Today we will talk about how technology is used in industry. In our recent article on helmets, we received a request to reveal a topic with examples. We ask all those interested under cat.
Let's start with a brief history
As we mentioned above, the technology was not available to everyone before. This was primarily due to the complexity and high cost of equipment: instead of VR helmets, virtual reality rooms (CAVE), which are a complex of projection systems, were widely used. As a rule, this required a separate room, compliance with certain technical requirements and many, many green pieces of paper with the image of American presidents.
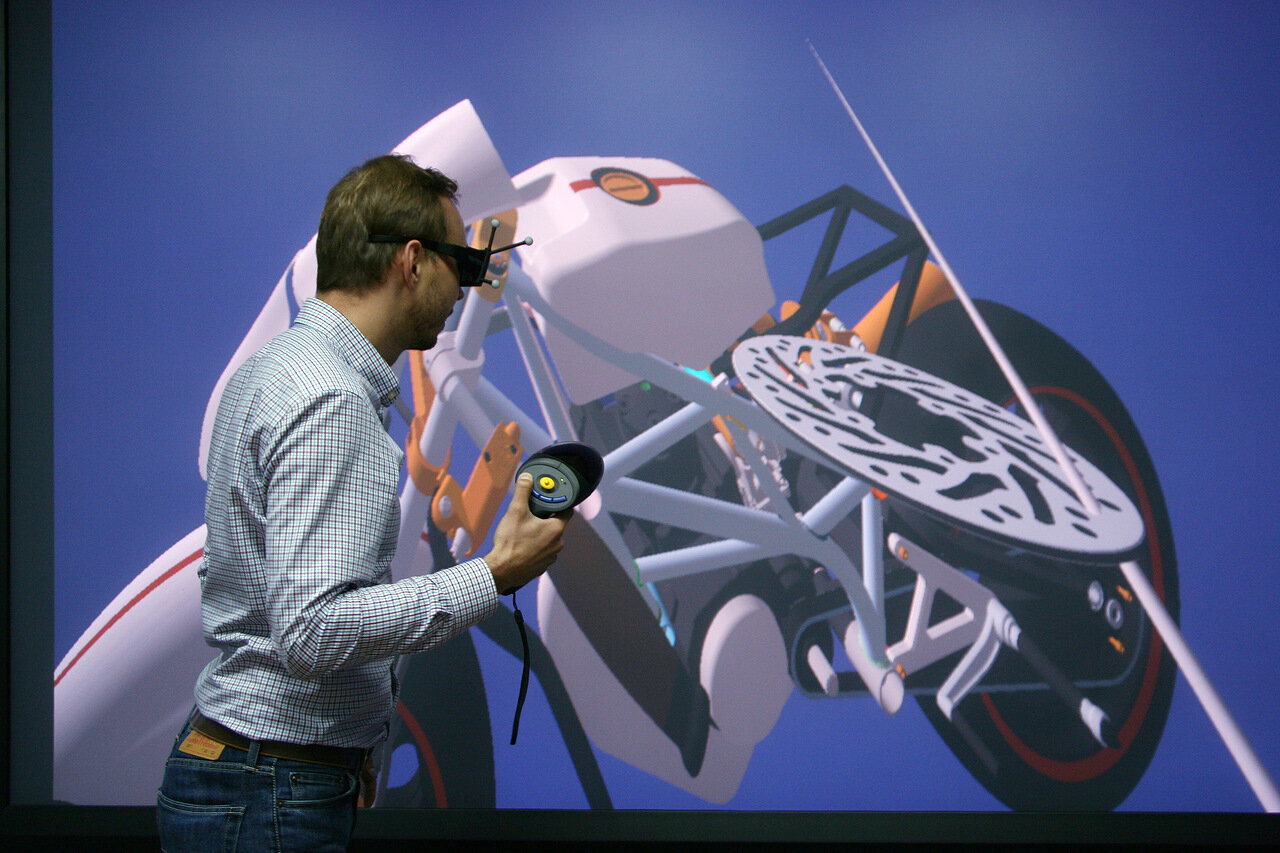
What for?
First of all, in order to reduce design errors and accelerate the approval of a complex technical project. Discussing a project on a 1: 1 scale with all participants in the process is clearer than using drawings, miniature copies (models) or watching a 3D model on a "flat" screen.
Secondly, for ergonomics testing and staff training. When creating a new product, a company must be sure that it will be convenient to operate and maintain. The use of a virtual reality system, coupled with tactile feedback systems, can reduce costs and time for creating full-scale prototypes.
In 1999, the Ford concernreported that the use of virtual design systems provided $ 40 million in savings in engineering costs and more than $ 1 billion due to related changes in the production cycle.
With the advent of Oculus Rift and HTC VIVE helmets, the range of tasks to be solved has significantly expanded. So did the number of companies that could afford the technology.
Having worked with industrial companies to integrate VR into business processes for over 15 years, we have accumulated a large number of examples of how virtual reality helps industrial companies solve their business problems. We share them with you. We will describe in the format “problem - solving a problem using VR”.
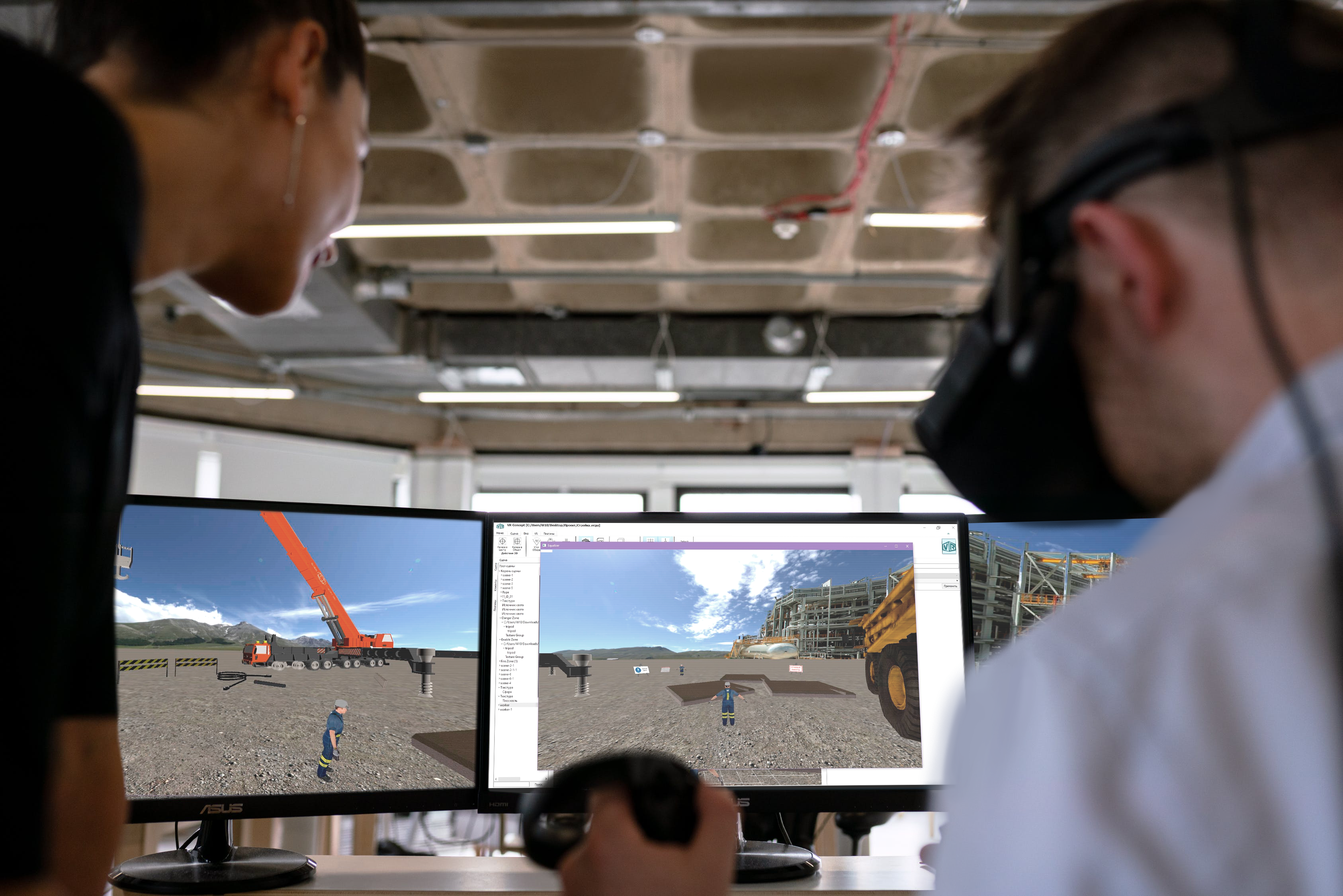

Case 1.
Problem: design errors (new buildings, factories, warehouses) and high costs for project development
What VR gives: by loading a 3D model of a projected building / room into VR, a designer can see the project at a 1: 1 scale and better assess the design quality and ergonomic characteristics of the object, which is impossible to do by looking at a 3D model on a monitor screen. Together with specialists from the logistics and security departments, they can agree on the location of equipment in the room, the organization of production facilities and test scenarios and compliance with safety requirements before putting the building into operation.
In addition, such a virtual building can be shown to internal and external clients of the project, partners and investors
Example:Safran Nacelles saved € 300,000 in less than a year through an investment in a VR system. The French company began to develop new gondolas in just 42 months, and previously this process took 60 months. Safran Nacelles was also able to complete the project 8 months earlier, with a project duration of around 18 months. Thus, the savings amounted to 40% of the budget.
Case 2.
Problem: high costs for approving projects based on full-scale prototypes
What VR gives:discussion of the project not with drawings and images on the monitor, but with a prototype on a 1: 1 scale reduces the costs and time for preparing for the prototype commission. Such visualization acts as a kind of common "language" in which all participants in the process can speak: both design engineers and CEOs with customers. In addition, visual inspection of the project and the ability to feel it helps to identify errors in the early stages of design.
Example:Automotive company SEAT has reduced production times and reduced the number of layouts by using virtual reality. During the development of a new vehicle, up to three million parts are analyzed. Thanks to VR viewing technologies, where the model is presented in real scale, design analysis time and the number of physical prototypes have been reduced. As a result, thanks to this approach, production time was reduced.

Case 3.
Problem: due to a lack of practical experience, specialists get injured and damage expensive equipment
How VR helps:discussion of the evacuation plan, training and testing of personnel not with drawings and images, but with a prototype of a building on a 1: 1 scale allows to increase the speed and quality of training, and reduce the cost of training specialists to work with complex equipment, reduce the risk of an industrial accident or breakdown of expensive equipment. The mistake will not lead to an accident or breakdown, and the employee will have real experience. Simultaneously with the design of the same workshops, parallel training of operators who will work there in the future is possible. Thus, when opening the updated site, employees will be able to immediately get down to work and not waste time on training. You can also test factory line settings in VR. Production speed, product quality play an important role in the success of the enterprise,Therefore, it is so important to save time on processes that can run in parallel with each other using VR, you can simulate emergency situations. It is often either dangerous or too expensive to reproduce such cases in real life, so the staff knew only in theory how to get out of a difficult or emergency situation. With the use of virtual reality technologies, staff can be prepared for any problem.
Example: The same Ford has reduced occupational injuries by 70% and reduced ergonomic problems by 90%. With the help of VR, laboratories are striving to improve and make safe the assembly line and operator's workspace. More than 52 sensors are used for analysis, which are located on the human body. They read the movements and transfer the coordinates to the database. An ergonomist, having received the values, can play out certain scenarios and secure the worker's life:
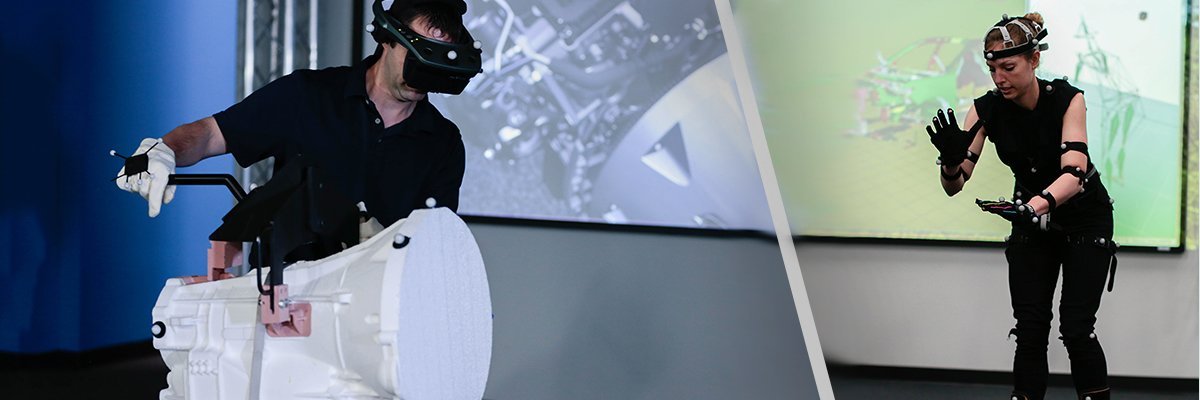

Case 4.
Problem: a long time for project approval due to the large number of participants from different departments and different cities, which is accompanied by high travel costs
How does VR help:you don't need to be in the same room to discuss a project, but it is important to be in the same virtual space, which is provided by virtual reality helmets and the corresponding software. Collective discussion and project demonstration in VR reduces travel costs and project approval time.
Example:CNES, the French National Space Center, has saved about 12 months through the use of virtual reality in the Callisto project for a period of 4 years. The rocket booster was designed in CAD, and in VR, a detailed analysis of the aircraft and auxiliary elements for launch was carried out. This made it possible to discuss the project remotely, analyze what tools are needed for assembly, the size of the building, the process of transportation to the launch site, and test the entire system as a whole. This project showed the possibility of simultaneously solving various problems.

Summing up, we can say that in foreign practice VR has long been an indispensable assistant for solving industrial problems. After all, thanks to the use of VR technologies to solve their "pains", the world's leading corporations managed in some cases to save from 8 to 12 months of the total time spent on project development, reduce the number of injuries in new production by 70% and get rid of ergonomic problems.
Among Russian companies that use virtual reality to solve business problems, we can single out Sinara - Transport Machines, AgroTechHolding, Severstal, Alrosa. Separately, we would like to note Gazprom Neft, whose digitalization strategy includes many innovative technologies, and VR is assigned the role of a tool for training employees in labor protection and industrial safety, which will reduce risks by 30% by 2025. In addition, according to the roadmap, up to 90% of engineering models will be accepted using VR, which will reduce design time by 10% and construction time by 7%. Over the past 2 years, such large companies as Sberbank, Lanit, Sibur and others have formed their AR / VR laboratories.
Was the material interesting? We will be glad to receive feedback in the comments!