Together with Elena Gerasimova, Head of Analytics and Data Science in Netology, we figure out what the VUCA world is, what VUCA leaders should be, how to develop in conditions of uncertainty and why curiosity helps in developing VUCA skills.
What is VUCA
The acronym VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity, ambiguity - instability, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity) characterizes the changeable and complex environment of the modern world, where there is no guaranteed stability. The term was coined in the 1990s by the US military, and today it is used in the business environment to refer to the conditions in which companies operate.
Instability is characterized by unstable situations and unpredictable changes - in nature, speed, volume, dynamics. The duration of this state of affairs is unclear. Many businesses are now operating in volatile markets with rapidly changing circumstances.
Uncertaintymeans the lack of information to predict the consequences and plan the necessary actions. What was once considered incontrovertible is no longer valid, and leaders can no longer base their decisions on past experience. For example, the expected market launch of a new competitor's product calls into question the future of the business and market.
Complexity implies situations where there are many interconnected elements and a huge amount of information. Such a large number of factors greatly complicates the decision-making and planning process. For example, entering international markets involves following numerous rules and regulations.
Ambiguitydetermined by the lack of a clear understanding of the rules of the game. Sometimes this is due to situational novelty and doubts that can arise when trying to make decisions in a new context. The shift from print newspapers to digital media is an example of a new business model and an ambiguous situation where customer behavior in a new environment is not fully understood.
Instability, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity have come to define the digital economy as an extremely destructive environment and a potential danger for companies focused on gradual growth. Therefore, finding “leverage” for a breakthrough is a key component of the strategies of successful companies. And more often than not, this "lever" is of the nature of the latest technology (Gartner technology maturity cycle).
The rate of change in many industries is now much faster than it was ten or twenty years ago. With digital technology and changing customer needs, this increased volatility is real for many companies.
Before the pandemic, many may not have paid attention or seen examples of threats to the economic balance. The chaos that reigns as a result of rapid, unforeseen changes will build up for years to come.
Living in chaos means being flexible and willing to change your mind, drop past beliefs, and then drop them over and over again. Thus, movement and change become part of the DNA of any of us - the guarantor of antifragility.
However, the sense of uncertainty is as old as the world. The current situation is hardly more complicated than during the plague or World War.
How we perceive the world as more uncertain and ambiguous depends largely on our ability to cope with its volatility and complexity.
How to live in uncertainty
Entrepreneurs and specialists can only treat the changes in the world as a normal existence: movement = life.
“When life gives you lemons, make a lemonade” may sound like advice from the captain Obvious, but new conditions mean new opportunities. They are definitely worth using, especially if the previous features are no longer available.
It is important to remember that every new day = new you. This means that you should not postpone development until "next year" or "Monday." Getting started is always difficult, so it’s worth making it a habit to develop and make mistakes. So you don't have to experience a cold start every time.
In a post-coronavirus world, the ability to work remotely helps companies survive: it means that it is worth mastering a profession that allows you to do this, or digital tools in the current profession or business.
Projects speak better than words. Today, it is worth collecting a portfolio not only from work projects, but also from pet projects or hobbies, if professional skills are used in them.
Don't quit your job to learn. By asking yourself a drive, it is easier to join a new activity when it ends. A new job is always stressful, even if it is associated with the joy of applying successfully acquired knowledge.
When determining the learning path, it is better to choose skills that will be applicable in different scenarios of the future - universal, metaskills. They will be useful both in a crisis situation, when it is important not to cling to a straw, but to move on your own, and in a quiet time - what is valuable is what you can and can apply, and not just know.
VUCA Prime: meeting the challenges of the VUCA world
To effectively interact with the VUCA environment, it is important to develop appropriate skills. The managerial competencies that distinguish VUCA leaders are described by Bob Johansen in Leaders Create the Future: Ten New Qualities for an Uncertain World . The author - a scientist from the Institute for the Future - says that the leaders of the new generation are distinguished by V ision (vision), U nderstanding (understanding), C larity (clarity) and A gility (speed) - the VUCA Prime model.
Vision counteracts volatility .
In hectic times, shaping the company's vision for the future is more important than in normal times. This will help withstand turbulence, crisis, or withstand competition. It is also important that employees also understand where and why the company is going.
Understanding counteracts uncertainty .
To identify new opportunities, the leader needs to go beyond the boundaries of his competence. It is important to be flexible and communicate with employees of different levels. And here soft skills play an important role, in particular communication skills and empathy.
Clarity counteracts complexity .
In the VUCA environment, chaos ensues quickly and violently. It is necessary to quickly determine which strategic directions to focus on in order to get out of the crisis situation as soon as possible.
Agility counteracts ambiguity .
Speed refers to the ability to communicate effectively, make and execute decisions quickly.
Hiring flexible leaders is not enough for a company to live in the VUCA world. It is important that they create a VUCA culture that is focused on innovation, adaptive behavior and thoughtful risk-taking.
As you can see, developed soft skills play an important role in the VUCA world. The importance of soft skills has been proven by many studies. For example, 92% of LinkedIn respondents equated the importance of soft skills with hard skills .
The role of curiosity in the development of soft skills for the VUCA environment
The word "curiosity" comes from the Latin "cura" - "care, attention". It means inquisitive thinking and manifests itself in the form of studying and learning something new. Curiosity is a driving force not only in human development, but also in science, language and industry.
Curiosity helps accelerate research, be open to new experiences, creative problem solving, build resilience to uncertainty, and collaborate and learn. All this makes it possible to develop basic soft skills - empathy, situational and interpersonal adaptability, cross-cultural sensitivity, logical thinking.
Let's look at specific examples of why a business benefits from cultivating curiosity among its teams.
Generation of ideas
Curiosity helps employees become more engaged, generate new ideas, and share them with others, according to a survey by business school INSEAD and SurveyMonkey . 73% of those surveyed who are interested at work admitted that they "exchange ideas more" and "generate new ideas for their organizations."
Growth mindset
Curiosity is characteristic of a growth mindset, such as transforming failure into learning opportunities and choosing activities that improve current skills and develop new ones.
Companies that adhere to a growth mindset and create an environment conducive to failures benefit.
92% , 52% 17% , .
This means that professionals from different disciplines who develop a growth mindset are better able to adapt to the VUCA environment. In particular, to the consolidation of the industry, technological, regulatory and geopolitical shocks, as well as to shifting consumer preferences.
Curiosity has become the new gold rush. When looking for employees, companies are waiting for employees who are open to new knowledge, and in different areas - from a sales manager to a data analyst.
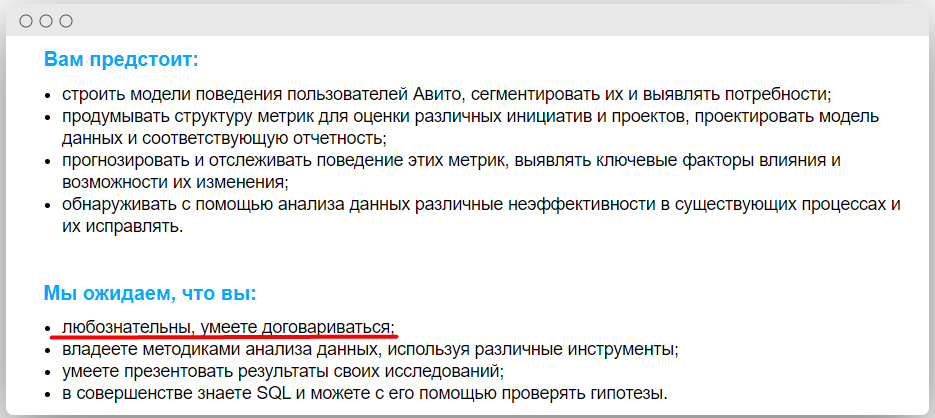
Data analyst vacancy from Avito
There is a shortage of employees with creativity, communication skills and adaptability.
But not everything is simple even in those companies where there are such employees. According to the surveyINSEAD and SurveyMonkey, 83% of C-level executives believe that curiosity is encouraged “very strongly” or “good” in their company, while only 52% of employees agreed.
About half (49%) of top managers say that curiosity is rewarded with a rise in salary, but 81% of employees answered that inquisitiveness does not significantly affect their income.
This is a big problem for business: if employees do not see value in curiosity, then they are less likely to use new information in their work.
A successful business relies on the curiosity of its employees. To generate new ideas and create added value for the company, employees of all levels need an environment where they can take an interest in new things, seek and absorb new information, and establish new connections.
An openness to diverse experiences, exploratory behavior, and a drive for employee knowledge can help companies better deal with market uncertainty and volatility.
Development in the VUCA world
Employees will have to adapt, acquire new skills in order to keep up with the changes. At the same time, it is more difficult for adults to adapt to changes in the labor market and technological innovations, therefore lifelong learning is of particular importance - the education system is changing.

Experience is accumulated in each person under the influence of the external environment, and it is impossible to transfer experience in the context in which it was acquired by one person to another. The look at this experience, its processing, scaling, transformation into knowledge are individual: they cannot be conveyed without distortion. The seamlessness of experience is important for the objectivity of assessing expectations from its application. The most common problem is “I do everything exactly like X, but I failed - why?”.
Even if there are many smart people in the company, their experience will belong only to them.
The solution can be a carefully designed corporate training system - a kind of corporate university 2.0, in which the methodology is a living and dynamically developing product. Such training systems have the potential to grow into commercial products for a broad market.
Because of the difficulties in transferring knowledge from person to person, it has become much more important to find new, more effective ways to solve company problems in the VUCA environment.
Usually people use only the knowledge that they have been able to test in practice. Otherwise, new information is forgotten or questioned and is still discarded. Therefore, the value of constant independent acquisition of new skills arose. The willingness to search, process and transmit information further helps to better accumulate and apply knowledge.
It can be argued that humanity will only benefit from change. Many systems are already too "stagnant" and need a shake-up and a bit of chaos to develop to a new level.
Lifelong learning: lifelong learning
Such training includes:
- formal education in (non) public educational institutions;
- informal (including corporate) - mentoring, internships, coaching, trainings;
- Self-education - online courses, TED conferences, YouTube channels, and more.
Traditional higher education is the basis, but in most cases it does not guarantee the necessary highly specialized training. And after five to six years of study, a graduate often lacks the practical skills to be useful to the employer immediately after graduation. Moreover, it happens that studying at a university is demotivating to continue studying in principle.
Meanwhile, education is closely related to income levels. According to UNESCO data for 2019, an increase in the average length of education of the adult population (from 24 years) by one year in the long term leads to an increase in economic growth by 4%, and per capita income by 6% .
UNESCO indicates that the rate of return for each additional year of study is 9.7% - this is more profitable than keeping money in deposits and deposits.
Continuing education is not a matter of choice, but already a given. The constant change in technology, production and market conditions leads to the fact that in developed countries, an employee, on average, changes his specialty at least five times during his working life.
At the same time, education has ceased to be functional. The “I'm going to learn Python because I need to learn Python” approach is rare.
Today, people are looking for new opportunities, ways and directions of development in education.
According to McKinsey estimates , by 2030, due to the development of technology, from 75 to 375 million people, that is, 3-14% of the total workforce in the world, will become unemployed or will be forced to change their profession.
The atlas of new professions is merciless: 57 professions, according to its creators - the agency for strategic initiatives and Skolkovo - are doomed to extinction and falling into a career dead end. Managers, administrators, lawyers, drivers, dispatchers, operators, economists, accounting and procurement specialists, cashiers and others - until 2030 will begin to lose their jobs at different rates if they do not undergo additional training.
95% «» .
70% : , , -. — , .
The most growing demand for technology skills (and programming): now they are employed in 11% of working hours, in 2030 it will be 17%.
The ability to work in a team, lead others, negotiate and show empathy will have to grow by 24%. And here (oddly enough) remote work can help, as it develops collaboration skills well. Gaps, shortcomings in this format of work appear faster - you can quickly work out and improve them.
Learning to learn: how to get from the current point A to the desired point B

Think about how learning makes you feel. We hope that among them there is a place of joy, satisfaction, pleasure from the result, when “I could” :-)
You can start from this point - to learn for the sake of emotions, the cherished pleasure from the result at the end.
If the goal is complex, it is more convenient to decompose it into its component parts. Then it will not seem so unattainable.
For each step, you need to choose an approach: master it myself, find a mentor, go to the assistant (I will observe), buy or find a free course on the topic, read a book - any way you can.
The next step is to find a way to practice - this is how skills are formed from knowledge.
After all, it is important to evaluate the result obtained - perhaps, it will be necessary to work more, or perhaps new knowledge will already be enough for use on real problems. Be that as it may, at the end you should definitely praise yourself for the efforts made - and rejoice at the result.
The changes affect not only the education system, but also the labor market. First of all, this concerns the increase in the number of distributed teams, since many companies began to rebuild themselves on the online rails.
Office is no longer an advantage
A quarter of Russian companies have remote employees ( Superjobs ) .
It is generally accepted that remote work is difficult to organize and control. It also entails the costs of converting workplaces into digital format: here is security, and availability, and completeness of information.
And in general, who is not pleased to change the environment and come to the office. Unless in IT, remote work has long become the gold standard.
Among the rest - ⅓ works from home one day .
When we say remote work, we mean full-time employees.
According to various estimates, after the pandemic in 2020, 5-10% of employees will remain remote and further .
Few of the full-time employees will continue to work remotely. The need to equip a home office plays a role, for which the employer is not obliged to pay.
A business affected by the pandemic will cut office costs and increase funds for remote team work .
Companies are willing to buy licenses and invest in digital workplaces to ensure business continuity and hedge against malware or counterfeit problems.
Savings in office, electricity, stationery and multiple administrative functions can reallocate costs and possibly even win.
The transformation of physical jobs into digital ones is inevitable for those industries where such a transfer will allow businesses to benefit from an economic point of view.
At the same time, the culture of remote work in non-digital areas of the economy is still far from ideal, but the good news is that you can use the experience of IT and digital agencies.
Which companies grow in crisis
Startups
In a time of chaos and uncertainty, those whose “genes” already have an expectation of difficulties and flexibility in adapting to any situation in the world around them feel best.
One example is startups. These are services and businesses that rely on fast and painless closing of user and market needs.
Better to continue rather than start a career in a startup. Any non-digital experience will come in handy if you find a business in your field.
Startup employees are constantly learning, so this is a fertile ground for self-development.
Product and service companies with distributed teams
There are quite a few companies that adhere to the remote-first concept. Their founders and employees initially live in different cities and even countries. All communication is usually organized through video communication and collaboration tools such as whiteboards for notes and instant messengers.
In such teams - without being tied to the business sphere - soft skills come to the fore, that is, flexible work with people and the presence of emotional intelligence.
The spheres include EdTech, telemedicine, online streaming, FoodTech, online retail.
Russian representative offices of foreign companies
Companies whose headquarters are located abroad and where, as a rule, service employees are located in Russia, feel good.
You can save on salaries (even giving them on average above the market) and relocation. At the same time, require appropriate experience and proficiency in corporate tools.
What is the result
We live in a VUCA world that requires us to change.
Next-generation leaders are distinguished by Vision, Understanding, Clarity and Agility - the VUCA Prime model.
Lifelong learning is a must. In addition, it is recognized as one of the most profitable investment items for adults.
“You have to run with all your might to stand still” is the best advice for the VUCA world.
Digital skills are associated not only with technology, but also with fruitful interactions with people.
Curiosity helps to develop soft skills such as empathy, adaptability, cross-cultural sensitivity, logical thinking.
Curiosity also helps employees become more involved in their work, generate new ideas and share them with others.
Everyone can find a profession for themselves.
Moving to a position with related tasks using new technologies will help to get out of a career impasse: for example, a journalist can become a data journalist, and an accounting specialist can become an analyst.
There is no stability. Do you agree?