
Recently, more and more companies are ripening to echeloned protection, when one solution protects the network perimeter, the other - end stations, the third constantly monitors the network, detecting anomalies, the fourth scans the network for open vulnerabilities, and so on. At the same time, the need for various integrations is growing and it's good when they are out of the box, that is, you don't need to write complex scripts.
We recently wrote about a new TS Solution service - CheckFlow . This is a free audit of network traffic (both internal and external). Flowmon- a telemetry analysis and network monitoring solution that provides valuable information for both network administrators and security guards: anomalies, scans, illegitimate servers, loops, illegitimate interactions, network intrusions, zero-day attacks and much more.
I also recommend referring to article 9 common network problems that can be detected using analysis with Flowmon .
Integration Flowmon & FortiGate
Integration was mentioned on our blog . In general, it consists in the fact that the Next-Generation Firewall (such as FortiGate) protects the perimeter, and Flowmon monitors the network infrastructure, thereby giving the customer full network visibility. However, Flowmon can only detect, but not prevent attacks and anomalies, because it works on telemetry, which is obtained using Netflow / IPFIX. An NGFW or NAC (Network Access Control) solution can be used to quarantine a suspicious or infected host.
So, the vendor Flowmon released a shell script that, in response to security incidents, can perform the following actions on FortiGate:
- Block the infected host by IP address (IP Ban);
- Quarantine the host using FortiClient at MAC address (Quarantine with FortiClient);
- Dynamic quarantine for all infected hosts by MAC addresses (Access Layer Quarantine);
Setting up
1. I will not go into the details of the script itself, I will only say that there are two versions: one for FortiGate above version 6.4.0, the other for earlier versions. The code is shown below.
Script code for FortiGate below version 6.4.0
#!/bin/bash
# Author: Jiri Knapek
# Description: This script is to quarantine IP on Fortigate Firewalls for FortiOS before 6.4.
# Version: 1.3
# Date: 8/3/2020
# Debug 1 = yes, 0 = no
DEBUG=0
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "Starting mitigation script" >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log
# Management IP/hostname of Firewall/ Core device
IP='10.10.30.210'
API_KEY='fp8114zdNpjp8Qf8zN4Hdp57dhgjjf'
# Default timeout for action is
# value in seconds or never
TIMEOUT='300'
# FortiGate API URL
BAN="https://$IP/api/v2/monitor/user/banned/add_users?access_token=$API_KEY"
function usage {
cat << EOF >&2
usage: mitigation_script.sh <options>
Optional:
--fw IP / hostname of Fortigate firewall
--timeout Timeout in seconds
--key FortiGate API key
EOF
exit
}
params="$(getopt -o f:t:k:h -l fw:,timeout:,key:,help --name "mitigation_script.sh" -- "$@")"
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "Params $params" >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log
if [ $? -ne 0 ]
then
usage
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "Got to usage." >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log
fi
eval set -- "$params"
unset params
while true
do
case $1 in
-f|--fw)
IP=("${2-}")
shift 2
;;
-k|--key)
API_KEY=("${2-}")
shift 2
;;
-t|--timeout)
TIMEOUT=("${2-}")
shift 2
;;
-h|--help)
usage
;;
--)
shift
break
;;
*)
usage
;;
esac
done
# we dont support any other args
[ $# -gt 0 ] && {
usage
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "INFO: Too many arguments. Got to usage." >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log 2>&1
}
cat << EOF >&2
----- My params are ------------------
FW = $IP
API KEY = $API_KEY
TIMEOUT = $TIMEOUT
TOKEN = $TOKEN
---------------------------------------
EOF
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && cat >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log << EOF >&2
----- My params are ------------------
FW = $IP
API KEY = $API_KEY
TIMEOUT = $TIMEOUT
TOKEN = $TOKEN
---------------------------------------
EOF
echo "Stdin read started..." >&2
LINE_NUM=1
array=()
while read line
do
IFS=$'\t'
array=($line)
echo "$LINE_NUM - ID ${array[0]} - type ${array[4]} - source ${array[10]}"
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo "$LINE_NUM - ID ${array[0]} - type ${array[4]} - source ${array[10]}" >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log 2>&1
LINE_NUM=$((LINE_NUM+1))
# BAN the source IP of the event
if [ $DEBUG -ne 0 ]; then
/usr/bin/curl -k -X POST -H "Content-Type": "application/json" --data "{ \"ip_addresses\": [\"${array[10]}\"], \"expiry\": $TIMEOUT}" $BAN >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log 2>&1
else
/usr/bin/curl -k -X POST -H "Content-Type": "application/json" --data "{ \"ip_addresses\": [\"${array[10]}\"], \"expiry\": $TIMEOUT}" $BAN
fi
done < /dev/stdin
echo "---- Everything completed ----"
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "---- Everything completed ----" >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log
Script code for FortiGate version 6.4.0 and higher
#!/bin/bash
# Author: Jiri Knapek
# Description: This script is to quarantine IP or MAC on Fortigate Firewalls and Security Fabric
# Version: 2.0
# Date: 7/8/2020
# Debug 1 = yes, 0 = no
DEBUG=0
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "Starting mitigation script" >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log
# Flowmon API access
USER='admin'
PASS='admin'
# Management IP/hostname of Firewall/ Core device
IP='10.10.30.210'
WEBHOOK='FlowmonADS'
API_KEY='s4mQH9j88kt1hkd4dsyjtsg8thghc4'
MAC=0
URL="https://$IP/api/v2/monitor/system/automation-stitch/webhook/$WEBHOOK"
function usage {
cat << EOF >&2
usage: mitigation_script.sh <options>
Optional:
--fw IP / hostname of Fortigate firewall
--user Username to be used for Flowmon API authentication
--pass Password for the user
--key FortiGate API key
--mac Add this parameter to enable MAC mitigation
EOF
exit
}
params="$(getopt -o f:u:p:k:h:m: -l fw:,key:,pass:,user:,help,mac: --name "mitigation_script.sh" -- "$@")"
if [ $? -ne 0 ]
then
usage
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "Got to usage." >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log
fi
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "Params $params" >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log
eval set -- "$params"
unset params
while true
do
case $1 in
-f|--fw)
IP=("${2-}")
shift 2
;;
-k|--key)
API_KEY=("${2-}")
shift 2
;;
-p|--pass)
PASS=("${2-}")
shift 2
;;
-u|--user)
USER=("${2-}")
shift 2
;;
-m|--mac)
MAC=1
shift 2
;;
-h|--help)
usage
;;
--)
shift
break
;;
*)
usage
;;
esac
done
# we dont support any other args
[ $# -gt 0 ] && {
usage
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "INFO: Got to usage." >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log 2>&1
}
if [ $MAC -ne 0 ];
then
# authenticate to localhost
OUTPUT="$(/usr/bin/curl "https://localhost/resources/oauth/token" -k -d 'grant_type=password' -d 'client_id=invea-tech' -d "username=$USER" -d "password=$PASS")"
TOKEN=""
echo "${OUTPUT}" > /tmp/access_token.json
if [[ $OUTPUT == *"access_token"* ]]; then
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "Successfully authenticated to Flowmon Collector!" >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log
TOKEN="$(cat /tmp/access_token.json | jq '.access_token')"
TOKEN="${TOKEN//\"}"
TOKEN="Authorization: bearer "$TOKEN
fi
fi
cat << EOF >&2
----- My params are ------------------
FW = $IP
API KEE = $API_KEY
URL = $URL
MAC = $MAC
TOKEN = $TOKEN
---------------------------------------
EOF
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && cat >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log << EOF >&2
----- My params are ------------------
FW = $IP
API KEE = $API_KEY
URL = $URL
MAC = $MAC
TOKEN = $TOKEN
---------------------------------------
EOF
echo "Stdin read started..." >&2
LINE_NUM=1
array=()
while read line
do
IFS=$'\t'
array=($line)
echo "$LINE_NUM - ID ${array[0]} - type ${array[4]} - source ${array[10]}"
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo "$LINE_NUM - ID ${array[0]} - type ${array[4]} - source ${array[10]}" >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log 2>&1
# Call a webhook
if [ $MAC -ne 0 ];
then
MAC_ADDR="$(/usr/bin/curl "https://localhost/rest/ads/event/${array[0]}" -G -k -H "$TOKEN" | jq '.macAddress')"
if [ $DEBUG -ne 0 ]; then
/usr/bin/curl -k -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" --data "{ \"srcip\": \"${array[10]}\", \"mac\": $MAC_ADDR, \"fctuid\": \"A8BA0B12DA694E47BA4ADF24F8358E2F\"}" $URL >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log 2>&1
else
/usr/bin/curl -k -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" --data "{ \"srcip\": \"${array[10]}\", \"mac\": $MAC_ADDR, \"fctuid\": \"A8BA0B12DA694E47BA4ADF24F8358E2F\"}" $URL
fi
else
if [ $DEBUG -ne 0 ]; then
/usr/bin/curl -k -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" --data "{ \"srcip\": \"${array[10]}\", \"fctuid\": \"A8BA0B12DA694E47BA4ADF24F8358E2F\"}" $URL >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log 2>&1
else
/usr/bin/curl -k -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" --data "{ \"srcip\": \"${array[10]}\", \"fctuid\": \"A8BA0B12DA694E47BA4ADF24F8358E2F\"}" $URL
fi
fi
LINE_NUM=$((LINE_NUM+1))
done < /dev/stdin
echo "---- Everything completed ----"
[ $DEBUG -ne 0 ] && echo `date` "---- Everything completed ----" >> /tmp/fg-mitigation.log
2. I am using FortiGate version 6.4.2. In the script itself, on lines 13 and 14, you should add your username and password to Flowmon , as well as add the API key from clause 5 , the FortiGate IP address and the Webhook name (the name of the automation mechanism).

3. In the web interface, FortiGate should be added in the Security Fabric> Automation> New Automation Stitch tab . Name - FlowmonADS , Status - Enabled , Trigger - Incoming Webhook , Action - IP BAN, Access Layer Quarantine, Quarantine with FortiCLient (if used).
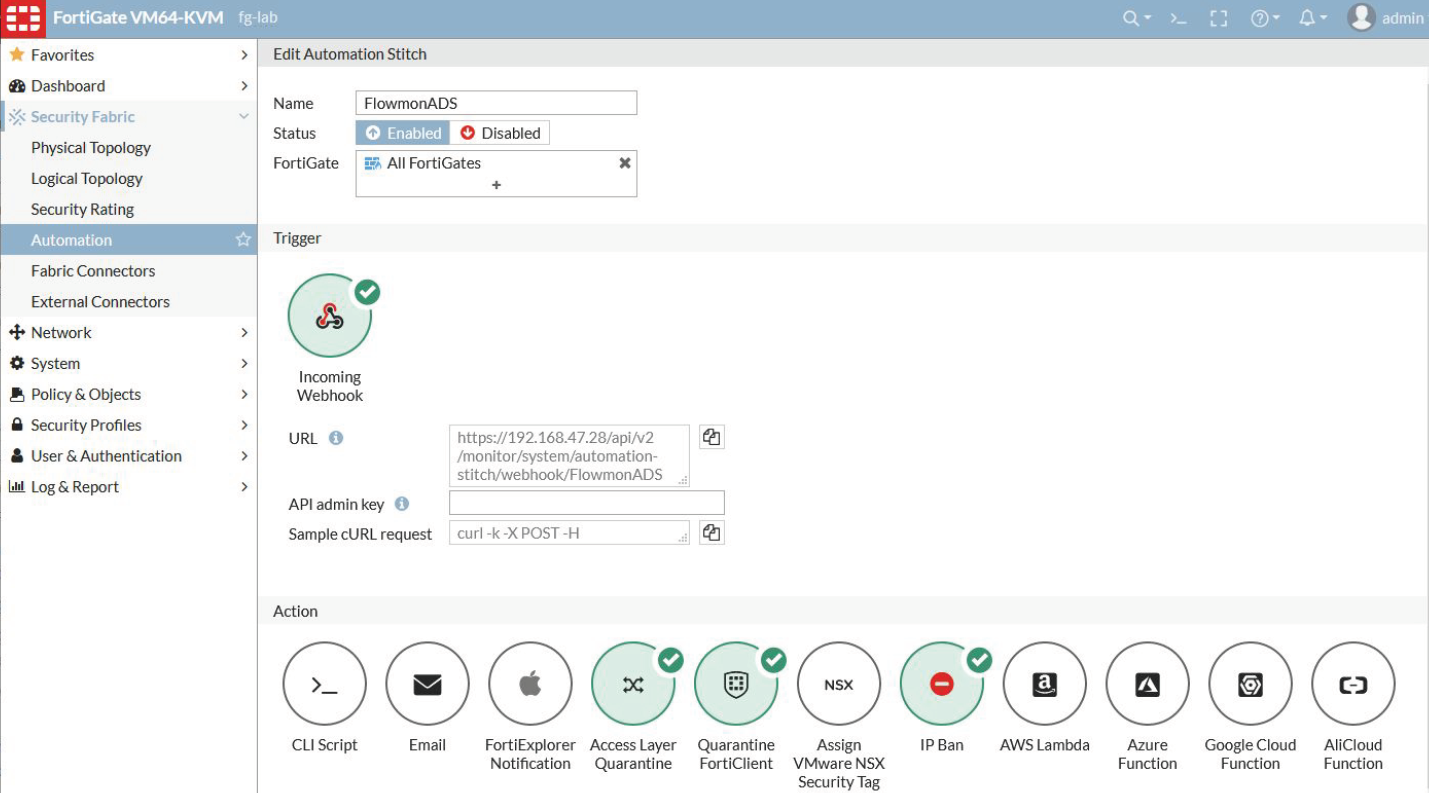
4. Then you will see a window as in the screenshot below with the FortiGate URL for this Webhook, a field for the admin token API (we will create it later) and an example request.

5. Next, you need to create an administrator profile, which will have rights. System tab > Admin Profiles> Create New .
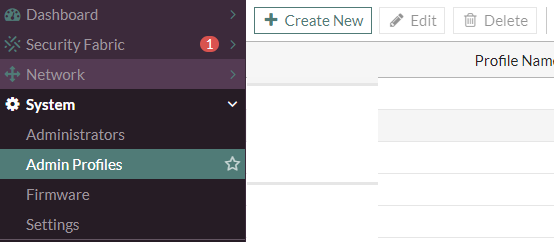
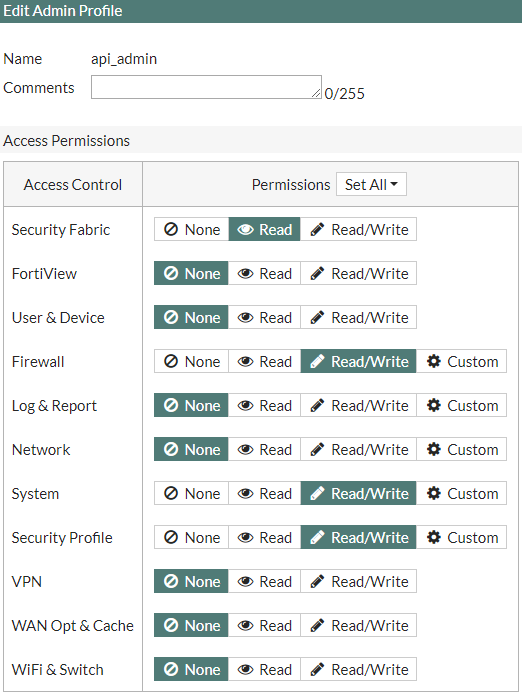
6. Assign the rights to Security Fabric - Read, Firewall - Read / Write, System - Read / Write, Security Profile - Read / Write .
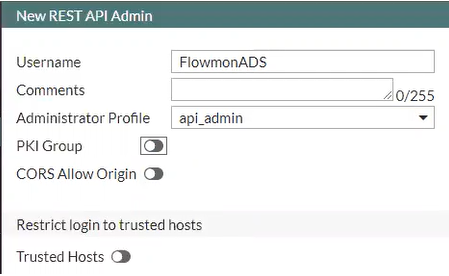
7. After that, in the System> Administrators tab, create a new administrator with the api_admin profile . Additionally, in the Trusted Hosts field, you can specify trusted networks or the IP address of the Flowmon.
Note : Trusted Hosts parameterallows you to hard- code IP segments from which api_admin can send API requests to FortiGate, thus this is the recommended setting.
8. After this step, an API key is generated , which must be added to the initial script along with other data specified in paragraph 1 and in the webhook in paragraph 4.
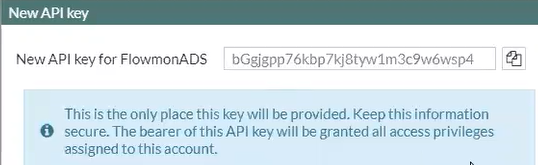
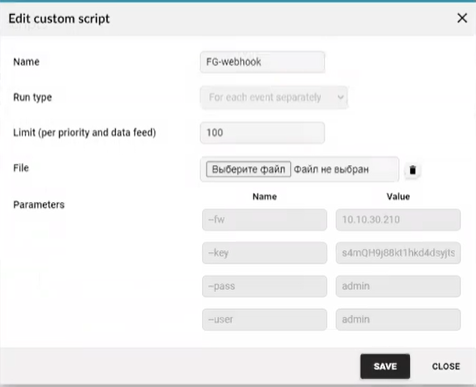
9. Next, go to Flowmon in the ADS (Anomaly Detection System) module in the System> System tab Settings> Custom Scripts> New Custom Script> Select file with .sh extension . Next, you should set the parameters --fw (FortiGate IP address), --key (API token), --mac (nothing), --pass (password from REST API Flowmon), --user (REST API user Flowmon). Then click the Save button .
Note : --pass and --user are admin / admin by default.
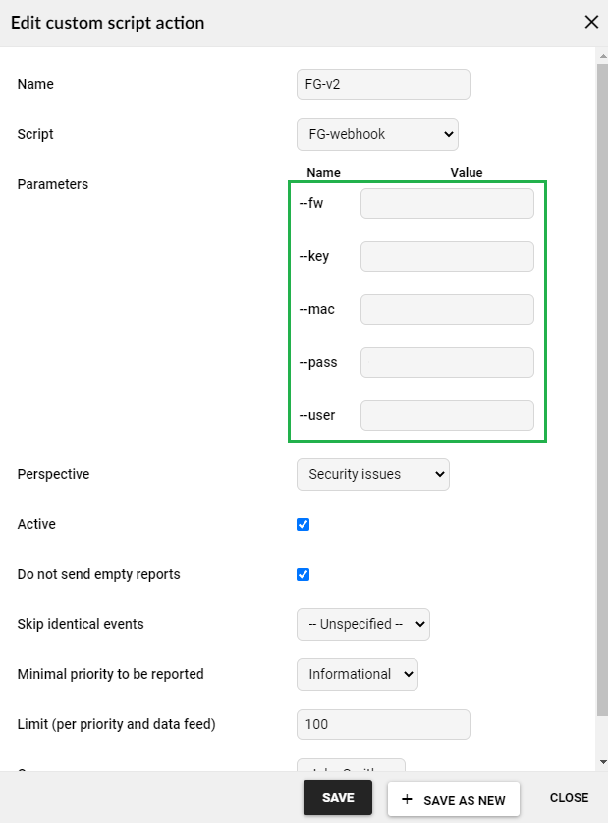
10. The final step is to establish the events to which the given program code will be triggered. In the Settings> Processing> Custom Scripts> New Custom Script Action tab, change the Perspective parameterto Security Issues , set the Minimal priority to be reported and check the parameters from the previous step.
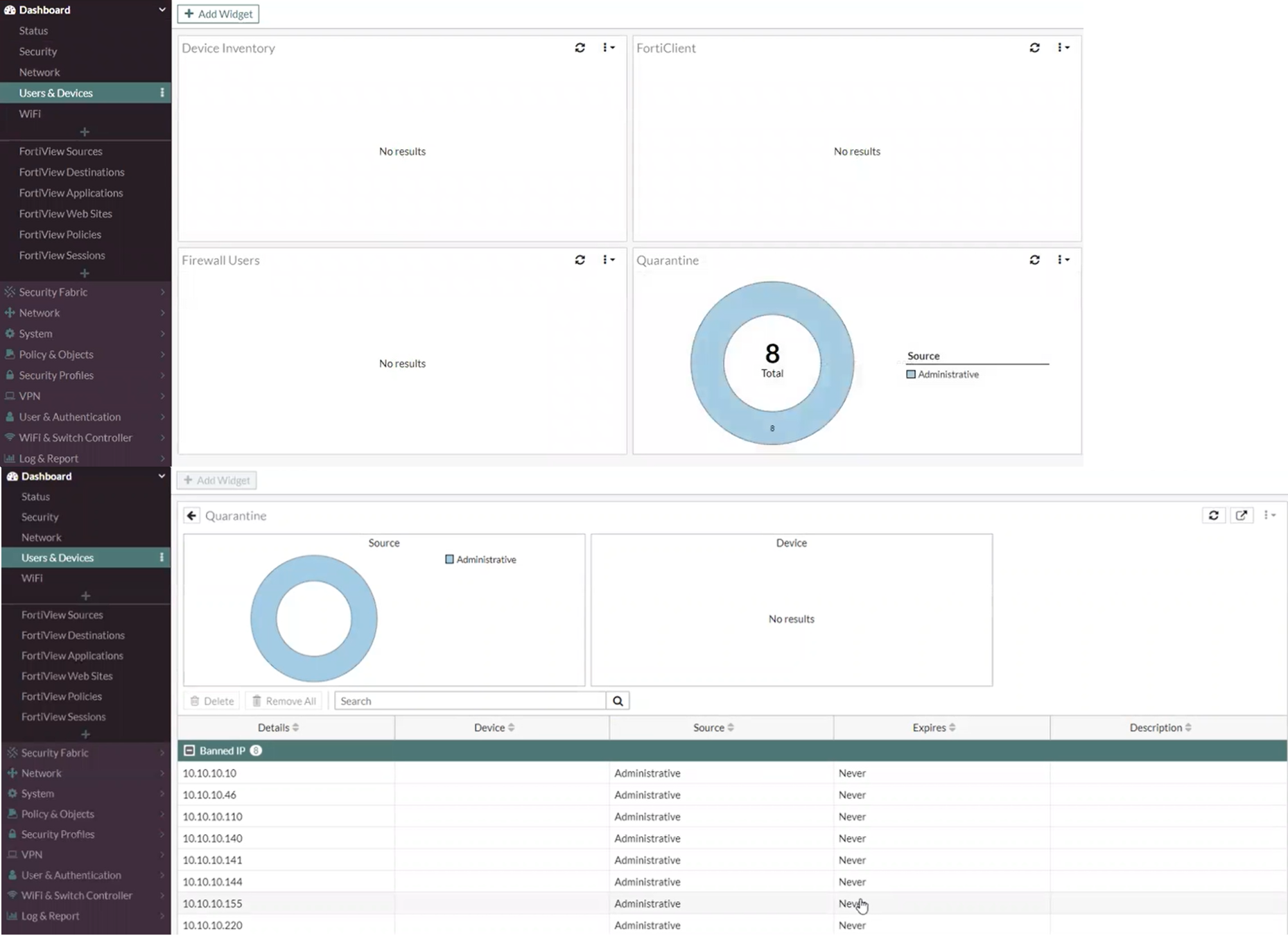
Check
If an event from the Security Issues category is triggered on Flowmon, FortiGate will block this host. Further, in the convenient Quarantine widget, you can view potentially infected hosts by falling inside. Or through the command in the CLI diagnose user quarantine list .
After information security, the administrator can start investigating the incident using Flowmon ADS, identifying the initially infected host, through which ports the malware spreads and its behavior. With the help of solutions to protect workstations, for example, FortiEDR, you can cure the machine and conduct an investigation of a security incident.
In order to remove a host from quarantine, select it and click the Delete or Remove All buttonto move all hosts out of quarantine.
Conclusion
The ubiquitous approach to defense in depth is pushing many vendors to integrate with other solutions out of the box. This article covered how to integrate, configure and demonstrate how Flowmon and FortiGate work together.
In the near future, we are planning a webinar, where we will tell in more detail how Flowmon and Fortinet complement each other, their integration with each other, and also answer your questions. Registration is available here .
If you are interested in this topic, then stay tuned in our channels (Telegram, Facebook, VK, TS Solution Blog)!