- Limit the number of places and applied technologies for converting an electronic document into analog.
- Limit the number of places and the circle of persons allowed to familiarize themselves with the content of analogue documents.
- Equip places for familiarization with the content of an analog document with video recording and visual control
- etc.

In addition to the high cost, the use of such methods dramatically reduces the efficiency of working with documents.
A compromise can be found in our SafeCopy product .
Document protection principle
With SafeCopy, a unique copy of the document is made for each recipient, into which hidden markings are introduced using affine transformations. At the same time, the spacing between lines and characters of the text, the slope of characters, etc. The main advantage of this marking is that it cannot be removed without changing the content of the document. Watermarks are washed off with regular Paint, this trick will not work with affine transformations.
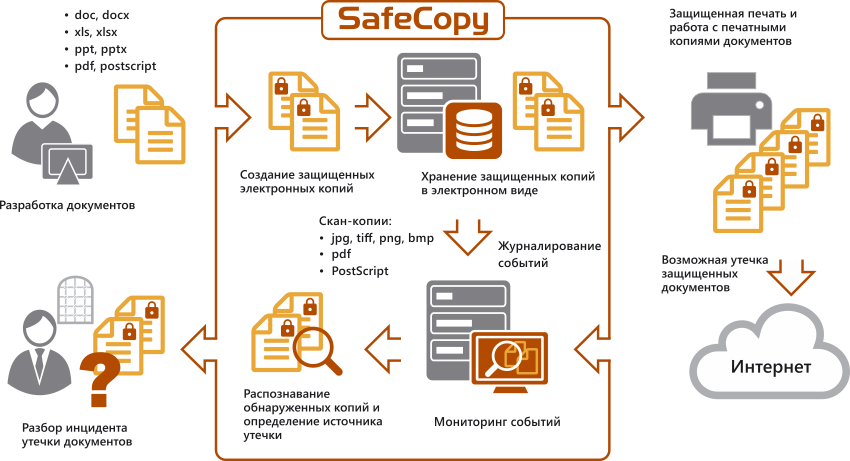
Copies are issued to recipients in hard copy or electronic pdf format. In the event of a leaked copy, the recipient can be reliably identified by the unique set of corruptions introduced into each copy. Since the entire text is marked, just a few paragraphs are enough for this. The rest of the page may be missing / wrinkled / covered with a palm / filled with coffee (underline the necessary). What we just did not see.
What is labeling useful for?
Protection of confidential documents . The scenario is described above. Briefly: we marked the copies, gave them to the recipients and vdim. As soon as a copy of the document “showed up in unauthorized places”, they compared it with all marked copies and promptly identified the owner of the “declared copy”.
To determine the spyena, one by one we overlay the “advertised copy” on the copy of each recipient of the document. Whoever has a higher percentage of coincidence of pixels is a spy. But it is better to see it once in the picture.

The overlay of the "advertised copy" on all marked copies is done not manually, but automatically. Labeled copies are not stored on the system in order not to waste gigabytes of disk. The system stores only a set of unique marking features for each recipient and generates copies instantly.
Authentication of documents . You can read about the methods of manufacturing secure printed products at Vicki . In fact, they boil down to the production of forms with various kinds of markings - watermarks, special ink, etc. Examples of such products are banknotes, insurance policies, driver's licenses, passports, etc. Such products cannot be produced with a conventional printer. But on it you can print a document with affine text transformations. What does it do?
By printing a form with invisible text markings, you can check its authenticity simply by the presence of the markings. At the same time, the uniqueness of the marking allows not only to verify the authenticity, but also to establish a specific natural or legal person to whom the form was transferred. If there is no marking or it indicates a different recipient, then the form is fake.
Such marking can be used both independently, for example, for strict reporting forms, and in conjunction with other methods of protection, for example, to protect passports.
Bringing violators to justice... Large leaks cost companies a lot of money. To punish the offender is not limited to a reprimand, it is necessary to bring him to justice in court. We have patented our own way to protect documents so that SafeCopy results are accepted as evidence in court.
What marking cannot?
Marking is not a panacea in the fight against data leaks and the protection of copies of documents. When implementing it in your enterprise, it is important to understand three key limitations:
Marking protects the document, not its text . The text can be remembered and retelling. Text from a marked copy can be rewritten and sent in the messenger. Nothing will save you from these threats. It is important to understand here that in the world of total fake, draining only part of the text of a document is no more than electronic gossip. For a leak to have value, it must contain data to verify the authenticity of the information being leaked - a seal, a signature, etc. And here the marking will already be useful.
Marking does not prohibit copying and photographing copies of the document... But if scans or photos of documents "come up", it will help in finding the offender. In essence, copy protection is preventive in nature. Employees know that they are guaranteed to be able to identify and punish them based on photographs and copies of documents, and either look for other (more laborious) ways to "drain", or completely abandon it.
Marking identifies whose copy is leaked, not who leaked it... An example from life - a document leaked. Marking showed that a copy of Ivan Neudachnikov had leaked (name and surname changed). The security service begins an investigation and it turns out that Ivan left a document on the table in his office, where the intruder took a picture of it. Ivan - a reprimand, the security service - a quest to find the culprit among the people who visited the office of Neudachnikov. Such a quest is non-trivial, but simpler than searching among people who have visited the offices of all recipients of the document.
Mix but do not shake
If you do not integrate the labeling system with other corporate systems, then the scope of its application will most likely be limited only to paper workflow, which is getting smaller over the years. And in this case, the use of marking can hardly be called convenient - you will have to manually download each document and make copies for it.
But if you make the labeling system part of the overall IT and information security landscape, a synergistic effect becomes noticeable. The following integrations are most useful:
Integration with EDMS . The EDMS distinguishes a subset of documents that require marking. Each time a new user requests such a document from the EDMS, he receives a labeled copy.
Integration with print management systems... Print management systems act as proxies between users' PCs and printers in an organization. They can determine that a document sent to print requires labeling, for example, by the presence of a sensitive label in file attributes or by the presence of a file in a corporate sensitive document repository. In this case, the user who sent the document for printing will receive a marked copy from the printer tray. In a simpler scenario, you can make a separate virtual printer, sending documents to which, stamped copies will come out of the tray.
Integration with email... Many organizations cannot use email to send out confidential documents, but these prohibitions are often violated. Somewhere due to carelessness, somewhere due to tight deadlines or direct instructions from the management. To prevent information security from being a stick in the wheel of progress and bringing the company money, we propose to implement the following scenario, which allows you to safely send by internal e-mail and save on sending documents by courier.
When sending a document, the user adds a sign of the need for marking. In our case, this is a business email address. The mail server, receiving a letter with such a sign, makes copies of all attachments for each recipient and sends them instead of the original attachments. To do this, a marking system component is installed on the mail server. In the case of Microsoft Exchange, it acts as a so-called. transport agent. This component does not interfere with the work of the mail server.