal Rule ML Node elements Edge elements, . ( ) () , .

Agent ( , ), Figure (, , ) Role (, ). , , .
Legal Rule ML ( ), , ( , .), , .
Legal Rule ML, , , , . . , Rule ML. , Legal Rule ML , , . , OASIS , , , Legal AI .
2.1.4. UFO
Unified Fundamental Ontology (UFO) 2004 G. Guizzardi . . , , .
UFO 0.1 , :
- General Formal Ontology (GFO), General Ontological Language (GOL) ( OntoMed Research group ());
- Descriptive Ontology for Linguistic and Cognitive Engineering (DOLCE), OntoClean ( ISTC-CNR-LOA Research group ()).
UFO , . UFO , -, . UFO OntoUML, .
UFO : UFO-A, UFO-B, UFO-C. UFO (UFO-A) G. Guizzardi (NEMO) (Gerd Wagner) (LOA). UFO-A , , , , , , . UFO (UFO-B), (UFO-C). UFO-A, UFO-B UFO-C , , , , , , , .

: Particular (Individual) Universal (Type). Particulars — , . Universals, , , (Particulars). UFO-A Substances — (Particulars). (Moment), , /, . (Relations) — , . Relators — , .
UFO-A — Endurants. Endurants — , . , . UFO-B — Perdurants (), , . « » , , . Endurants, Perdurant , , . UFO-B «» (Event), Perdurant. : ( ) ( ). , , , .
UFO- (Endurants Perdurants). Agents () Objects (), , — (), — , , . «» (Intentional Moments). Intentional Moment (, Belief, Desire, Intention) (Proposition). — , Intention. (propositional content) — (Goal). — (Belief) (Desire). , — , - . (Actions). — , Instance (Plan), . (Communication Act), (Social Moments). , , (Interaction).

, UFO, . . , 2015 . UFO UFO-L, . , , . UFO , :
- Griffo, C., Almeida, J. P. A., & Guizzardi, G. A systematic mapping of the literature on legal core ontologies. Ontobras. In CEUR Workshop Proceedings: 1442. CEUR-WS.org, 2015;
- Rodrigues, C. M. O., Freitas, F. L. G., & Azevedo, R. R. An ontology for property crime based on events from ufo-b foundational ontology. 5th Brazilian conference on intelligent systems (bracis), 2016 .
2.1.5. FBO
Frame-based ontologies (FBO), , (, , ) , . , .
(GLO), , . : , . ( ), , .
, , . :
- ( );
- ( , );
- ( );
- ( );
- (, );
- ( , );
- (, , , );
- ( ).
, . . . , . . , () () , ( — ). , :
- ( );
- ( );
- ( );
- ( , , );
- ( , , );
- ( , );
- (, );
- ( , , , , . ., , . .);
- ( , );
- ( , );
- ( );
- (, );
- ( );
- ( ).
. , . , , . , -, , .
, , . , . , . GLO :
- ( — , );
- , ;
- , .
FBO , GLO. , , . , , FBO, Legal AI, , .
2.2.
, . , . , . - .
, , , .
. 5- 6 .
1. .
, . , . , , . :
- 0 — ;
- 1 2 — , (, , .);
- 3 4 — , ;
- 5 — , .
2. .
. . :
- 0 — ;
- 1 2 — , ;
- 3 4 — , ;
- 5 — .
3. .
. :
- 0 — ;
- 1 2 — ;
- 3 4 — , ;
- 5 — .
4. .
. :
- 0 — ;
- 1 2 — , ;
- 3 4 — , ;
- 5 — .
5. .
, . : « ?». :
- 0 — ;
- 1 2 — , ;
- 3 4 — , ;
- 5 — , .
6. .
. , , , , / . :
- 0 — ;
- 1 2 — , ;
- 3 4 — ;
- 5 — .

LKIF, Legal Rule ML, FBO , . , . , ., «reusable». , , , . Legal AI.
UFO FIBO. UFO , . UFO-L , UFO . FIBO - , . , , , . , FIBO , .
, , Legal AI , , , . ( ), Legal AI .
: « ?».
, , , , CIDOC CRM (Committee on Documentation «Conceptual Reference Model»).
CIDOC CRM CIDOC . , . , CIDOC CRM , , . , , . , , , , , . , MIDAS XML, IST Project SCULPTEUR, IST Project I-Mass .
, , . , .
CIDOC CRM ( ), . 5.0.1 CIDOC CRM 82 142 , , , , , , . ( ) .


, : , , , .

, : , . , : , , , . CIDOC CRM 2 : . . , : «», « ()», « » ( ), «» ( ). «».
. 10-15 , -. , , , . , . , . , , .


Ontology Design Patterns. , , . , (, , , .), . ( , , .) . , , . , , , . , ODPA (Ontology Design Patterns), , .
2.3.
. ̆ ̆ ̆ ̆ . , , - . , , .
-, , , . , Legal AI, ̆ . ̆ ̆ n*(n-1)/2, n — ̆ , , , ̆ . , ̆ . , (is-a, subclass of).
-, : , (legal practice). — , , , , , , 30% .
, . ̆ ̆ . , 6 (. 125-129 ). , ( , ̆ ̆ ), . ( , , .) , , .
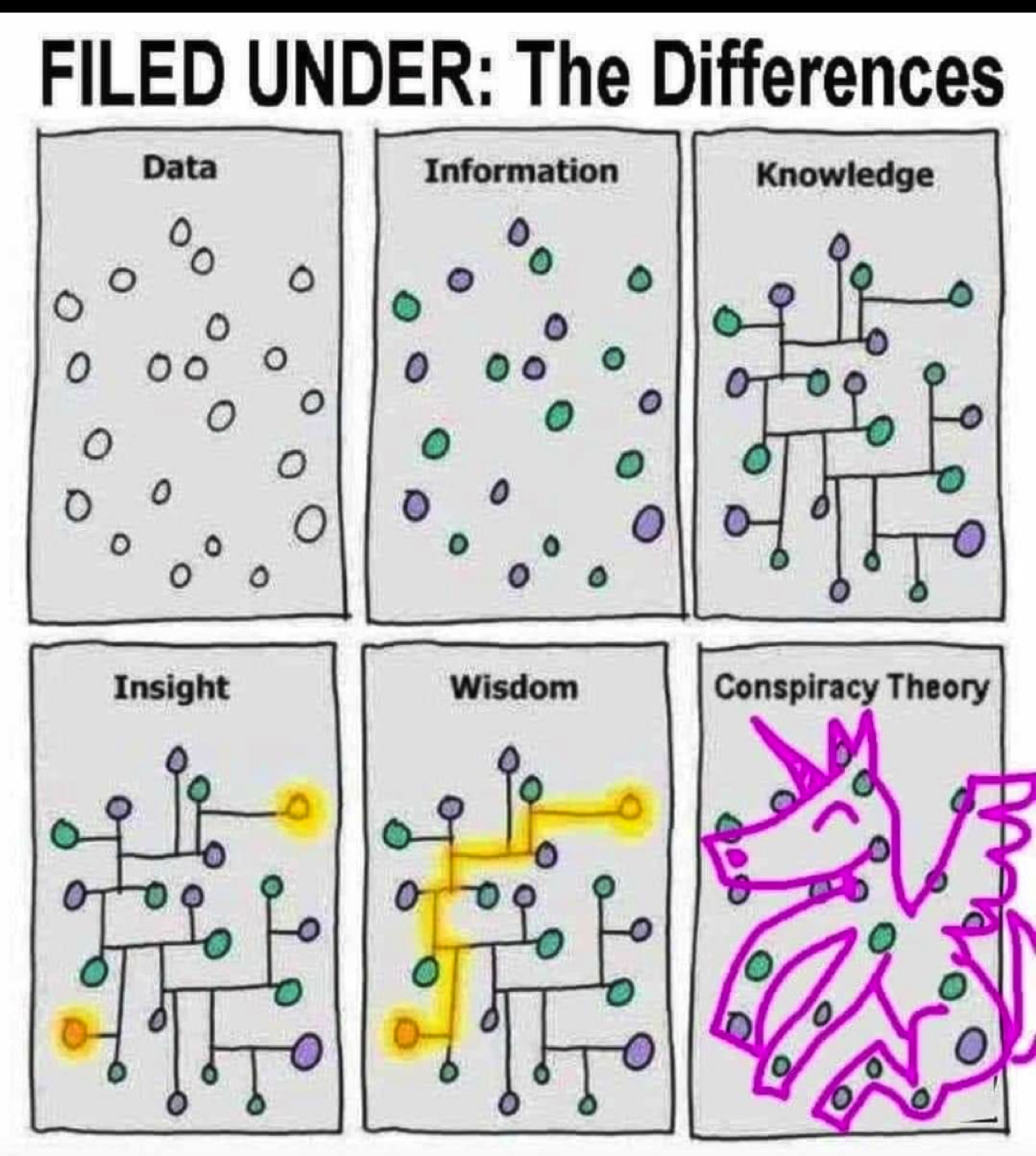
-, ( ), data (, ), information ( , ), knowledge () wisdom (), , ML DL 90 % 10% . knowledge wisdom, .
.
, , , . — end-to-end , (, .) . common sense .
3.
: , Legal AI, . , . Legal AI — . , (reasoning). , .
ML DL. , , (data) — Asscoation, , . — knowledge () wisdom (). , , , Legal AI.
, Legal AI. . . . reasoning, instances , , , .
- OWL Web Ontology Language Use Cases and Requirements: http://www.w3.org/TR/webont-req/
- FIBO OWL: https://spec.edmcouncil.org/fibo/OWL
- .., .. - // . . 63. 2/2013.
- The LKIF Core Ontology of Basic Legal Concepts: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/9368/e80bc052760d840305858ba57ef88a437c9e.pdf?_ga=2.29733564.2032886675.1596192665-1398097709.1596192665
- Legal Rule ML Core Specification: http://docs.oasis-open.org/legalruleml/legalruleml-core-spec/v1.0/legalruleml-core-spec-v1.0.html
- G. Guizzardi, G. Wagner. Using the Unified Foundational Ontology (UFO) as a Foundation for General Conceptual Modeling Languages (http://www.inf.ufes.br/~gguizzardi/TAO-CR.pdf)
- J. Kingston, W. Vandenberghe. A Comparison of a Regulatory Ontology with Existing Legal Ontology Frameworks (https://www.researchgate.net/profile/John_Kingston2/publication/220830541_A_Comparison_of_a_Regulatory_Ontology_with_Existing_Legal_Ontology_Frameworks/links/0fcfd51063b0034b07000000/A-Comparison-of-a-Regulatory-Ontology-with-Existing-Legal-Ontology-Frameworks.pdf)
- V. Leone, L. Di Caro, S. Villata. Taking stock of legal ontologies: a feature‐based comparative analysis, Springer Nature B.V. 2019
- C. Rodrigues, R. Azevedo, A.Trigueiro. Legal ontologies over time: A systematic mapping study. University of Pernambuco, Garanhuns-PE, ZIP 55294-902, Brazil
- Ontology Design Patterns (http://ontologydesignpatterns.org/wiki/Main_Page)
- CIDOC CRM (http://www.cidoc-crm.org/Version/version-5.0.4)
- The British Nationality Act as a logic program (https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/5689.5920)