Static code analysis shows the greatest efficiency when making changes to a project, since errors are always more difficult to fix in the future than to prevent them from occurring in the early stages. We continue to expand the options for using PVS-Studio in continuous development systems and show how to set up the analysis of pull requests using self-hosted agents in Microsoft Azure DevOps, using the example of the Minetest game.
Briefly about what we are dealing with
Minetest is an open source cross-platform game engine containing about 200,000 lines of C, C ++ and Lua code. It allows you to create different game modes in voxel space. Supports multiplayer, and lots of community mods. The project repository is hosted here: https://github.com/minetest/minetest .
The following tools were used to set up a regular error search:
PVS-Studio is a static code analyzer in C, C ++, C # and Java to find errors and security defects.
Azure DevOps is a cloud-based platform that provides the ability to develop, run applications, and store data on remote servers.
You can use Windows and Linux virtual machines to perform development tasks in Azure. However, running agents on local hardware has several significant advantages:
- Localhost may have more resources than Azure VM;
- The agent does not "disappear" after completing its task;
- The ability to directly customize the environment, and more flexible control over the build processes;
- Storing intermediate files locally has a positive effect on build speed;
- You can complete over 30 tasks per month for free.
Preparing to use a self-hosted agent
The process of getting started in Azure is described in detail in the article " PVS-Studio Goes to the Clouds: Azure DevOps ", so I'll go straight to creating a self-hosted agent.
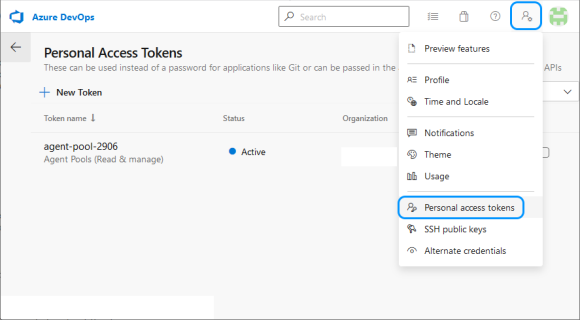
In order for agents to have the right to connect to project pools, they need a special Access Token. You can get it on the "Personal Access Tokens" page, in the "User settings" menu.
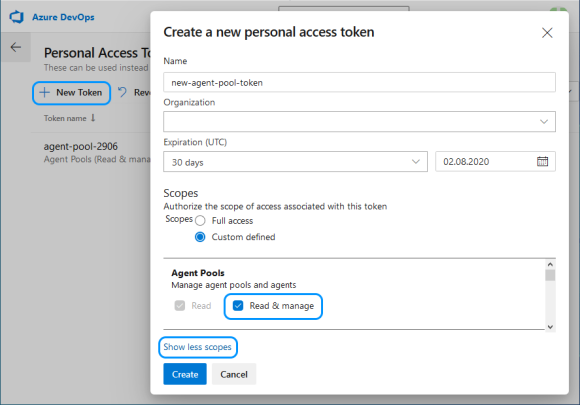
After clicking on "New token", you need to specify a name and select Read & manage Agent Pools (you may need to expand the full list through "Show all scopes").
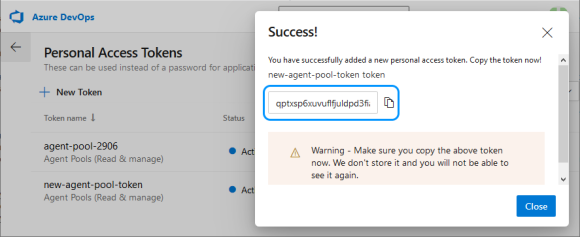
You need to copy the token, as Azure will no longer show it, and you will have to make a new one.
A Docker container based on Windows Server Core will be used as an agent. The host is my work computer on Windows 10 x64 with Hyper-V.
First, you need to expand the amount of disk space available to Docker containers.
On Windows, for this you need to modify the 'C: \ ProgramData \ Docker \ config \ daemon.json' file as follows:
{
"registry-mirrors": [],
"insecure-registries": [],
"debug": true,
"experimental": false,
"data-root": "d:\\docker",
"storage-opts": [ "size=40G" ]
}To create a Docker image for agents with a build system and everything you need, add a Docker file in the 'D: \ docker-agent' directory with the following content:
# escape=`
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/framework/runtime
SHELL ["cmd", "/S", "/C"]
ADD https://aka.ms/vs/16/release/vs_buildtools.exe C:\vs_buildtools.exe
RUN C:\vs_buildtools.exe --quiet --wait --norestart --nocache `
--installPath C:\BuildTools `
--add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Workload.VCTools `
--includeRecommended
RUN powershell.exe -Command `
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; `
[System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol =
[System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; `
iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient)
.DownloadString('https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1')); `
choco feature enable -n=useRememberedArgumentsForUpgrades;
RUN powershell.exe -Command `
choco install -y cmake --installargs '"ADD_CMAKE_TO_PATH=System"'; `
choco install -y git --params '"/GitOnlyOnPath /NoShellIntegration"'
RUN powershell.exe -Command `
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/vcpkg.git; `
.\vcpkg\bootstrap-vcpkg -disableMetrics; `
$env:Path += '";C:\vcpkg"'; `
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(
'"Path"', $env:Path, [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine); `
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(
'"VCPKG_DEFAULT_TRIPLET"', '"x64-windows"',
[System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)
RUN powershell.exe -Command `
choco install -y pvs-studio; `
$env:Path += '";C:\Program Files (x86)\PVS-Studio"'; `
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(
'"Path"', $env:Path, [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)
RUN powershell.exe -Command `
$latest_agent =
Invoke-RestMethod -Uri "https://api.github.com/repos/Microsoft/
azure-pipelines-agent/releases/latest"; `
$latest_agent_version =
$latest_agent.name.Substring(1, $latest_agent.tag_name.Length-1); `
$latest_agent_url =
'"https://vstsagentpackage.azureedge.net/agent/"' + $latest_agent_version +
'"/vsts-agent-win-x64-"' + $latest_agent_version + '".zip"'; `
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $latest_agent_url -Method Get -OutFile ./agent.zip; `
Expand-Archive -Path ./agent.zip -DestinationPath ./agent
USER ContainerAdministrator
RUN reg add hklm\system\currentcontrolset\services\cexecsvc
/v ProcessShutdownTimeoutSeconds /t REG_DWORD /d 60
RUN reg add hklm\system\currentcontrolset\control
/v WaitToKillServiceTimeout /t REG_SZ /d 60000 /f
ADD .\entrypoint.ps1 C:\entrypoint.ps1
SHELL ["powershell", "-Command",
"$ErrorActionPreference = 'Stop';
$ProgressPreference = 'SilentlyContinue';"]
ENTRYPOINT .\entrypoint.ps1The result will be a build system based on MSBuild for C ++, with Chocolatey for installing PVS-Studio, CMake and Git. For convenient management of the libraries on which the project depends, Vcpkg is built. And also the latest version of the Azure Pipelines Agent is downloaded.
To initialize the agent from the ENTRYPOINT Docker file, the PowerShell script 'entrypoint.ps1' is called, to which you need to add the project "organization" URL, agent pool token, and PVS-Studio license parameters:
$organization_url = "https://dev.azure.com/< Microsoft Azure>"
$agents_token = "<token >"
$pvs_studio_user = "< PVS-Studio>"
$pvs_studio_key = "< PVS-Studio>"
try
{
C:\BuildTools\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat
PVS-Studio_Cmd credentials -u $pvs_studio_user -n $pvs_studio_key
.\agent\config.cmd --unattended `
--url $organization_url `
--auth PAT `
--token $agents_token `
--replace;
.\agent\run.cmd
}
finally
{
# Agent graceful shutdown
# https://github.com/moby/moby/issues/25982
.\agent\config.cmd remove --unattended `
--auth PAT `
--token $agents_token
}Commands for building the image and starting the agent:
docker build -t azure-agent -m 4GB .
docker run -id --name my-agent -m 4GB --cpu-count 4 azure-agent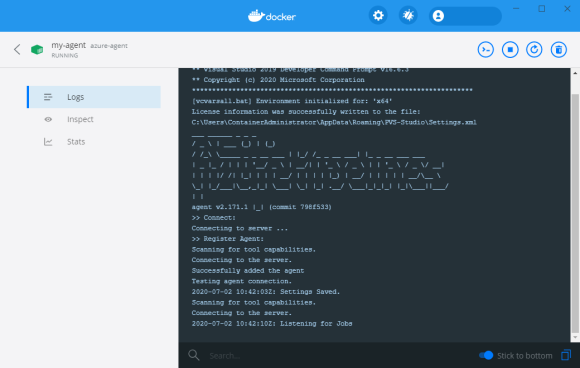
The agent is running and ready to perform tasks.
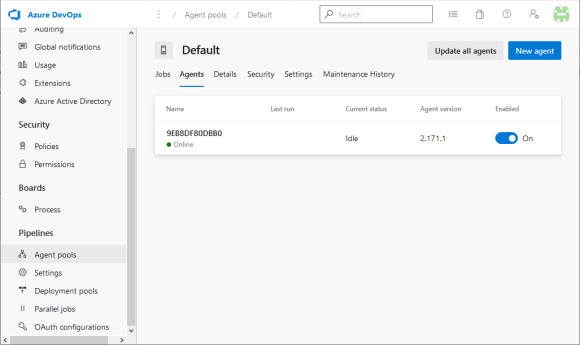
Running analysis on a self-hosted agent
For PR analysis, a new pipeline is created with the following script:
trigger: none
pr:
branches:
include:
- '*'
pool: Default
steps:
- script: git diff --name-only
origin/%SYSTEM_PULLREQUEST_TARGETBRANCH% >
diff-files.txt
displayName: 'Get committed files'
- script: |
cd C:\vcpkg
git pull --rebase origin
CMD /C ".\bootstrap-vcpkg -disableMetrics"
vcpkg install ^
irrlicht zlib curl[winssl] openal-soft libvorbis ^
libogg sqlite3 freetype luajit
vcpkg upgrade --no-dry-run
displayName: 'Manage dependencies (Vcpkg)'
- task: CMake@1
inputs:
cmakeArgs: -A x64
-DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=C:/vcpkg/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DENABLE_GETTEXT=0 -DENABLE_CURSES=0 ..
displayName: 'Run CMake'
- task: MSBuild@1
inputs:
solution: '**/*.sln'
msbuildArchitecture: 'x64'
platform: 'x64'
configuration: 'Release'
maximumCpuCount: true
displayName: 'Build'
- script: |
IF EXIST .\PVSTestResults RMDIR /Q/S .\PVSTestResults
md .\PVSTestResults
PVS-Studio_Cmd ^
-t .\build\minetest.sln ^
-S minetest ^
-o .\PVSTestResults\minetest.plog ^
-c Release ^
-p x64 ^
-f diff-files.txt ^
-D C:\caches
PlogConverter ^
-t FullHtml ^
-o .\PVSTestResults\ ^
-a GA:1,2,3;64:1,2,3;OP:1,2,3 ^
.\PVSTestResults\minetest.plog
IF NOT EXIST "$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)" ^
MKDIR "$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)"
powershell -Command ^
"Compress-Archive -Force ^
'.\PVSTestResults\fullhtml' ^
'$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)\fullhtml.zip'"
displayName: 'PVS-Studio analyze'
continueOnError: true
- task: PublishBuildArtifacts@1
inputs:
PathtoPublish: '$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)'
ArtifactName: 'psv-studio-analisys'
publishLocation: 'Container'
displayName: 'Publish analysis report'This script will run when the PR is received and will be executed on agents assigned to the default pool. You only need to give him permission to work with this pool.
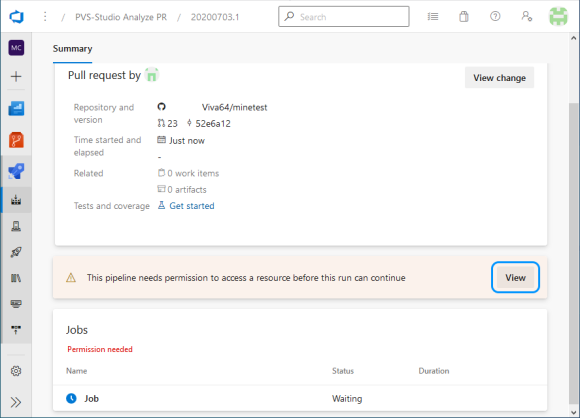
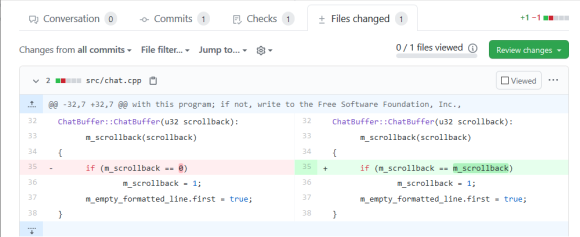
The script saves the list of changed files obtained using git diff. Then the dependencies are updated, the project solution is generated through CMake, and it is built.
If the build was successful, the analysis of the changed files is started (flag '-f diff-files.txt'), ignoring the auxiliary projects created by CMake (select only the required project with the '-S minetest' flag). To speed up the search for links between header and C ++ source files, a special cache is created, which will be stored in a separate directory (flag '-DC: \ caches').
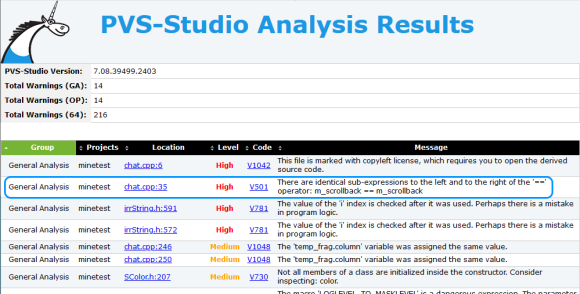
Thus, we can now receive reports on the analysis of changes in the project.
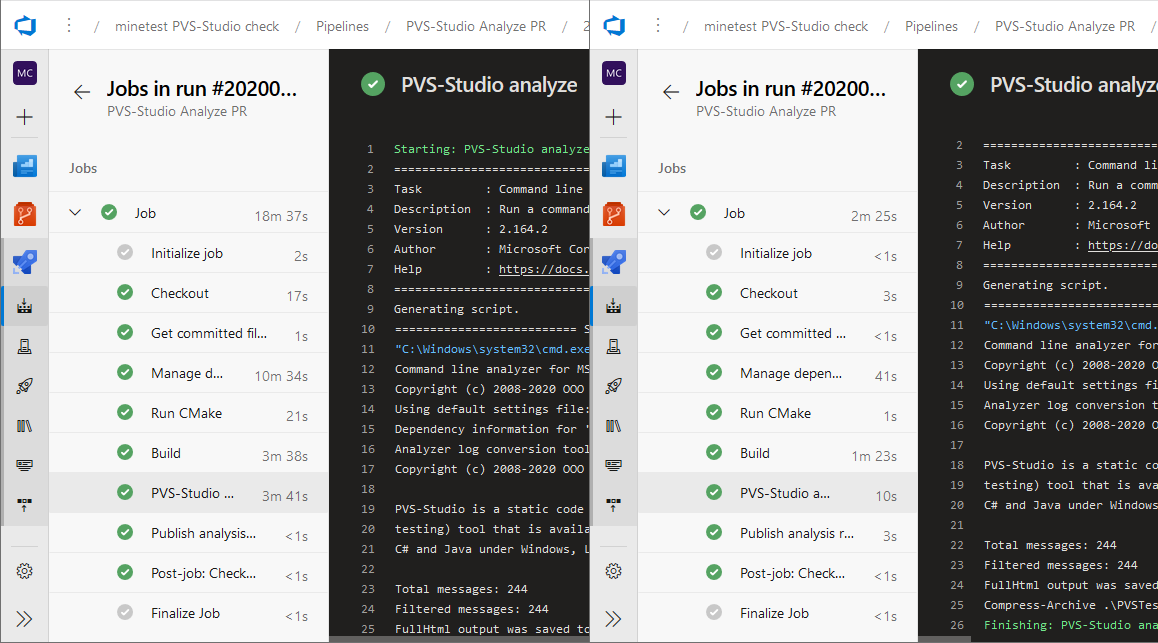
As it was said at the beginning of the article, a pleasant bonus of using self-hosted agents is a noticeable acceleration of tasks execution due to local storage of intermediate files.
Some bugs found in Minetest
Overwriting result
V519 The 'color_name' variable is assigned values twice successively. Perhaps this is a mistake. Check lines: 621, 627. string.cpp 627
static bool parseNamedColorString(const std::string &value,
video::SColor &color)
{
std::string color_name;
std::string alpha_string;
size_t alpha_pos = value.find('#');
if (alpha_pos != std::string::npos) {
color_name = value.substr(0, alpha_pos);
alpha_string = value.substr(alpha_pos + 1);
} else {
color_name = value;
}
color_name = lowercase(value); // <=
std::map<const std::string, unsigned>::const_iterator it;
it = named_colors.colors.find(color_name);
if (it == named_colors.colors.end())
return false;
....
}This function should parse a color name with a transparency parameter (for example, Green # 77 ) and return its code. Depending on the result of checking the condition, the result of the line splitting or a copy of the function argument is passed to the color_name variable . However, then not the resulting string itself is converted to lowercase, but the original argument. As a result, it cannot be found in the color dictionary if the transparency parameter is present. We can fix this line like this:
color_name = lowercase(color_name);Unnecessary condition checks V547 Expression 'nearest_emergefull_d == -1' is always true. clientiface.cpp 363
void RemoteClient::GetNextBlocks (....)
{
....
s32 nearest_emergefull_d = -1;
....
s16 d;
for (d = d_start; d <= d_max; d++) {
....
if (block == NULL || surely_not_found_on_disk || block_is_invalid) {
if (emerge->enqueueBlockEmerge(peer_id, p, generate)) {
if (nearest_emerged_d == -1)
nearest_emerged_d = d;
} else {
if (nearest_emergefull_d == -1) // <=
nearest_emergefull_d = d;
goto queue_full_break;
}
....
}
....
queue_full_break:
if (nearest_emerged_d != -1) { // <=
new_nearest_unsent_d = nearest_emerged_d;
} else ....
}The nearest_emergefull_d variable does not change during the loop operation, and its checking does not affect the algorithm execution. Either this is the result of inaccurate copy-paste, or they forgot to carry out some calculations with it.
V560 A part of conditional expression is always false: y> max_spawn_y. mapgen_v7.cpp 262
int MapgenV7::getSpawnLevelAtPoint(v2s16 p)
{
....
while (iters > 0 && y <= max_spawn_y) { // <=
if (!getMountainTerrainAtPoint(p.X, y + 1, p.Y)) {
if (y <= water_level || y > max_spawn_y) // <=
return MAX_MAP_GENERATION_LIMIT; // Unsuitable spawn point
// y + 1 due to biome 'dust'
return y + 1;
}
....
}The value of the ' y ' variable is checked before the next iteration of the loop. The subsequent, opposite, comparison will always return false and, in general, does not affect the result of the condition test.
Loss of pointer checks
V595 of The 'm_client' pointer WAS Utilized the before IT WAS verified Against nullptr. Check lines: 183, 187. game.cpp 183
void gotText(const StringMap &fields)
{
....
if (m_formname == "MT_DEATH_SCREEN") {
assert(m_client != 0);
m_client->sendRespawn();
return;
}
if (m_client && m_client->modsLoaded())
m_client->getScript()->on_formspec_input(m_formname, fields);
}Before accessing the m_client pointer, it is checked if it is not null using the assert macro . But this only applies to debug build. Such a precaution, when building into release, is replaced with a dummy, and there is a risk of dereferencing a null pointer.
Bit or not bit?
V616 The '(FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL)' named constant with the value of 0 is used in the bitwise operation. CGUITTFont.h 360
typedef enum FT_Render_Mode_
{
FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL = 0,
FT_RENDER_MODE_LIGHT,
FT_RENDER_MODE_MONO,
FT_RENDER_MODE_LCD,
FT_RENDER_MODE_LCD_V,
FT_RENDER_MODE_MAX
} FT_Render_Mode;
#define FT_LOAD_TARGET_( x ) ( (FT_Int32)( (x) & 15 ) << 16 )
#define FT_LOAD_TARGET_NORMAL FT_LOAD_TARGET_( FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL )
void update_load_flags()
{
// Set up our loading flags.
load_flags = FT_LOAD_DEFAULT | FT_LOAD_RENDER;
if (!useHinting()) load_flags |= FT_LOAD_NO_HINTING;
if (!useAutoHinting()) load_flags |= FT_LOAD_NO_AUTOHINT;
if (useMonochrome()) load_flags |=
FT_LOAD_MONOCHROME | FT_LOAD_TARGET_MONO | FT_RENDER_MODE_MONO;
else load_flags |= FT_LOAD_TARGET_NORMAL; // <=
}The FT_LOAD_TARGET_NORMAL macro expands to zero, and the bitwise "or" will not set any flags in load_flags , the else branch can be removed.
Rounding integer division
V636 The 'rect.getHeight () / 16' expression was implicitly cast from 'int' type to 'float' type. Consider utilizing an explicit type cast to avoid the loss of a fractional part. An example: double A = (double) (X) / Y ;. hud.cpp 771
void drawItemStack(....)
{
float barheight = rect.getHeight() / 16;
float barpad_x = rect.getWidth() / 16;
float barpad_y = rect.getHeight() / 16;
core::rect<s32> progressrect(
rect.UpperLeftCorner.X + barpad_x,
rect.LowerRightCorner.Y - barpad_y - barheight,
rect.LowerRightCorner.X - barpad_x,
rect.LowerRightCorner.Y - barpad_y);
}Getters rect returns an integer value. The result of division of integers is written to a floating point variable, and the fractional part is lost. It looks like there are mismatched data types in these calculations.
Suspicious sequence branching statements
V646 Consider Inspecting the application's logic. It's possible that 'else' keyword is missing. treegen.cpp 413
treegen::error make_ltree(...., TreeDef tree_definition)
{
....
std::stack <core::matrix4> stack_orientation;
....
if ((stack_orientation.empty() &&
tree_definition.trunk_type == "double") ||
(!stack_orientation.empty() &&
tree_definition.trunk_type == "double" &&
!tree_definition.thin_branches)) {
....
} else if ((stack_orientation.empty() &&
tree_definition.trunk_type == "crossed") ||
(!stack_orientation.empty() &&
tree_definition.trunk_type == "crossed" &&
!tree_definition.thin_branches)) {
....
} if (!stack_orientation.empty()) { // <=
....
}
....
}Here are the else-if sequences in the tree generation algorithm. In the middle, the next if block is on the same line with the closing parenthesis of the previous else . Perhaps the code works correctly: before this if -a, the trunk blocks are created, and then the leaves; or maybe they missed the else . Surely this can only be said by the developer.
Incorrect memory allocation check
V668 There is no sense in testing the 'clouds' pointer against null, as the memory was allocated using the 'new' operator. The exception will be generated in the case of memory allocation error. game.cpp 1367
bool Game::createClient(....)
{
if (m_cache_enable_clouds) {
clouds = new Clouds(smgr, -1, time(0));
if (!clouds) {
*error_message = "Memory allocation error (clouds)";
errorstream << *error_message << std::endl;
return false;
}
}
}In case new fails to create an object, a std :: bad_alloc exception will be thrown and must be handled by a try-catch block. And checking in this form is useless.
Reading an array out of
bounds V781 The value of the 'i' index is checked after it was used. Perhaps there is a mistake in program logic. irrString.h 572
bool equalsn(const string<T,TAlloc>& other, u32 n) const
{
u32 i;
for(i=0; array[i] && other[i] && i < n; ++i) // <=
if (array[i] != other[i])
return false;
// if one (or both) of the strings was smaller then they
// are only equal if they have the same length
return (i == n) || (used == other.used);
}The array elements are accessed before checking the index, which can lead to an error. It might be worth rewriting the loop like this:
for (i=0; i < n; ++i) // <=
if (!array[i] || !other[i] || array[i] != other[i])
return false;Other Errors
This article is about analyzing pull requests in Azure DevOps and is not intended to provide a detailed overview of the errors in the Minetest project. Here are just some of the code snippets that I found interesting. We suggest that the authors of the project not follow this article to fix errors and perform a more thorough analysis of the warnings that PVS-Studio will issue.
Conclusion
Thanks to the flexible configuration in the command line mode, PVS-Studio analysis can be embedded in a wide variety of CI / CD scenarios. And making the right use of available resources pays off in increased productivity.
It should be noted that the pull request check mode is available only in the Enterprise edition of the analyzer. To get a demo Enterprise license, please indicate it in the comments when requesting a license on the download page . More details about the difference between licenses can be found on the PVS-Studio order page .

If you want to share this article with an English-speaking audience, please use the translation link: Alexey Govorov. PVS-Studio: analyzing pull requests in Azure DevOps using self-hosted agents .