content-visibilityin Chromium 85. It should significantly affect the speed of the first load and first render on the site; moreover, you can interact with the newly rendered content immediately, without waiting for the rest of the content to load. content-visibilityforces the user agent to skip marking and painting elements that are not on the screen. In fact, it works like a lazy-load, only not on loading resources, but on their rendering.
In this demo
content-visibility: auto, when applied to split content, it gives a 7x faster render speed.
Support
content-visibilitybased on primitives from the CSS Containment specification . While currently content-visibilityonly supported in Chromium 85 (and considered "prototypable" in Firefox), the Containment specification is supported in most modern browsers.
Principle of operation
The main goal of CSS Containment is to improve the rendering performance of web content by providing predictable isolation of the DOM subtree from the rest of the page.
Basically, the developer can tell the browser which parts of the page are encapsulated as a set of content, allowing browsers to manipulate the content without having to consider state outside the subtree. The browser can optimize page rendering by knowing which subtrees contain isolated content.
There are four types of CSS Containment, each serving as a value for a CSS property
containand can be combined with others:
size: , . , , .layout: . , , , .style: , , , (, ). , , , — .paint: . , , . , .
content-visibility
It may be confusing which values are
containbest to use, since browser optimizations can only work with the correct set of parameters. It's worth playing around with the values to empirically find out what works best. Better to use it content-visibilityfor automatic tuning contain. content-visibility: autoguarantees the maximum possible increase in productivity with the minimum of effort.
In automatic mode, the property gets the layout, style and paint attributes, and when the element goes off the edges of the screen, it gets size and stops painting and checking the content. This means that as soon as an element leaves the render area, its descendants stop rendering. The browser recognizes the dimensions of the element, but does nothing else until rendering is needed.
Example - travel blog
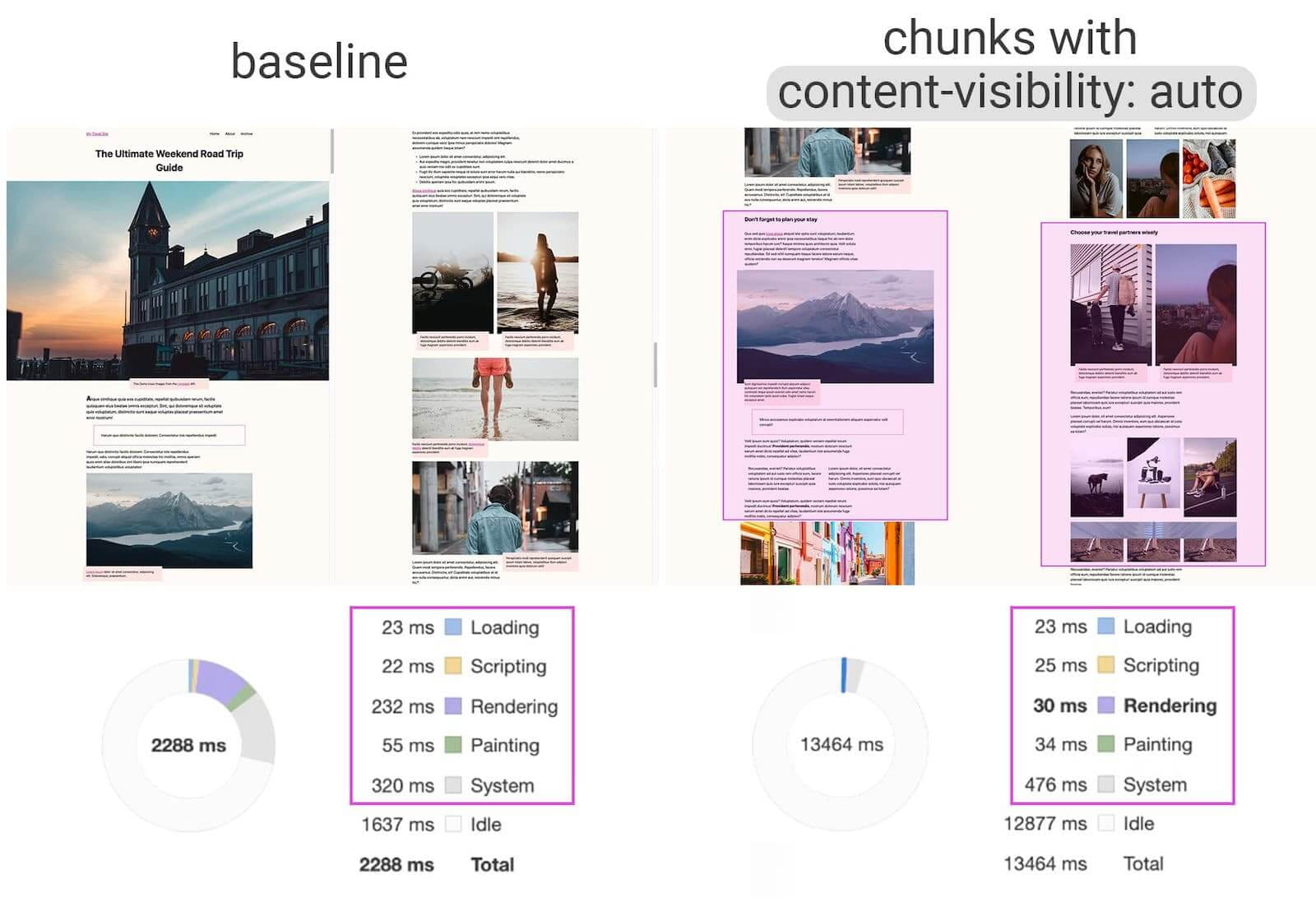
Usually a travel blog has several stories with images and descriptions. Here's what happens in a typical browser when it goes to a travel blog:
- Part of the page is loaded from the network along with the necessary resources
- The browser styles and places all content on the page without distinguishing between visible and invisible content
- Browser goes to step 1 until all resources are loaded
In step 2, the browser processes the content, trying to find changes. It updates the styles and layout of any new element, along with elements that may have changed as a result of the updates. This is rendering. It takes time.

Now let's imagine what we put
content-visibility: autoon each blog post. The basic system is the same: the browser downloads and renders parts of the page. However, the difference in the amount of work done in step 2.Ccontent-visibilitythe browser will style and place the content that the user is currently seeing (on the screen). But when handling off-screen stories, the browser will skip rendering of the entire element and only host the container. The loading performance of this page will be as if it had filled posts on the screen and empty containers for each post outside of it. It turns out much faster, gaining up to 50% of the loading time. In our example, we see an improvement from 232ms rendering to 30ms, which is a 7x improvement in performance.
What do you need to do to take advantage of these benefits? First, we split the content into parts:

After, we apply the subsequent styling to the parts:
.story {
content-visibility: auto;
contain-intrinsic-size: 1000px; /* */
}
, , . , , , .
contain-intrinsic-size
To understand the potential benefits
content-visibility, the browser must enforce sizing constraints to ensure that the rendering of the content does not affect the dimensions of the elements. This means that the item will be placed as if it were empty. If the element has no height defined, then it will be equal to zero.
Fortunately, css has another ability,
contain-intrinsic-sizwhich provides the ability to determine the actual size of an element if it has been compressed. In our example, we set the width and height to roughly 1000px.
This means that it will be positioned as if there is a single "internal size" file, while ensuring that the div still takes up space.
contain-intrinsic-siz .
Hide content from content-visibility: hidden
content-visibility: hiddendoes what it content-visibility: autodoes with offscreen content. However, unlike auto, it does not automatically start rendering content to the screen.
Compare this to the usual ways to hide element content:
- display: none: Hides the element and removes the rendering state. This means that retrieving an item will cost the same load as creating a new item.
- visibility: hidden: hides the element and leaves the rendering state. This doesn't actually remove the element from the document, as it (and its subtree) still takes up geometric space on the page and can still be clicked. It also updates the rendering state whenever needed, even if hidden.
content-visibility: hiddenon the other hand, hides the element while maintaining the rendering state so that if any changes are needed, they will only happen when the element is shown on screen.
Conclusion
content-visibilityand the CSS Containment Spec allow you to significantly speed up the rendering and loading of pages without any complex manipulations, on bare CSS.
The CSS Containment Spec
MDN Docs on CSS Containment
CSSWG Drafts
The following information was used in the preparation of the material - web.dev/content-visibility
Advertising
Servers for hosting sites - this is about our epic ! All servers "out of the box" are protected from DDoS attacks, automatic installation of a convenient VestaCP control panel. Better to try it once;)
